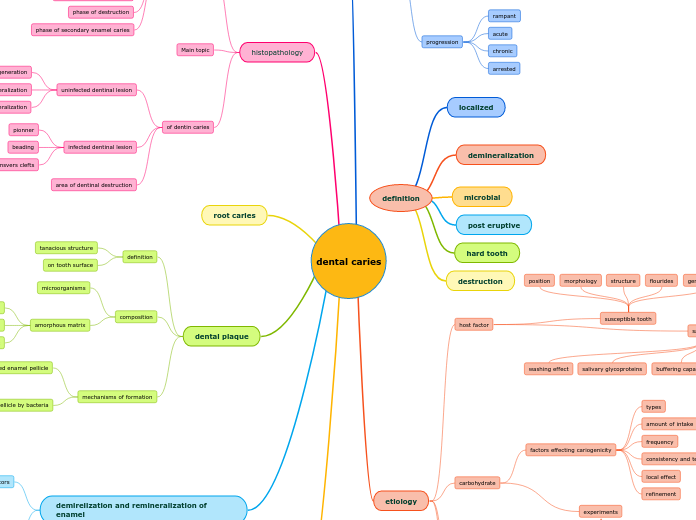
dental caries
types
site
Subtopic
pits and fissures
smooth surface
root cavity
stage
spot
enamel
dentin
deep dentin
progression
rampant
acute
chronic
arrested
etiology
host factor
susceptible tooth
position
morphology
structure
flourides
genetic effects
saliva
washing effect
salivary glycoproteins
buffering capacity
antimicrobial effect
supply of ions remineralization
carbohydrate
factors effecting cariogenicity
types
amount of intake
frequency
consistency and texture
local effect
refinement
experiments
turku study
vipeholm
hopewood house
cariogenic bacteria
experiments
millers
orlands
features
acidogenic
aciduric
synthesis of extracellular polysaccharides
actively transport
synthesis of intracellular storage polysaccharides
firm adhesion to tooth surfaces
time
histopathology
of enamel caries
phase of initiation
translucent zone
dark zone
body of the lesion
surface zone
phase of bacteria invasion
phase of destruction
phase of secondary enamel caries
Main topic
of dentin caries
uninfected dentinal lesion
zone of fatty degeneration
zone of hypomineralization
zone of hypermineralization
infected dentinal lesion
pionner
beading
liquefaction foci transvers clefts
area of dentinal destruction
root caries
dental plaque
definition
tanacious structure
on tooth surface
composition
microorganisms
amorphous matrix
protein
carbohydrate
inorganic content
mechanisms of formation
formation of an acquired enamel pellicle
coionization of cell free pellicle by bacteria
pioneer community
intermediate community
mature community
demirelization and remineralization of enamel
demineralization pathological factors
acid producing bacteria
sub-normal salivary flow or function
frequent eating or drinking of CHO
poor oral hygiene
remineralization protective factors
fluoride, calcium and phosphate
antibacterial
good oral hygiene
throies of dental caries
the acidogenic theory
proteolysis chelation theory
proleolytic theory