Reference 6 General Types of Disabilities. (2020, April 02). from https://changingpaces.com/6-general-types-of-disabilities/
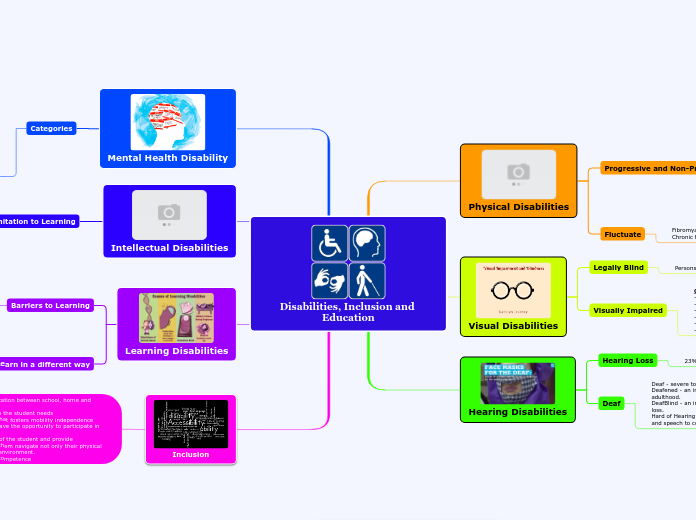
Disabilities, Inclusion and Education
Conflict is present everywhere in the world around us. We experience conflict on a daily basis, and it can be minor or major.
Conflict in a story is a struggle between opposing forces. Characters must act to confront those forces and there is where conflict is born. If there is nothing to overcome, there is no story. Conflict in a story creates and drives the plot forward.
Inclusion
- Ensure open communication between school, home and community partners.
- Effective IEP tailored to the student needs
- Physical environment that fosters mobility independence
- Ensure that students have the opportunity to participate in social activities.
- Understand the needs of the student and provide accommodation to help them navigate not only their physical but also their academic environment.
- Respect the student's competence
Learning Disabilities
In this type of conflict, a character must take on society itself, and not a single person. The character stands at odds with societal norms and realizes the necessity to work against these norms. This is an external conflict.
Learn in a different way
Give examples of man versus society conflict in the real world.
- Having a learning disability does not mean a person is incapable of learning; rather that they learn in a different way.
- Many people with a learning disability develop strategies to compensate for or to circumvent their difficulties.
Barriers to Learning
Give examples of man versus society conflict in a literary work.
- A learning disability is essentially a specific and persistent disorder of a person’s central nervous system affecting the learning process.
- This impacts a person’s ability to either interpret what they see and hear, or to link information from different parts of the brain.
- One of the most common indicators of a learning disability is a discrepancy between the individual’s potential (aptitudes and intellectual capacity) and his or her actual level of achievement.
Intellectual Disabilities
This situation results from a protagonist working against what has been foretold for that person. While this conflict was more prevalent in stories where gods could control fate, such as in ancient Greek dramas, there are still examples of this type of conflict in more contemporary literature.
Permanent Limitation to Learning
Give examples of man versus fate conflict in a literary work.
- Any condition that impairs development of the brain before birth, during birth, or in childhood years
- Genetic conditions
- Illness affecting the mother during pregnancy
- Use of alcohol or drugs by pregnant mothers
- Childhood diseases
- Poverty — resulting in malnutrition, disease-producing conditions, inadequate medical care, and environmental health hazards.
Mental Health Disability
A more contemporary type of conflict, this situation results from humans involved in a struggle with man-made machines. This is an external conflict.
Categories
Give examples of man versus machine conflict in a literary work.
Schizophrenia – About 1% of Canadians.
Mood Disorders (Depression and Manic Depression) – About 10% of the population. Depression is the most common mood disorder.
Anxiety Disorders – About 12% of Canadians. They include phobias and panic disorder as well as obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Eating Disorders – Includes anorexia nervosa and bulimia and are most common in men and women under the age of 30.
Personality Disorders – There are many different personality disorders. People with these disorders usually have difficulty forming relationships with people. They are the most difficult disorders to treat.
Hearing Disabilities
This conflict develops from a protagonist’s inner struggles and may depend on a character trying to decide between good and evil or overcoming self-doubt. This conflict has both internal and external aspects, as obstacles outside the protagonist's force them to deal with inner issues.
Deaf
Give examples of man versus self conflict in the real world.
Deaf - severe to profound hearing loss.
Deafened - an individual who has acquired a hearing loss in adulthood.
DeafBlind - an individual who has both a sight and hearing loss.
Hard of Hearing - an individual who uses their residual hearing and speech to communicate.
Hearing Loss
Give examples of man versus self conflict in a literary work.
23% of Canada's population experience hearing loss
Visual Disabilities
In this type of conflict, a character is tormented by natural forces such as storms or animals. This is also an external conflict.
Visually Impaired
Give examples of man versus nature conflict in the real world.
Common causes of vision loss include:
- Cataracts (cloudy vision – treatable)
- Diabetes (progressive blindness)
- Glaucoma (loss of peripheral vision)
- Macular Degeneration (blurred central vision)
- Retinal Detachment (loss of vision)
- Retinitis Pigmentosa (progressive blindness)a
Legally Blind
Give examples of man versus nature conflict in a literary work.
Persons with 10% or less of normal vision
Physical Disabilities
A situation in which two characters have opposing desires or interests. The typical scenario is a conflict between the protagonist and antagonist. This is an external conflict.
Fluctuate
Give examples of man versus man conflict in the real world.
Fibromyalgia – chronic pain condition
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome – chronic fatigue condition
Progressive and Non-Progressive
Give examples of man versus man conflict in a literary work.
Non-Progressive
- Cerebral Palsy – neurological condition
- Spina Bifida – congenital malformation of the spinal cord
- Spinal Cord Injury – neurological damage resulting from trauma
- Absent limb
Progressive
- Multiple Sclerosis
- neurological deterioration
- Muscular Dystrophy – muscular disorders
- Chronic Arthritis – inflammation of the joints