Microbiology

Protist
protist
Chlamydomanous
4
10
move with double flagellum
Live in fresh water
40
Different Types of Protist
Plant like
all autographs contain CHLOROPHYLL that have cell walls 2 major groups
Unicellular algae

Diatoms
multicultural algae
/GettyImages-584940470-57df14cc5f9b5865168b3fde.jpg)
Brown algae
Animal Like
all heterotrophes, classified by how they move
sacodines - amoeba
ameoba
they use there pseudopods to move and eat
Amoeba 4
Amoeba 10
Amoeba 40
This amoeba likes to live in warm water, including warm lakes and rivers, as well as hot springs.

reproduce by binary fission
Ciliates - paramecium
paramecium
cilia to move and eat
paramecium 4
paramecium 10
paramecium 40
live in aquatic environments, usually in stagnant, warm water.
Algal photosynthesis provides a food source for Paramecium.
Flagellates - euglena
Euglena
flagella or flagellum
live in fresh and brackish water rich in organic matter and can also be found in moist soils.
Sporozoans - plasmodium
reproduce by asexually by spores
have no means of locomotion
many parasites, which depends on host body fluids to move
Fungus Like
multi-cellular body (like giant amoeba) called plasmodium
They roll over forest floor feeding on dead organic matter
move very slowly

few mm a day

reproduce asexually with spores (like fungi) in fruiting bodies
Fungus
Reproduction
asexually
spores
budding
fragmentation
Description
Fungi includes a vast variety of organisms such as mushrooms, yeast, and mold, made up of feathery filaments called mycelium.
Fungi are multicellular and eukaryotic.
They are also heterotrophs, and gain nutrition through absorption.
diseases

Mucormycosis

Fungal Nail Infections

Coccidioidomycosis
pathogen: Cryptococcus neoformans
human infections result from the
inhalation of spores and or dried yeast farms made
airborne

Candidiasis

Aspergillosis
Example organisms
Mycelium
Coprinus
Sporangia
good fungus

Yeast for beer or bread
Outbreaks

Butterball brand ground turkey
bacteria that caused outbreak was
Salmonella
6 cases, 0 deaths, 1 hospitalization. Wisconsin, north carlolina, minnesota
diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps
Throw away the meat, see a doctor for medical attention if consumed

Candida
Why is it a concern
It is often multidrug-resistant, meaning that it is resistant to multiple antifungal drugs commonly used to treat Candida infections.
It is difficult to identify with standard laboratory methods, and it can be misidentified in labs without specific technology. Misidentification may lead to inappropriate management.
It has caused outbreaks in healthcare settings. For this reason, it is important to quickly identify C. auris in a hospitalized patient so that healthcare facilities can take special precautions to stop its spread.
What types of infections can C. auris cause
blood stream infections
wound infections
ear infections
who is at risk
People who have recently spent time in nursing homes and have lines and tubes that go into their body (such as breathing tubes, feeding tubes and central venous catheters), seem to be at highest risk for C. auris infection.

measles
Measles, also known as Red Measles or Rubeola, is a serious disease caused by a virus. It is
spread very easily through the air when someone with measles coughs or sneezes, and by
direct contact with infected nose or throat secretions.
who can get measles
Anyone who has been in close contact with someone who has measles can get the disease
symptoms

runny nose
fever
red watery eyes

pink eye
cough

rash
complications
Most people recover from measles. Measles can cause serious complications in 20% of
cases, including ear infections, pneumonia, encephalitis (swelling or inflammation of the
brain), seizures, and deafness. In Canada, measles causes death in approximately 1 out of
every 3,000 cases.
Measles can be avoided if everyone takes
the vaccine

Bacteria
Bacteria is ALIVE
They reproduce
Grow in number not size

Make copies of themselves by dividing in half
They need to eat
some make their own food from sunlight - like plants
some are scavengers - share the environment around them
some are warriors (pathogens) - they attack other living things
A pathogen is bacteria that makes you sick
they make you sick to get food they need to survive and reproduce
They produce poisons (toxins) that make you sick
Fever
Headache
vomiting
diarrhea
can destroy body tissue
you can get a pathogen from human contact with someone who is sick
Direct or indirect
Food
Water
other surfaces that are contaminated
To avoid Pathogens
wash your hands often so you wont transfer bacteria to your mouth or food
warm water with soap for 20 seconds rub hard between fingers and nails
cook food thoroughly to kill any pathogens that may be in your food
store food properly to limit pathogen growth
cold temperatures (40 F)
Harmful pathogens are

