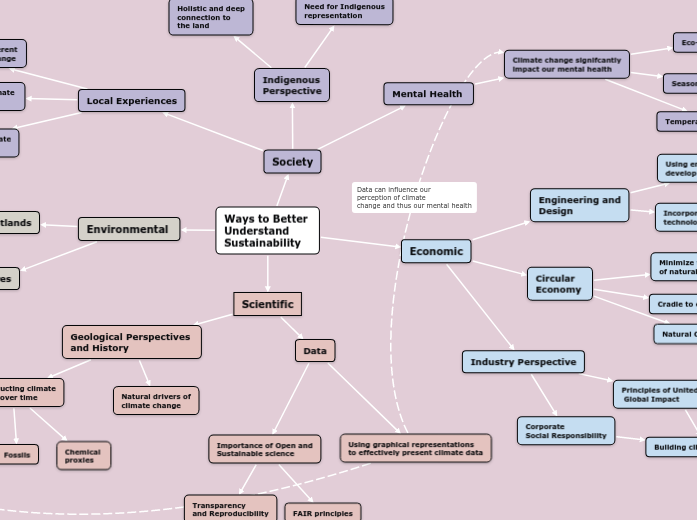
Ways to Better
Understand
Sustainability
Environmental
Peatlands
Method for greenhouse gas
emission regultaion
Important for biodiversity conservation
Soil fertility
Water regulation
Fires
exacerbated by human activities
disruption to peatlands and natural
habitats
Economic
Circular
Economy
Minimize waste and extraction
of natural resources
Cradle to cradle
Natural Capitalism
Radical Resource Productivity
Biomimicry
Service and flow economy
Engineering and
Design
Using engineering principles to
develop sustinable solutions
Incorporate sustainable
technologies and systems
Industry Perspective
Corporate
Social Responsibility
Building climate resiliency
climate mitigation
climate adaptation
Principles of United Nations
Global Impact
Society
Local Experiences
Local communities face different
challenges from climate change
Local communities deal with climate
change in different ways
Importance of studying climate
change ethnographically
Indigenous
Perspective
Holistic and deep
connection to
the land
Need for Indigenous
representation
Mental Health
Climate change signifcantly
impact our mental health
Eco-anxiety
Seasonality and suicide
Temperature and suicide
Scientific
Data
Importance of Open and
Sustainable science
Transparency
and Reproducibility
FAIR principles
Using graphical representations
to effectively present climate data
Geological Perspectives
and History
Reonstructing climate
change over time
Sediemtns
& Rocks
Fossils
Chemical
proxies
Natural drivers of
climate change