Cook - Macromoleules
Carbohydrates
Monomer of carbohydrates is monosaccharides
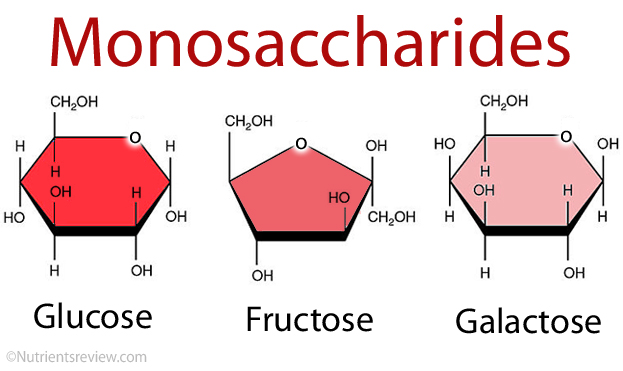
Carbohydrates are an easy way for organisms to get energy. They are made up of C H O (Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen). They are found as starch in plants, and glycogen in animals.
The elements in Carbohydrates are C H O, which stand for Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. These are the same elements in lipids, but in a different, but similar ratio. For every Carbon there are two Hydrogens, and one Oxygen.
There are many different types of carbohydrates. There is starch which is found in plants, glycogen, which is found in animals, cellulose, which is found in plant's cell walls, and chitin, which is found in fungi. Mainly though carbohydrates are found in sugars, starches, cellulose, and glycogen.

Some common examples of carbohydrate found in food are:
Some functions of carbohydrates are quick energy, energy storage, and structure(Ex: Cellulose).
Lipids
Monomer of a lipid is a triglyceride. It is made up of one glyceride and three fatty acids.

The elements of Lipids are C H O, which stand for Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. For every one Carbon, there are two Hydrogens, and less then one Oxygen.
Lipids are very good a energy storage. And they also cushion muscles, and insulate muscles.
A big example of lipids is fats. There are saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats are long straight chains for their fatty acids. Unsaturated fats have a bent chain, as their fatty acid. Also lipids are in Oils, Phosphlipids, Steroids, and Wax.

Nucleic Acid
Monomer of a Nucleic Acid is a Nucleotide. The four Nucleotide in DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine



Nucleic Acids are the macromolecules that store information. Two examples of Nucleic Acids are DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acid's monomers are Nucleotide. In DNA there are Adenine and, Thymine(Together), and Guanine, and Cytosine. RNA is DNA's "worker", because it carries DNA's information around the cell. Nucleic acids are made up of C H O N(Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen).
The elements in Nucleic Acids are C H O N P, which stand for Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, and Nitrogen.
The functions of Nucleic Acid is to store information in the cell. DNA keeps hereditary information. RNA helps transport DNA's information.
Some examples of Nucleic Acids are DNA and RNA.

Proteins
Monomer of a Protein is a Amino Acid. There are 20 Amino Acids in living organisms.
The bonds of a Protein is a peptide.
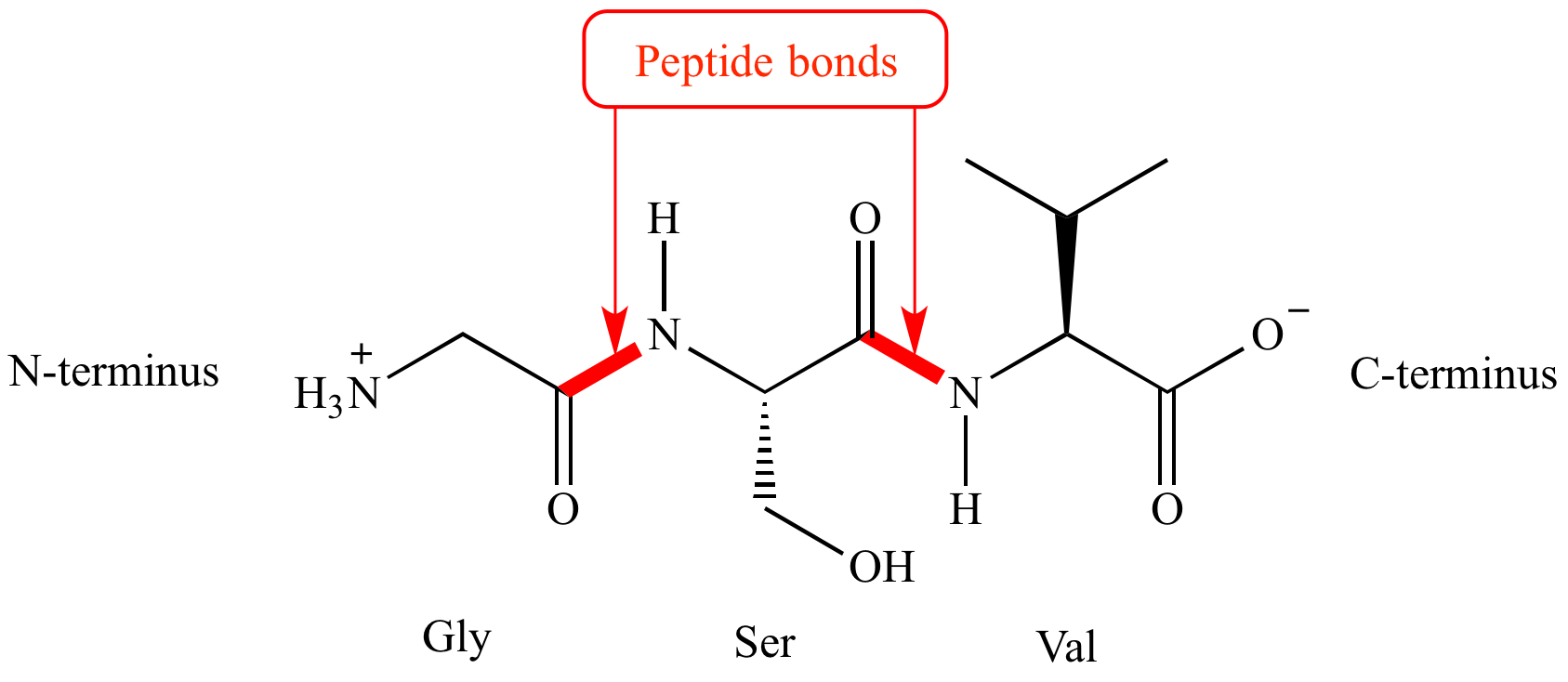

Proteins are another type of macromolecule. They are made up of Amino Acids. There are 20 different types of Amino acids in living organisms. In the Amino Acids there is are the same structure in all of them, but there is one part called the R group which is different all the Amino Acids. It is made up of C H O N(Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen).
Proteins are made up of four different elements. They are C H O N, which stand for Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen.
There are many function of proteins, but a few of them include Hormones(Insulin), Movement(Muscles), Immune System(Protect against germs), Enzymes(Help chemical reactions), Transport(Carries substances throughout body).
Some examples of proteins are muscles, fingernails, skin, hair, enzymes, and hormones.