E.coli - found in ground beef, contaminated fruits or vegtables
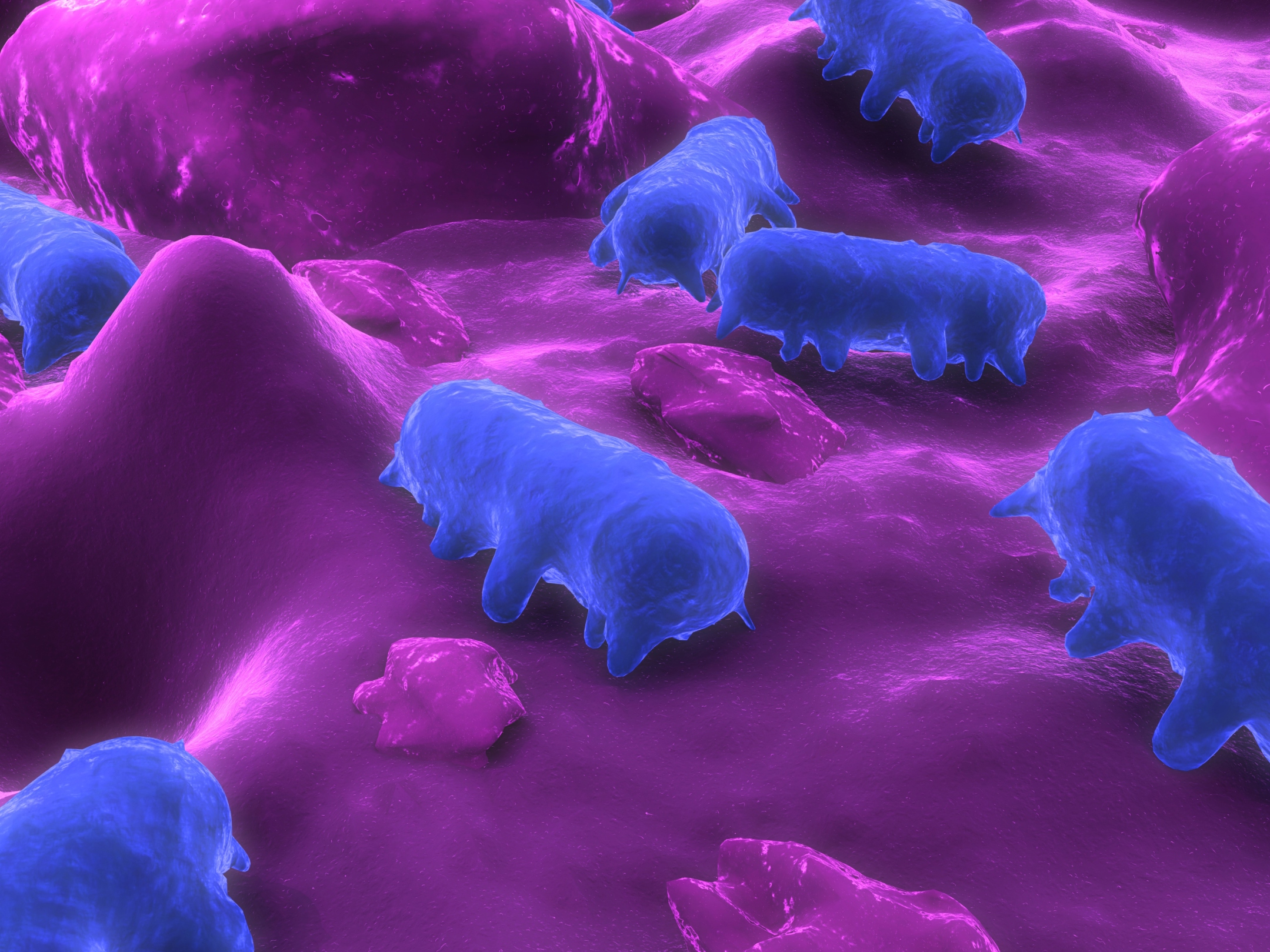
Salmonella - found in raw meats, poultry, eggs, sprouts, fruits and vegtables

