av Cristopher Coyago för 4 årar sedan
528
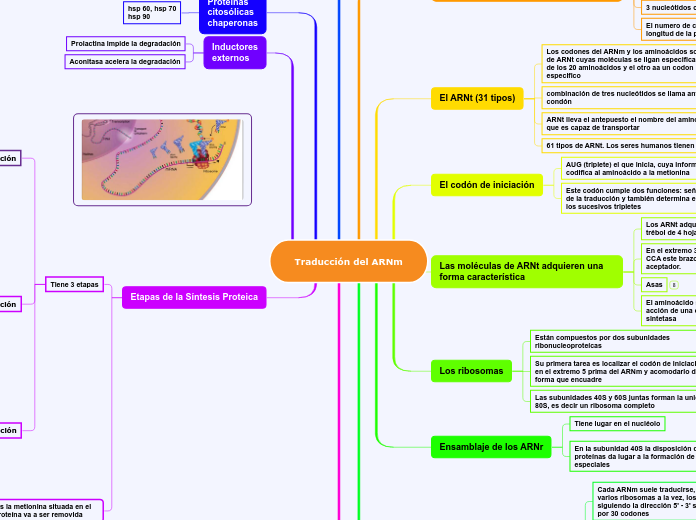
Traducción del ARNm
av Cristopher Coyago för 4 årar sedan
528

Mer av detta
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
Compound preposition consists of two or more words.
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
Este proceso es constante: el extremo 3' del ARNm se retiran los ribosomas y del 5' otros se ensamblan.
El polipéptido del peptidil-ARNt situado en el sitio P se desliga del ARNt y se une para formar un carboxilo libre a una molécula de H2O.
Esto hace que la proteína se libere del ribosoma.
Culmina cuando el ribosoma alcanza el codón de terminación (UAA, UGA, UAG) dejando el sitio A vacio.
La etapa termina cuando llega a 90 nucleótidos (30 codones), el proceso se repite dependiendo del largo del ARNm.
Factor EF1(alfa): mide la reacción entre el tercer codón del ARNm con ARNtAmi
El ARNm va al 5' por el proceso de TRANSLOCACIÓN y por la acción del factor EF2.
Comienza cuando se acerca el aminoacil-ARNtAmi compatible con el segundo codón de ARNm.
Esta etapa finaliza cuando la subunidad mayor y menor del ribosoma se combinan quedando un ribosoma completo.
El factor IF3 aparece cuando el proceso se ha completado y ayuda al anticodón UCA a unirse con el codón AUG.
Codón de iniciación en el sitio P y el codón de ARNm en el sitio A.
Regulada por factores de iniciación y da lugar a:
5' del ARNm: El factor IF4 reconoce al cap y a una serie de nucleótidos
Subunidad del ribosoma: El factor IF2 participa con la metionil-ARNt(i)met y el GTP que se une al ribosoma.
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
Las proteínas permanecen en la membrana del retículo endoplasmático para luego ser transportadas por medio de vesículas de transporte
Elaboran proteínas destinadas al núcleo
Por peptidil
Por aminoacil
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
Hacen referencia a sus coeficientes de sedimentación
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
Algunos aminoácidos pueden ser reconocidos por más de un ARNt
Une el aminoácido a su brazo CCA por señales emanadas por el anticodón
Identifica el ARNt correcto
Cada una diseñada para reconocer un tipo de aminoácido y a la vez el ARNt compatible
Reciprocal pronouns are used for actions or feelings that are reciprocated. The reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Su longitud difiere bastante en los distintos ARNt
Por la secuencia ribotimidinas y seudouridinas
Contiene el triplete de nucleótidos del anticodón
Contiene Dihidroxiuridinas
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.