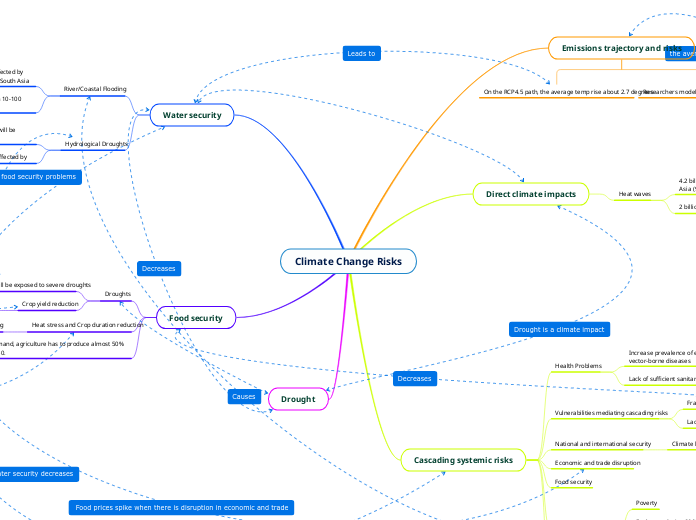
Climate Change Risks
Emissions trajectory and risks
On the RCP4.5 path, the average temp rise about 2.7 degrees
Researchers model trajectories of C02 emissions
Direct climate impacts
Heat waves
4.2 billion people are likely to experience heatwave by 2050 in Asia (90% population)
2 billion people will be affected by major heatwave
Cascading systemic risks
Health Problems
Increase prevalence of emerging infectious diseases and vector-borne diseases
Lack of sufficient sanitary and medical facilities
Vulnerabilities mediating cascading risks
Fragility of the food system
Lack of social safety nets and social cohesion
National and international security
Climate hazards and direct impacts
Economic and trade disruption
Food security
Migration pressures
Poverty
Each year during 2008-2020, an average of 21.8 million people has been displaced by weather related globally
Political discontent
Energy Security
Water security
River/Coastal Flooding
Around 20-30 million people are estimated to be affected by river and coastal flooding by 2100 in Southeast and South Asia
South Asia’s river flooding will affect anywhere from 10-100 million people.
Hydrological Droughts
By 2040, 230 million people in East and South Asia will be affected by drought
By 2040, 152 million people in Africa will be affected by drought
Food security
Droughts
By 2050 40% of crops will be exposed to severe droughts
Crop yield reduction
Crop price spike
Food riots
This has happened in 07-08 and 2010-11
Heat stress and Crop duration reduction
food hoarding
Due to global demand, agriculture has to produce almost 50% more food by 2050.