Listeria - found in deli foods, lunch meats, smoked fish and vegetables
not all pathogens are harmful, some of them are helpful

Lactobacillus: makes cheese, yogurt, buttermilk and produces vitamins in your intestine

Leuconostoc: makes pickles and sauerkraut

Pediococcus: makes pepperoni, salami and summer sausage
Size of Bacteria
single celled organisms
very small
Need a microscope to see
can be found on most materials and surfaces
Bacteria
causes diseases by
Metabolizing their host
Secreting toxins
Can be
Heterotrophic
Photosynthetic
Chemoautotrophic
Are unicellular
Can have shapes like

Coccus
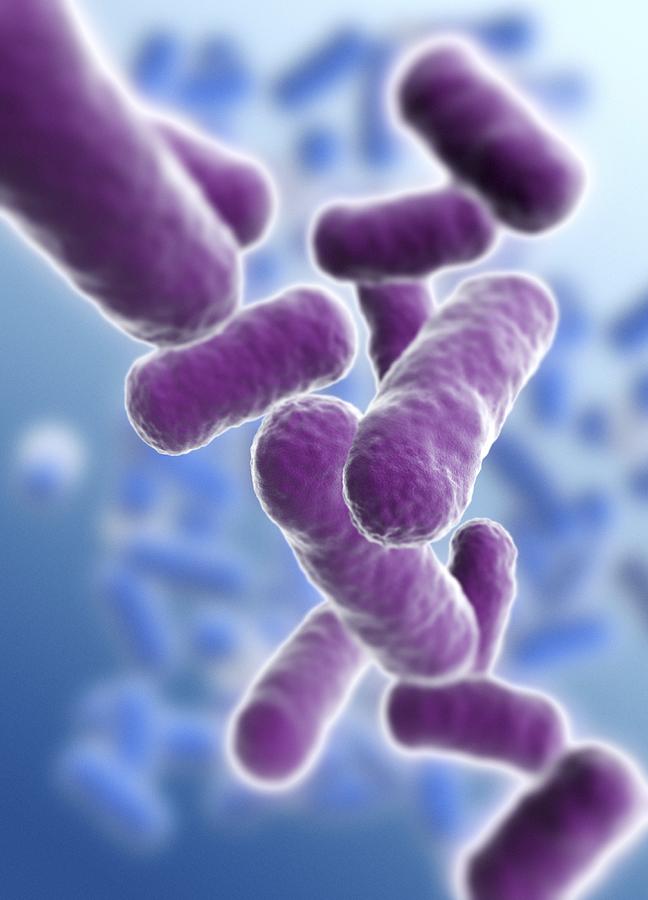
Bacillus (rod)

