av Nidia Choconta för 4 årar sedan
2217
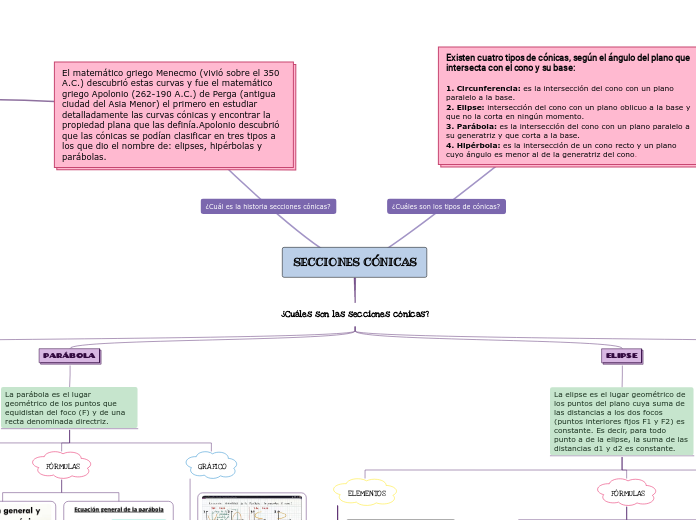
SECCIONES CÓNICAS
av Nidia Choconta för 4 årar sedan
2217

Mer av detta
Observa el grafico de cada ecuación canónica
Observa el video de las ecuaciones canónicas
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
6. Ejes de simetría: Son las rectas que contienen al eje real o al eje imaginario.
5. Radios vectores: Son los segmentos que van desde un punto de la hipérbola a los focos: PF y PF'.
4. Vértices: Los puntos A y A' son los puntos de intersección de la hipérbola con el eje focal.
3.Centro: Es el punto de intersección de los ejes.
2. 2Eje focal, principal o real: Es la recta que pasa por los focos.
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
Con centro en (h,k) vertical
Con centro en (h,k) horizontal
Con centro en (0,0) vertical
Con centro en (0,0) horizontal
7. Centro de simetría: Coincide con el centro de la elipse, que es el punto de intersección de los ejes de simetría.
6. Vértices: Son los puntos de intersección de la elipse con los ejes: A, A', B y B'.
5. Distancia focal: Es el segmento de longitud 2c, c es el valor de la semidistancia focal.
4. Centro: Es el punto de intersección de los ejes.
3. Eje secundario: Es la mediatriz del segmento FF'.
2. Eje focal: Es la recta que pasa por los focos.
1. Focos: Son los puntos fijos F y F'.
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
Enlace del video: https://youtu.be/GBJAYYvXCvI
6. Radio vector: Es un segmento que une un punto cualquiera de la parábola con el foco.
5. Vértice: Es el punto de intersección de la parábola con su eje.
4. Eje: Es la recta perpendicular a la directriz que pasa por el foco.
3. Parámetro: Es la distancia del foco a la directriz, se designa por la letra p.
2. Directriz: Es la recta fija d.
1. Foco: Es el punto fijo F.
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
¿Cuáles son las secciones cónicas?.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
GRÁFICO
Con centro en (h,k)
Con centro en (0,0)
FÓRMULAS
ELEMENTOS
Radio, el segmento que une el centro con un punto cualquiera de la circunferencia,
Centro, el punto interior equidistante de todos los puntos de la circunferencia