av Menen Duhaney för 4 årar sedan
239
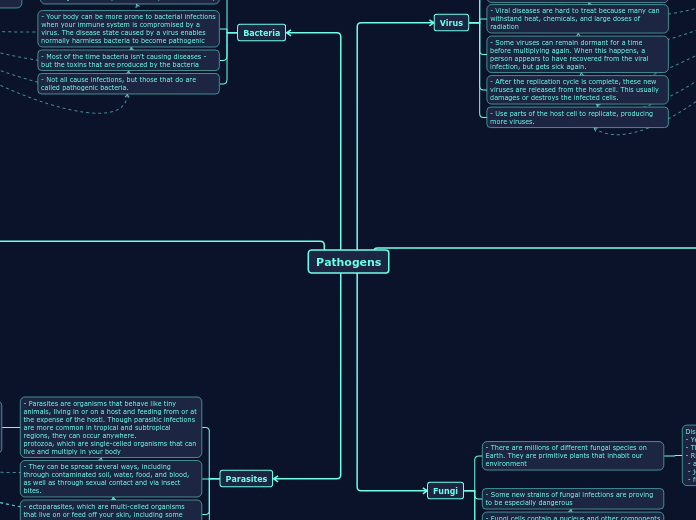
Pathogens
Pathogens are diverse organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and parasites, that can cause various diseases. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms present in numerous environments, including the human body.