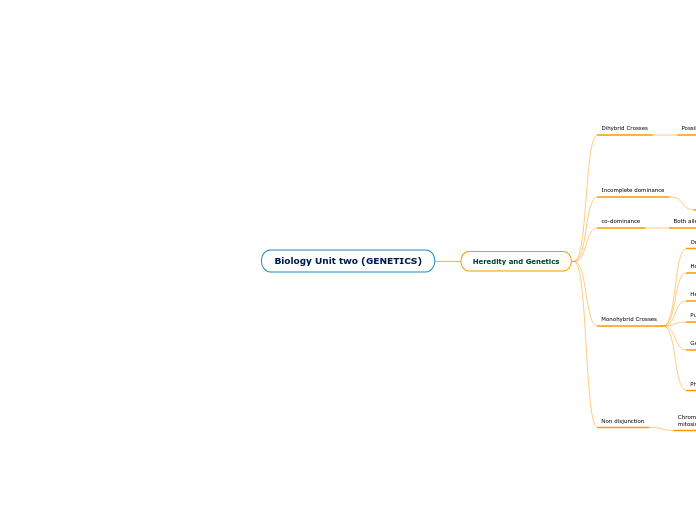
Biology Unit two (GENETICS)
Heredity and Genetics
Dihybrid Crosses
Possible offspring of TWO traits
BbRrxBbRr
"First, you must find ALL possible gametes that can be made from each parent.
Remember, each gamete must have one B and one R."
Possible gametes: Bb BB br bR
Gametes:
Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells. They are also referred to as sex cells. Female gametes are called ova or egg cells, and male gametes are called sperm. Gametes are haploid cells, and each cell carries only one copy of each chromosome.
Incomplete dominance
"In Incomplete Dominance, every genotype has its own phenotype. (One allele not completely dominant over the other.) Third phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits. (2 alleles produce 3 phenotypes.)
"
"Result: Heterozygous phenotype somewhere in between homozygous phenotype.
"
co-dominance
Both alleles contribute to the phenotype
Monohybrid Crosses
Only Involve One Trait
Homozygous
"Homozygous is a genetic condition where an individual inherits the same alleles for a particular gene from both parents."
Heterozygous
"having two different alleles of a particular gene or genes.
"the genetic study showed two heterozygous variants""
Punnett squares
Genotype
"A genotype is an individual's collection of genes. The term also can refer to the two alleles inherited for a particular gene. The genotype is expressed when the information encoded in the genes' DNA is used to make protein and RNA molecules."
Genes
Phenotype
"A phenotype is an individual's observable traits, such as height, eye color, and blood type. The genetic contribution to the phenotype is called the genotype. Some traits are largely determined by the genotype, while other traits are largely determined by environmental factors."
Physical traits
Non disjunction
Chromosones do not divide correctly during the meiosis or mitosis process.
Results with incorrect number of gametes