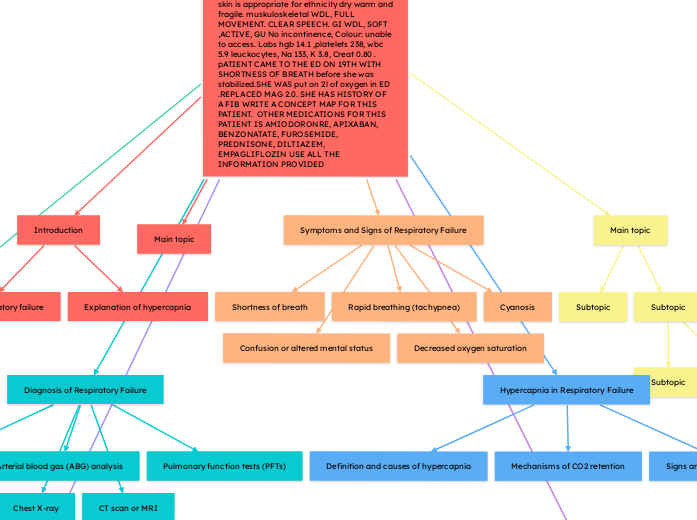
LW 88 YEARS OF age, code DNI/DNR ADM 2/19/25 ALLergies : hydroxyzine, meperidine. tubes Intravenous infusing Diltiazem. history : Congestive heartfailure, hyperlipidemia, atrial fibrilation paroxysmall, high fall risk, daily weights standing scale 71.5kg. Cheif complain Acute Respiratory Failure with hypoxia. pt on room air continous monitoring oxygen. pt was on a cardiac monitor with a regular diet.. anticipated diagonastic test Ecocardiogram. vital signs were as follows. 8:15 T 36.9,HR 102, RR 21, O2 93, 0 PAIN. AT 9:40 T 36.2, HR 87, RR 21, BP/MAP 101/68 O2 94 , 0 PAIN PATIENT IS alert and oriented times 3 pupil round 0 brisk. regular s1 and s2 symptoms :Edema. Respiratory breathing regular, unlaboured , expiratoey wheezes. skin is appropriate for ethnicity dry warm and fragile. muskuloskeletal WDL, FULL MOVEMENT. CLEAR SPEECH. GI WDL, SOFT ,ACTIVE, GU No incontinence, Colour: unable to access. Labs hgb 14.1 ,platelets 238, wbc 5.9 leuckocytes, Na 133, K 3.8, Creat 0.80 . pATIENT CAME TO THE ED ON 19TH WITH SHORTNESS OF BREATH before she was stabilized.SHE WAS put on 2l of oxygen in ED .REPLACED MAG 2.0. SHE HAS HISTORY OF A FIB WRITE A CONCEPT MAP FOR THIS PATIENT. OTHER MEDICATIONS FOR THIS PATIENT IS AMIODORONRE, APIXABAN, BENZONATATE, FUROSEMIDE, PREDNISONE, DILTIAZEM, EMPAGLIFLOZIN USE ALL THE INFORMATION PROVIDED
Introduction
Definition of respiratory failure
Explanation of hypercapnia
Symptoms and Signs of Respiratory Failure
Shortness of breath
Rapid breathing (tachypnea)
Cyanosis
Confusion or altered mental status
Decreased oxygen saturation
Main topic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Main topic
Diagnosis of Respiratory Failure
Clinical evaluation
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs)
Chest X-ray
CT scan or MRI
Hypercapnia in Respiratory Failure
Definition and causes of hypercapnia
Mechanisms of CO2 retention
Signs and symptoms of hypercapnia
Treatment Options
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV)
Supplemental oxygen therapy
Bronchodilators and corticosteroids
Mechanical ventilation
Addressing the underlying cause of respiratory failure
Prognosis and Complications
Prognosis of respiratory failure
Complications of hypercapnia
Long-term management and follow-up care