作者:ALLENE WIBISONO 2 年以前
215
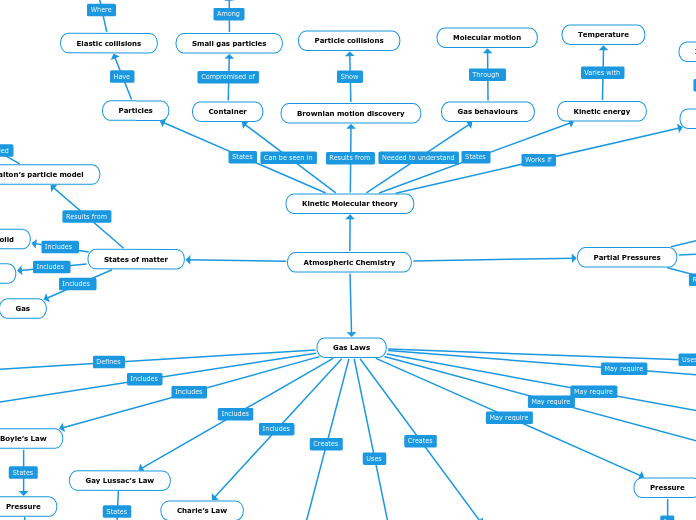
Atmospheric Chemistry
In the study of gases, several fundamental laws and principles govern the behavior and properties of gas particles. Kinetic Molecular Theory explains that gas particles are in constant motion, and their kinetic energy is directly related to temperature.