- More complicated pathway
- Happens in the mitochondria
- Needs many enzymes and several complex sub pathways leading to the complete breakdown of glucose fats and protein enter
- Faster pathway
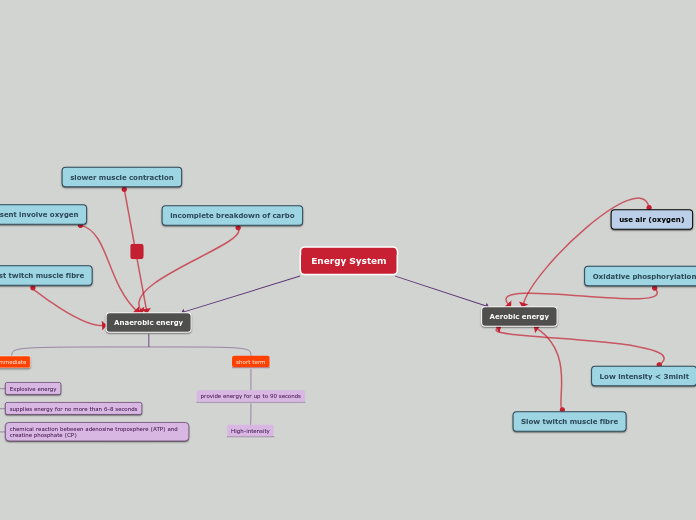
- Occurs in the muscle fibre
- Uses chemicals and enzymes
-Very powerful, but shortened during physical activity
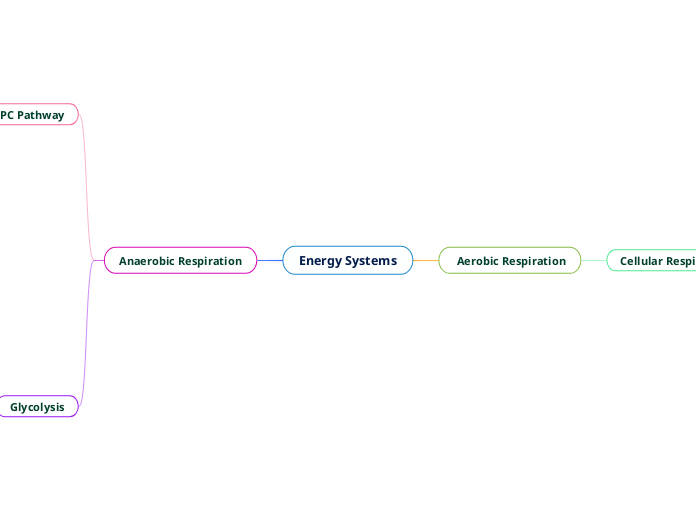
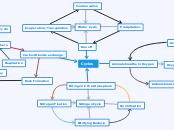
Energy Systems
Aerobic Respiration
Cellular Respiration
-Slow process which requires oxygen, without oxygen the energy can not be converted.
Involves three separate pathways
3) The Electron Transport Chain
-Yeilds large amounts of ATP (34)
-C02 and water are the byproduct
-Electrons get formed by water and that energy is then used to resynthesize ATP
-Carbon monoxide limits the ETC
-
2) The Krebs Cycle
-Has eight reactions
-Has 2 molecules of ATP
-Complete cycle of reactions occur
-Citric acid is formed
-Hydrogen peroxide limits the Krebs Cycle, which can limit the production of NADH
1) Glycolysis
-Enzymes split a molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, that then releases energy which is transferred to ATP.
-when oxygen is present pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl CoA instead of lactic acid
--the energy yield during the process is very low when compared to the energy that is utilized
water and CO2 is a byproduct
slow process which needs a lot of oxygen
yeilds 36 ATP
Uses a lot of ATP
Needs the complete breakdown of glucose
Preferred pathway after 90 seconds
Fats, proteins and carbohydrates are used
Anaerobic Respiration
Glycolysis
-Depletion of oxygen
-Overall glycolysis is an inefficient means of energy production.
-only small amounts of energy can be used from the glycogen when under anaerobic conditions.
-Lactic acid is formed, which limits the increase of chemical reactions and denatures enzymes.
-Lactic acid also causes sore muscles
The first Sequence of reactions
occurs in the cytoplasm
glycogen gets depleated
ATP-PC Pathway
Limitations
-Pc only lasts 10s.
-takes 3-4 minutes to regenerate.
- Just one molecule of ATP is resynthesized for every molecule of Pc
-Pc only gets resynthesized with oxygen present.
Does not produce lactic acid
Creatine phosphate resynthesizes ATP which is where is generates from
When there is large amounts of energy, the body releases creatine kinase which then breaks down phosphocreatine which then releases energy
Stored ATP in the muscle breaks down which forms energy
ADP + P = ATP - ATP is the byproduct
Has small amounts of stored energy
ADP releases kinase. Kinase breaks down the fuel source (Phosphocreatine) which releases energy
Yeilds enormus amounts of ATP