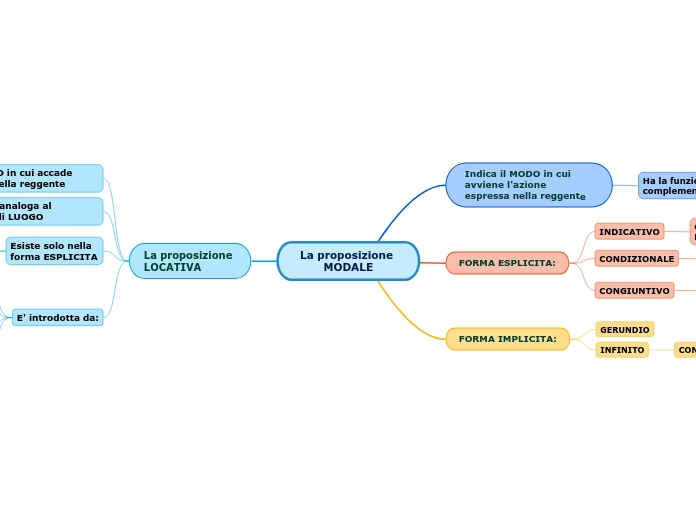
La proposizione MODALE
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
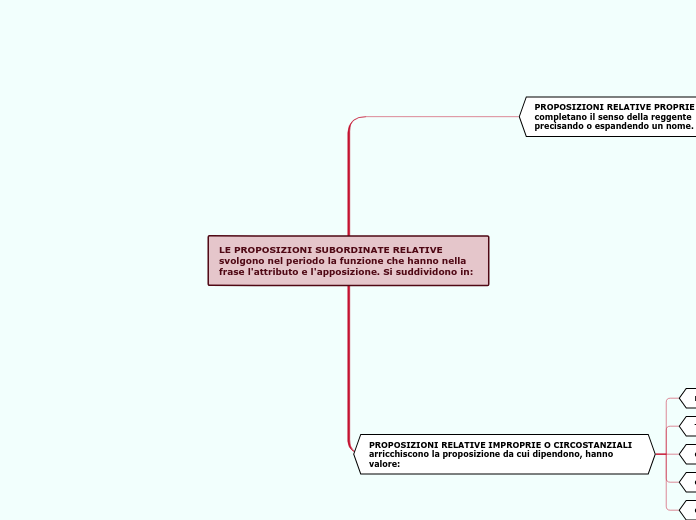
La proposizione LOCATIVA
E' introdotta da:
Nuclear energy originates from the splitting of uranium atoms – a process called fission.
This generates heat to produce steam, which is used by a turbine generator to generate electricity. Because nuclear power plants do not burn fuel, they do not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of Nuclear Energy.
DAL LUOGO IN CUI
NEL PUNTO IN CUI
DA DOVE
DOVE
Esiste solo nella forma ESPLICITA
A wind turbine, or alternatively referred to as a wind energy converter, is a device that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of Wind turbines.
Ha la funzione analoga al complemento di LUOGO
Solar energy begins with the sun. Solar panels are used to convert light from the sun, which is composed of particles of energy called 'photons', into electricity that can be used to power electrical loads.
Write down the benefits of using solar panels.
Indica il LUOGO in cui accade quanto detto nella reggente
Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen.
It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
Name the advantages and disadvantages of Hydrogen fuel.
FORMA IMPLICITA:
INFINITO
CON, A
GERUNDIO
FORMA ESPLICITA:
There are many different types of energy, which all fall into two primary forms – kinetic and potential.
Energy can transform from one type to another, but it can never be destroyed or created.
CONGIUNTIVO
Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms.
This energy is released when the nuclei are combined (fusion) or split apart (fission).
Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms to produce electricity.
What element do they use to fuel nuclear power plants?
COME SE, QUASI CHE, COME
CONDIZIONALE
Thermal energy is created from the vibration of atoms and molecules within substances. The faster they move, the more energy they possess and the hotter they become. Thermal energy is also called heat energy.
Give examples of heat energy.
PROPRIO COME
INDICATIVO
Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects; as objects move faster, more energy is stored.
Examples of motion energy include wind, a flowing river, etc.
Give more examples.
COME, NEL MODO IN CUI, NEL MODO CHE
Indica il MODO in cui avviene l'azione espressa nella reggente
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Ha la funzione analoga al complemento di MODO
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy.
Write down the main components of a typical flywheel.