Current Electricity
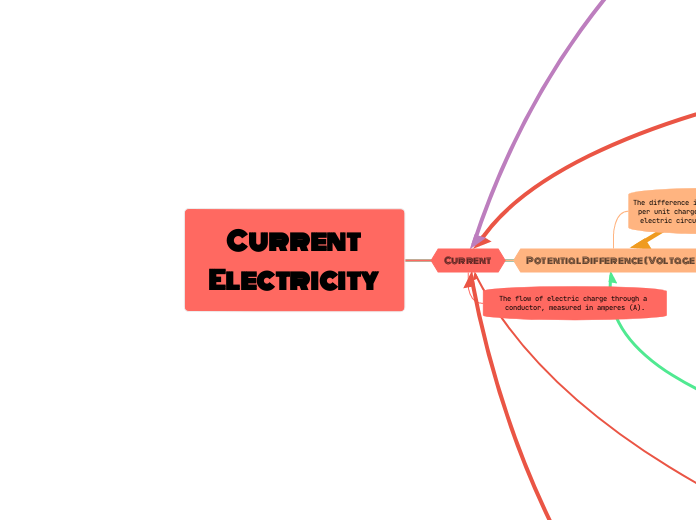
Current
The flow of electric charge through a conductor, measured in amperes (A).
Potential Difference (Voltage )
The difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points in an electric circuit, measured in volts (V).
Parallel
A circuit configuration where components are connected in separate branches, and the potential difference across each component is the same.

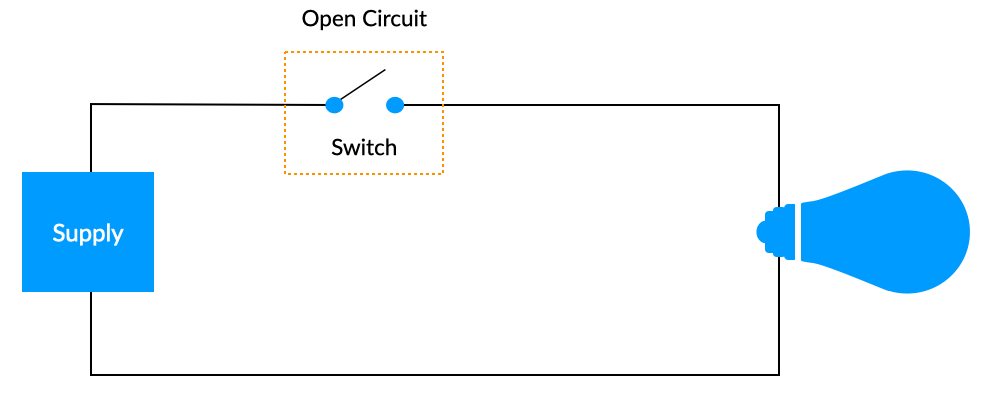
Open Circuit
A circuit in which there is a break, preventing the flow of current.
Load
A device or component in a circuit that consumes electrical energy.

A light bulb or an electric motor.
Battery
A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy and provides a potential difference in a circuit.

Double AA battery in a TV remote
Kirchoff’s law
Kirchhoff's Laws explain how electric currents and voltages work in circuits. Kirchhoff's Current Law tates that the total current into a point equals the total current out. Kirchhoff's Voltage Law states that the total voltage around a closed loop in a circuit is zero, indicating energy conservation.
Connecting Wires
Conductive materials used to establish connections between various components in an electric circuit.
A phone charger
Alternating Current
Electric current that periodically reverses direction, commonly used in household and industrial electricity.
Series
A circuit configuration where components are arranged sequentially along the same path, and the same current flows through each component.
Ohm's Law
An important part of physics stating that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage across the circuit and inversely proportional to the circuit's resistance (I = V/R).
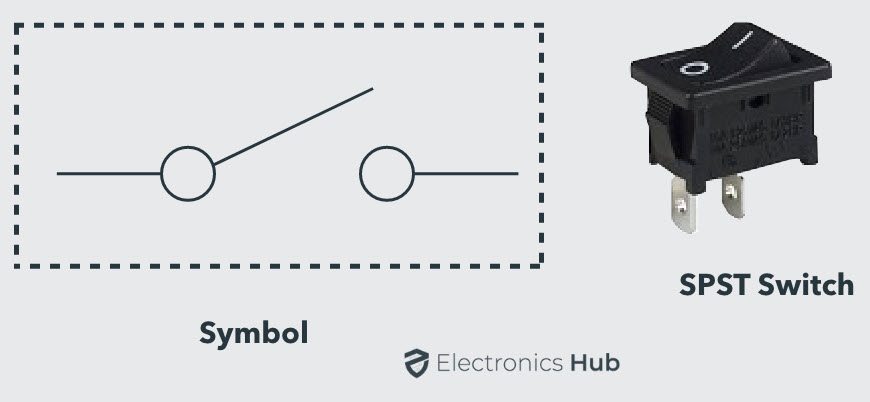
Switch
A device used to open or close an electric circuit, controlling the flow of current.
Voltmeter
An instrument used to measure the voltage or potential difference in a circuit.

Circuits
Paths or routes through which electric current can flow, typically consisting of components like resistors, capacitors, inductors, and sources like batteries.
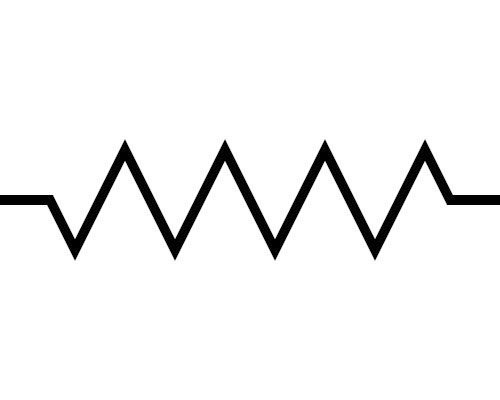
Resistor
A component in an electric circuit that resists the flow of electric current, generating heat in the process. It is measured in ohms (Ω). (Took me forever to find that symbol)
Short Circuit^
An unintended low-resistance path that allows a large current to flow, potentially causing damage or hazards in an electrical circuit.
Ammeter
An instrument used to measure the current flowing through a circuit.
Direct Current
Electric current that flows in one direction consistently over time, such as the current from a battery.
Voltage
The electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, measured in volts (V).
Resistance
The opposition that a material offers to the flow of electric current, measured in ohms (Ω).