Spirillum (spiral)
Are prokaryotic
Have no internal membrane system
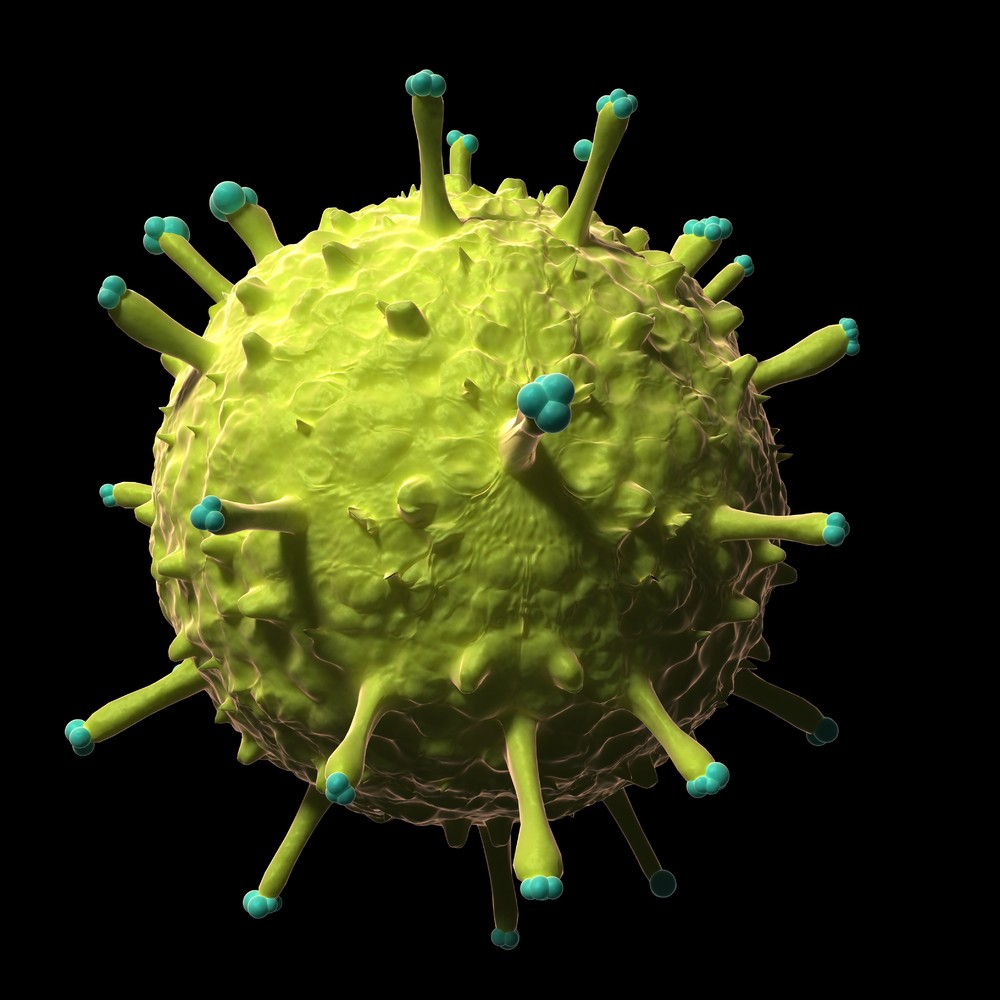
Virus
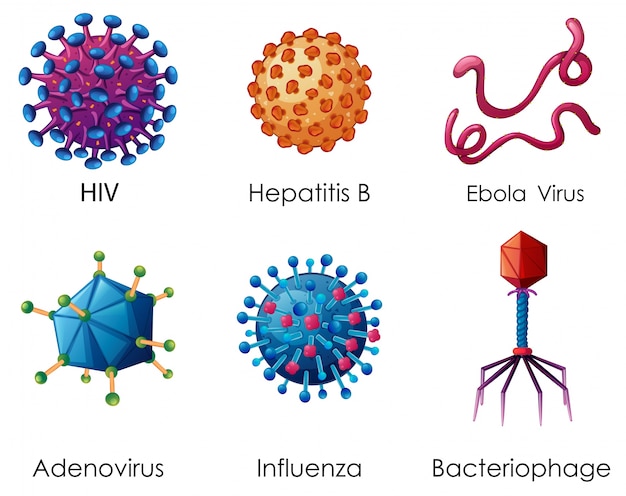
what is a virus?
Reproduce by infecting living things
viruses are non living

