作者:Diana Farisya 5 年以前
448
Leading
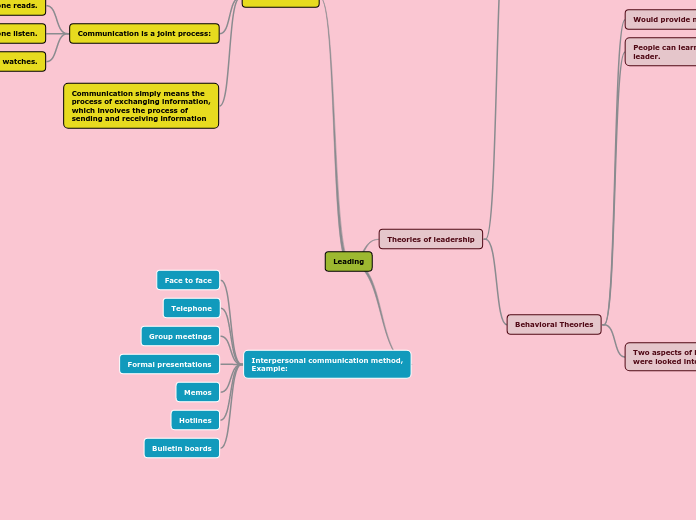
作者:Diana Farisya 5 年以前
448

更多类似内容
Contingency Theories of Leadership
Important variables to consider
Position power (strong or weak)
Task structure (repetitive or nonrepetitive
Leader- member relations (good or poor)
The contingency theory allows for predicting the characteristic of the appropriate situations for effectiveness
Determine the situational adorableness of particular situation.
It fit leadership effectiveness depend on the situation and another to be able to isolate situational conditions.
Leadership Styles
The managerial grid
Places managerial styles in five categories.
Team management
Country club management
Middle-of-the-road management
Task management
Impoverish management
A two- dimensional view of leadership style develop by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton in the 1960.
Concern for production
Concern for people
Leadership functions
University of lowa Studies -Autocratic style: Centralized authority, low participation -Democratic style: Involvement, high participation, feedback -Laissez faire style: Hands-off management