作者:Addison Gardner 3 年以前
185
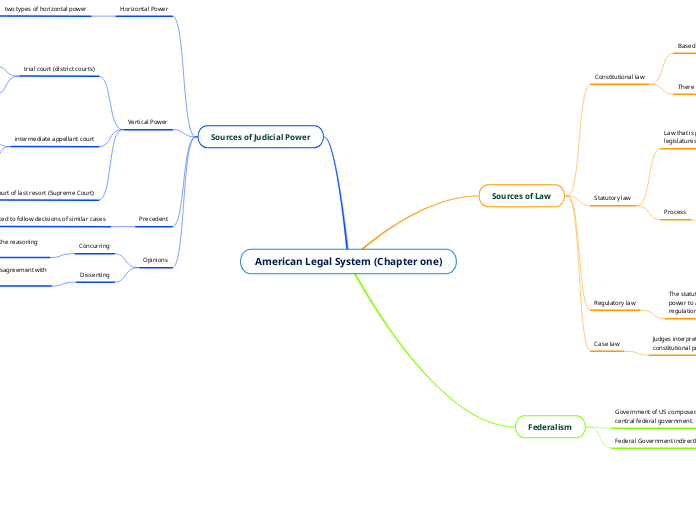
American Legal System (Chapter one)
作者:Addison Gardner 3 年以前
185

更多类似内容
when a judge or justice write a statement of disagreement with the results of the ruling.
when a judge agrees with a ruling but not with the reasoning behind the ruling.
Binding on all lower courts
They review the intermediate courts decision to see is laws were correctly applied.
Can appeal to higher court
Binding on courts of it's jurisdiction
They can reverse the trial courts decision if error is found/
Make sure the trial court did not have error and to develop laws,
can appeal to next highest court
Fact finding process occurs
Once facts are found they are the same when going to higher courts unless found that they are biased when they were found.
Limited power
The power is limited based on the legislative decision.
Supreme power
the power that the supreme courts act as the ultimate interpreter of the constitution.
The agencies within the department of the law that is in question investigates the situations.
The agencies create regulations that are additions to the law
The law is created by either the house of representatives or senate. The bill is then given to the appropriate committee of the given house. That house then gives it to a subcommittee and then it is reported by a full committee. The bill is then given to the house of senate to debate on and vote on the bill. The bill then passes or dies. If it passes it goes to the other house(house of representatives or senate) and is given to a committee, subcommittee, and then full committee and debated on and voted by the house. If passed by both houses it is given to the conference committee to develop compromise bill. If this is voted to pass then it is given to the president to pass or veto the bill. If the bill passes it becomes a law, if it is vetoed it can pass by a 2/3 vote of congress.
All states have educational mandates in their constitutions.
The state constitution can provide more rights beyond the federal constitution but cannot deny rights from the federal one.