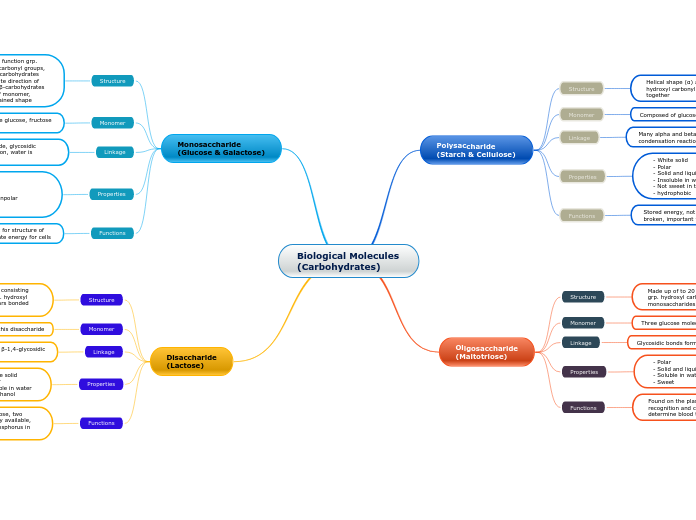
Biological Molecules (Carbohydrates)
Polysaccharide (Starch & Cellulose)
Structure
Helical shape (α) and straight chain shape (β), function grp. hydroxyl carbonyl groups, many monosaccharides bonded together
Monomer
Composed of glucose monomers joined in α 1,4 linkages
Linkage
Many alpha and beta glycosidic linkage formed by condensation reaction
Properties
- White solid - Polar - Solid and liquid - Insoluble in water - Not sweet in taste - hydrophobic
Functions
Stored energy, not immediate since many bonds need to be broken, important for cellular structure (cell wall)
Oligosaccharide (Maltotriose)
Structure
Made up of to 20 monosaccharides joined together, function grp. hydroxyl carbonyl groups, chain of many monosaccharides
Monomer
Three glucose molecules bonded together
Linkage
Glycosidic bonds formed by condensation reaction
Properties
- Polar - Solid and liquid - Soluble in water and acids, not in nonpolar solvents - Sweet
Functions
Found on the plasma membrane of animal cells for cell-cell recognition and cell binding, different oligosaccharide determine blood type of red blood cells,
Monosaccharide (Glucose & Galactose)
Structure
Molecules of C, O, H, function grp. consists of hydroxyl carbonyl groups, ring structure and α-carbohydrates the OH grp. is opposite direction of monomer (CH2OH), β-carbohydrates are same direction of monomer, helical or straight chained shape
Monomer
Monomers include glucose, fructose and galactose
Linkage
When bonded more than one monosaccharide, glycosidic bonds are formed using condensation reaction, water is removed for bonding capability
Properties
- Colourless - Polar - Solid and liquid - Soluble in water and acids, not in nonpolar solvents - Sweet in taste
Functions
Immediate source of energy, important for structure of organisms and cellular respiration, create energy for cells
Disaccharide (Lactose)
Structure
Two carbon rings bonded, consisting of of C, O, H, function grp. hydroxyl carbonyl groups, two sugars bonded together
Monomer
Glucose and galactose make up this disaccharide
Linkage
Galactose and glucose units joined by a β-1,4-glycosidic linkage, by a condensation reaction
Properties
- White solid - Polar - Soluble in water and ethanol
Functions
Lactose is composed of glucose and galactose, two simpler sugars used as energy more readily available, it aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in our bodies