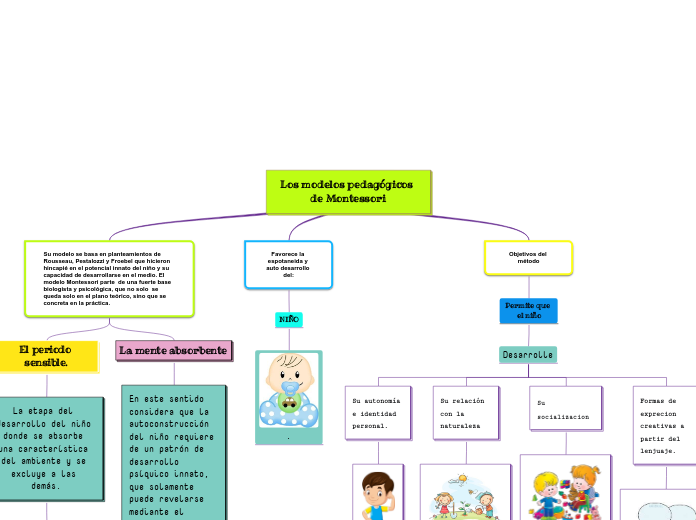
Los modelos pedagógicos de Montessori
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Objetivos del método
Permite que el niño
Desarrolle
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Objetivos del método.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Formas de exprecion creativas a partir del lenjuaje.
Su socializacion
Su relación con la naturaleza
Su autonomía e identidad personal.
Favorece la espotaneida y auto desarrollo del:
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
NIÑO
.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Favorece la espotaneida y auto desarrollo del:.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Su modelo se basa en planteamientos de Rousseau, Pestalozzi y Froebel que hicieron hincapié en el potencial innato del niño y su capacidad de desarrollarse en el medio. El modelo Montessori parte de una fuerte base biologista y psicológica, que no solo se queda solo en el plano teórico, sino que se concreta en la práctica.
La mente absorbente
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
En este sentido considera que la autoconstrucción del niño requiere de un patrón de desarrollo psíquico innato, que solamente puede revelarse mediante el proceso de desarrollo, y que requiere de una relación integral con el medio ambiente y la más completa libertad.
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
El periodo sensible.
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
La etapa del desarrollo del niño donde se absorbe una característica del ambiente y se excluye a las demás.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Su modelo se basa en planteamientos de Rousseau, Pestalozzi y Froebel que hicieron hincapié en el potencial innato del niño y su capacidad de desarrollarse en el medio. El modelo Montessori parte de una fuerte base biologista y psicológica, que no solo se queda solo en el plano teórico, sino que se concreta en la práctica..
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Estos períodos sensibles son:
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Orden:(primeros meses y segundo año de vida) plantea la necesidad de un régimen de vida y de la formación de hábitos, especialmente los de orden.
Uso de manos y lengua: son instrumentos de la inteligencia.
Marcha: permite el carácter activo en la búsqueda del conocimiento.
Interés por objetos diminutos: Manifiesta curiosidad intelectual.
Intenso interés social.