3U Chemistry
Reactions
Writing Chemical Equations
Solubility rules
shows you which elements are insoluble
Activity series
a list of decreasing order of their reactivity
Balancing equations
To even out the amount of an element on the other side of the reaction
types of reactions
Combustion (C2H2+O2=H2O+CO2)
can also be incomplete
Double displacement ( AB+CD=AD+CB)
Single displacement (A+BC=AC+B)
Decomposition (AB=A+B)
Synthesis ( A+B=AB)
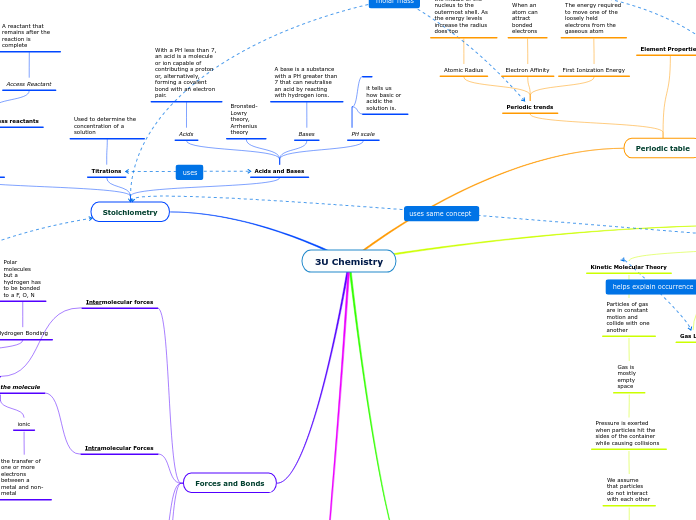
Forces and Bonds
Lewis Structures and VSEPR Diagrams
VSEPR diagrams are used to predict the geometry of a molecule from the number of atoms that are bordering the central atom
Lewis structures show which atoms are bonded together in a molecule
Chemical Bonding and Electronegativity
Electronegativity is When an atom is bonded, it has the potential to draw individual electrons to itself.
Ionic bonds
Polar covalent bonds
Non-polar covalent bonds
Intramolecular Forces
Occur within the molecule
ionic
the transfer of one or more electrons between a metal and non-metal
Covalent
sharing of electrons between two non-metals
Intermolecular forces
Occurs between molecules
Hydrogen Bonding
Polar molecules but a hydrogen has to be bonded to a F, O, N
Dipole-Dipole
Polar molecules only are held together due to their partial charges
London Dispersion
Polar and non-polar molecules form temporary bonds by the constant movement of electrons causing a short-term charge imbalance
Stoichiometry
Acids and Bases
PH scale
it tells us how basic or acidic the solution is.
Bases
A base is a substance with a PH greater than 7 that can neutralise an acid by reacting with hydrogen ions.
Bronsted-Lowry theory, Arrhenius theory
Acids
With a PH less than 7, an acid is a molecule or ion capable of contributing a proton or, alternatively, forming a covalent bond with an electron pair.
Titrations
Used to determine the concentration of a solution
The relationship between the relative quantities of the reactants in a reaction.
Limiting and access reactants
Access Reactant
A reactant that remains after the reaction is complete
Limiting Reactant
A reactant that is completely consumed during a chemical reaction
Calculated using mole to mole ratio, mass, volume, concentration, molar mass
Gases
Gas stoichiometry
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
STP and SATP
Gas Law
Gay-Lussak's Law
States that temperature and pressure are directly proportional while the volume remains constant
Charle's Law
States that temperature and volume are directly proportional as long as mass and pressure remain constant
Boyle's Law
States that pressure and volume are inversely proportional as the temperature and mass remain constant
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Particles of gas are in constant motion and collide with one another
Gas is mostly empty space
Pressure is exerted when particles hit the sides of the container while causing collisions
We assume that particles do not interact with each other
Average kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature
Periodic table
Element Properties
atomic weight is the number off neutrons
Atomic number is the amount of electrons and protons
Periodic table groups
alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, metalloids, other metals, non metals, halogens, noble gases and rare earth elements
Periodic trends
First Ionization Energy
The energy required to move one of the loosely held electrons from the gaseous atom
Electron Affinity
When an atom can attract bonded electrons
Atomic Radius
The distance from the middle of the nucleus to the outermost shell. As the energy levels increase the radius does too