Agonist Spectrum
Full Agonist
Molecules with high efficay that binds to activate a receptor; producing maximum bilogical response (Berg & Clarke, 2019).
Mechanism: Binds to receptor, includes conformational change, activities downstream siginaling.
Medications/Targeted Receptors
Oxycodone
Opioid receptors(primarily u-opioid)
Acts as an agonist at the opioid receptor; binding to the opioid receptor and triggers pain relief (Edinoff et al., 2021).
Aripiprazole
Partial Agonist
Molecules that bind to the receptor, while producing a submaximal response compared to the full agonists (Berg & Clarke, 2019).
Mechanism: Binds to the receptor, but induces a less pronounced conformational change than the full agonists.
Medications/Targeted Receptors
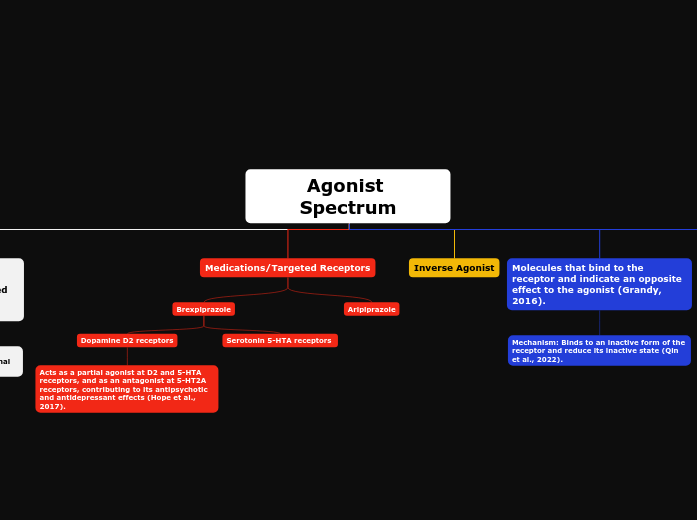
Brexpiprazole
Dopamine D2 receptors
Acts as a partial agonist at D2 and 5-HTA receptors, and as an antagonist at 5-HT2A receptors, contributing to its antipsychotic and antidepressant effects (Hope et al., 2017).
Serotonin 5-HTA receptors
Aripiprazole
Inverse Agonist
Molecules that bind to the receptor and indicate an opposite effect to the agonist (Grandy, 2016).
Mechanism: Binds to an inactive form of the receptor and reduce its inactive state (Qin et al., 2022).
Medications/Targeted Receptors
Pimavanserin
Serotonin 5-HT2A and Serotonin 5-HT2C (Muneta-Arrate et al., 2020).
Reduces the receptors constitutive activity to treat hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease psychosis (Howland, 2016).
Antagonists
Molecules that bind to the receptor, but do not activate it; thus blocking the action of agonists (Cleveland Clinic, 2024).
Mechanism: Competes with agonists for binding sites on the receptor without activating downstream siginaling.
Medications/Targeted Receptors
Naloxone
Opioid receptors (primarily u-opioid receptors).
Inhibits opioid receptors by reversing the effects of opioid overdose (Cleveland Clinic, 2024).
Risperidone
Dopamine D2 receptors and Serotonin 5-HT2A receptors
Blocks D2 and 5-HT2A receptors, balancing dopamine and serotonin activity to treat symptoms of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (Alvarez-Herrera et al., 2024).
Haloperidol
Dopamine D2 receptors
Binds to and blocks D2 receptors while reducing dopamine activity and treating symptoms of psychosis (Fan et al., 2020).