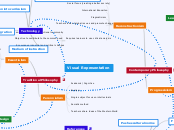
Visual Representation
Traditional Philosophy
Perennialism
Academic / Cognitive
Realism
Single subject focus on intellectuals
Socratic method
Teachers share ideas of the Western World
Essentialism
Academic / Technological
Idealism / Realism
Multi-subject approach
Students are taught by ability
Improving intellectual ability in one area transfers to others
Education of rational students
Contemporary Philosophy
Progressivism
Pragmaticism
Humanistic
Holistic approach to teaching
Teachers are seen as guides
Stays away from content or knowledge focus
Education based around interests
To foster active learning
Reconstructionism
Social focus (creating a better society)
International Educaiton
Pragmaticism
Teachers look at global issues and promote change
Requires learners to use critical analysis
Local, national, and international community
Objective to contribute to the common good
Encourages industrial and political changes
Subject Centered Design
Widely accepted by school systems
Knowledge & Content based
Heavily influenced by textbooks
Standardization
Strong academic focus
Based on essential knowledge (later further developed into sub-categories)
Content rely on teachers as Subject Matter Experts and textbooks adopted by particular schools
Learner Centered Design
Learning should match learner's development level
Learning should be integrated into learners' lives
Teachers work around students strengths
Student led instruction
Knowledge organized based on learners' perspective
Process oriented instruction
Learn through subject instead of learning the subject
Relevant and meaningful to the learner
Should occur in natural settings
Focus on more than academics
World Interaction
Physical Knowledge
Social knowledge
Emotional knowledge
Logical knowledge
Problem Centered Design
Focus on ill-structured problem solving
Requires learners to use past experience to analyze the problem
Uses both society's problem and learner's life situation as a basis for curriculum design
Social issues at the fore-front
Objective is for learners to be able to address the situation and involve them in improving society
Social improvement through the involvement of the schools and learners
Pushes cultural norms
Cultural centered
Technology
Incorporation into curriculum
Looks into the communication of knowledge
Looks at "how" to teach more than "what" to teach
Objective is to maximize learners' achievement through a systematic approach
Full integration
Medium of instruction
Subject matter as the main content source
Activities are planned according to the subject matter (key is the organization of knowledge for easier learning)