av MUTIS MORA LUIS CARLOS för 6 årar sedan
235
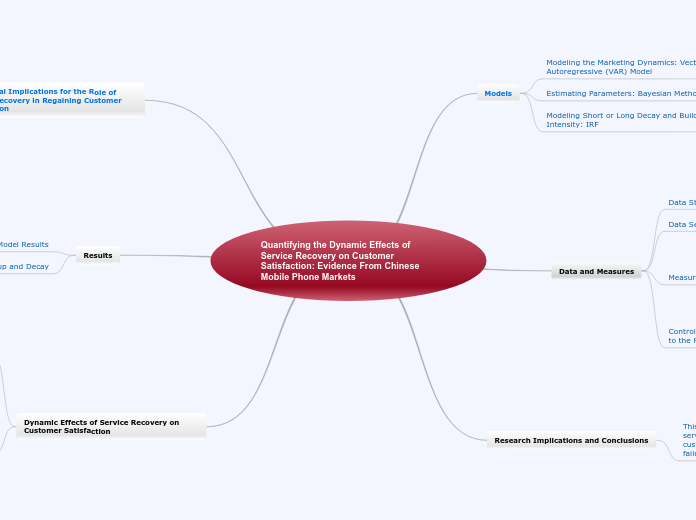
Quantifying the Dynamic Effects of Service Recovery on Customer Satisfaction: Evidence From Chinese Mobile Phone Markets
av MUTIS MORA LUIS CARLOS för 6 årar sedan
235

Mer av detta