Muscular System Anatomy

Types of Muscle
Skeletal
found in limbs
striated, multinucleated
voluntary, regulated by CNS
Cardiac
found in heart
striated, 1 nucleus
involuntary, regulated by ANS
Smooth
found in viscera
not striated, 1 nucleus
involuntary, regulated by ANS

Functions
Produces movement
maintains posture
stabilizes joints
generates heat

5 Golden Rules of Muscle Activity
1. All cross at least 1 joint
2. bulk lies proximal to joint crossed
3. All have at least 2 attachments: origin & insertion
4. Muscles can only pull, they never push
5. During contraction, the insertion moves towards origin
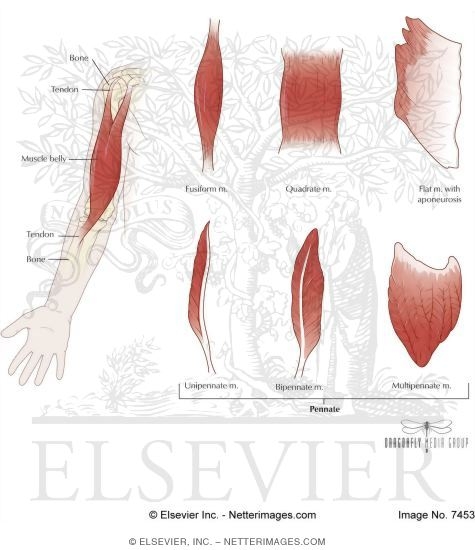
Shapes of Muscle
Triangular
shoulder, neck
Spindle
arms, legs
Flat
diaphragm, forehead
Circular
mouth, eyes

Factors when naming muscles
1. Size
2. Location
3. Movement/action it causes
4. Number of origins
5. Location of origin and insertion
6. shape
7. Direction of muscle fibers
Types of muscle responses
Graded Responses
how skeletal muscles react to stimuli
a. speed or b. number of cells stimulated
Twitch
single, brief contraction
not normal function
Tetanus
one contraction immediately followed by another
muscle never completely returns to a relaxed state
effects are compounded
Types of Exercise

Anaerobic
does not use oxygen
produces 2 molecules of glucose
Shortcoming: uses a lot of glucose and produces little ATP
increases strength

Aerobic
uses oxygen
produces 36 molecules of ATP
Shortcoming: requires continuous supply of oxygen and fuels
makes body more flexible and resistant to fatigue

Isotonic
muscles shorten
movement occurs
normal exercise

Isometric
tension in muscles increases
no movement occurs
pushing against concrete wall

Resistance
increases size of muscles
movement occurs
weightlifting