They have RNA or DNA and a protein coat
they enter living cells and once
inside the cell they use the machinery
of the infected cell to produce more
viruses
viruses are very small
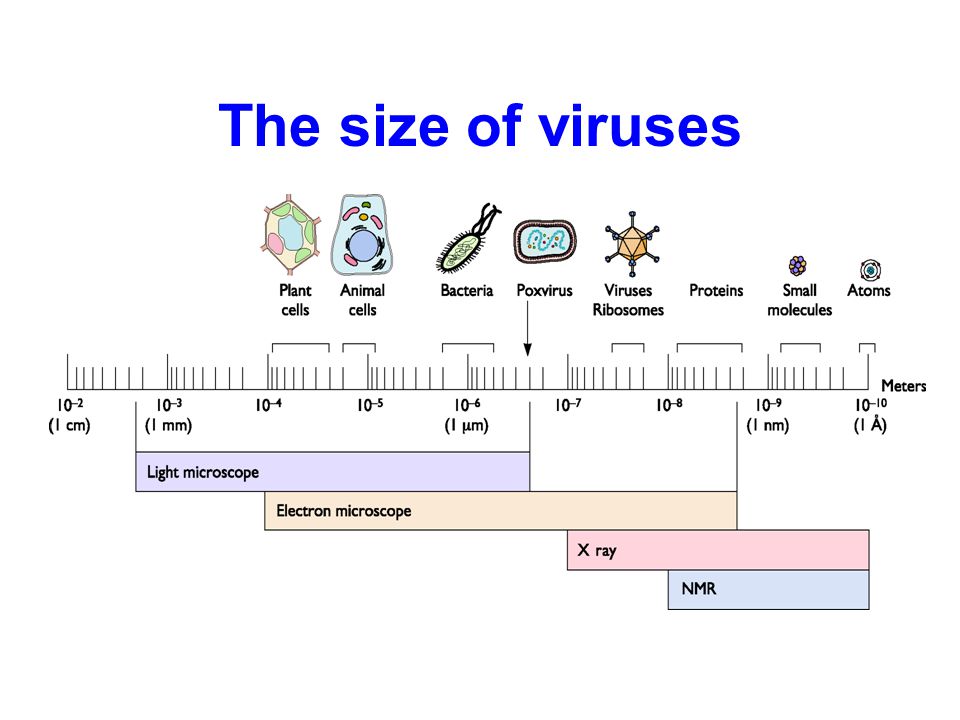
to see viruses you'll need the help
of an electron microscope

Zika Virus (My InfoGrapgh)
Reproduction
Viruses reproduce in 2 different ways
lysogenic and lytic
Lytic

host cell is lysed (bursts) and immediately destroyed

Lysogenic
The virus's embeds its DNA into the hosts DNA
The virus's DNA is replicated along with the host cells DNA
A host cell makes copies of the virus indefinitely
Lysogenic Infection

Viral DNA inserted into the host cell as a pro-phage
The host cell is not immediately destroyed

Vaccines
prevention form any viruses
stimulate the immune system to react against the actual diseases
few drugs treat or cure viral disease
antiviral drugs that are effective interfere with viral DNA or RNA synthesis
examples

polio
rubella

smallpox

mumps

antibiotics are useless against viruses
viruses do not contain the enzymes which antibiotics work
Viral Diseases
Animals

Rabies

Parvo

Hoof and mouth disease

Prions - protein infected particles
linked to several degenerative
brain diseases
mad cow
creutzfeldt-jacob
Transferred in food
prions are nearly indestructible
Cancer causing viruses
oncogenic viruses
Human papilloma virus
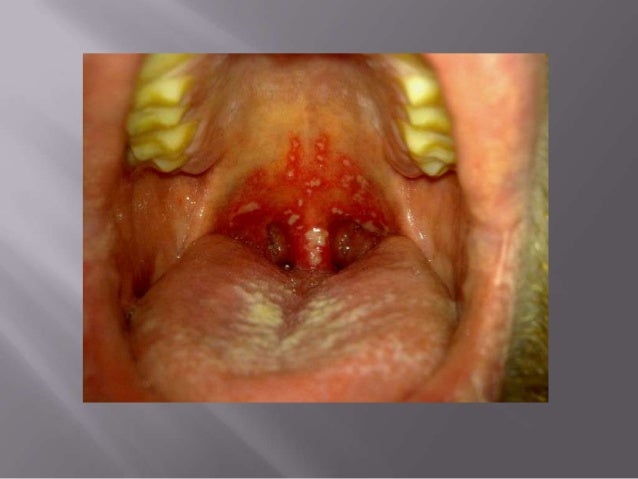
Human herpes virus

Hepatitis B

Plants

viruses have a difficult time invading plants because they have a cell wall but when plants do get the virus it can be very bad
insects can be carriers
plant injuries can make plants get the virus easier
Viroid's - small infectious molecules of single stranded RNA that have no surrounding capsids.

causes stunt growths
reduces harvest amount

Contagion
Contagion is a movie that we watched
in class about the spread of a virus (nipah)
The virus started when the lady touched
the chef who touched the infected pig
in the movie her husband didn't get infected because his immune system was strong and could protect him from the virus

The CDC was involved, there job was to create a vaccine and prevent the disease from spreading
the symptoms were
seizures
high fever
foaming at the mouth
The modes of transmission for this virus was
air bone (coughing)
touching something that was touched by an infected person