Psychedelics
psychotomimetic
disassociation
Sublingual
inhalation
How it is used
Recreational only because there is no legal medicinal use
Alters visual and auditory senses
Entheogen
Used for spiritual or religious experiences
ayahuasca
mushrooms
peyote
Entactogens
To produce feelings within ( heightened empathy)
ketamine
MDMA
Concerns
impaired memory
increased anxiety
decreased motivation
potential mental disturbances
Increased delusions
Bad trips
Dissociative
impaired speach
Disconnection from reality
nausea
increased blood pressure
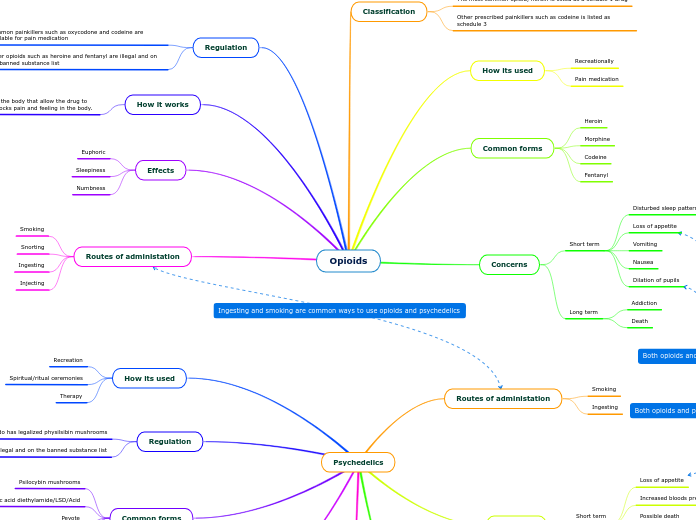
Regulations
Schedule I drug
since the 1970 controlled substances act
illegal to use
very limited medical research opportunities
Common Forms
Anticholinergics
Belladona, mandrakes, Datura, Henbane
Original deliriants
not popular because of adverse side effects
Dissociatives
Amphetamine Derivatives
MDMA and MDA
PCP
mescaline peyote
Hallucinogens
Ayahuasca
DMT
Psilocybin
LSD
3) brain contains less amounts then organs in the body
half of the LSD is metabolized every three hours
decreasing blook levels
2) Absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract rapidly
1) Taken by mouth
Tolerance to LSD is possible but not addiction
disorganized thinking
visual disturbances
hallucinogens
Intense feelings
alters sense
reality
time and space
dissociative
unable to feel pain
abnormal heart rate
possible seizure
Decreased breathing
Opioids
Effects
Mental fog
temporarily block pain
unconciousness
Nausea
Constipation
shallow breathing
Slowed heart rate
Drowsiness
severe abdominal pain
increased pain
hormonal problems
Weak bones
Irregular heartbeat
Routes of administration
Insuffilation
Nasal Spray
Executions
Fentanyl was used in the first execution in 2018
Anesthesia
Intestinal Disorder
Cough suppressant
Chronic pain
Natural forms
codeine
Semi-synthetics
Injected
no medical use in the united states
Can be ingested, insufflation, injected, or smoked
How it works
Attaches to inhibitory receptors in the VTA of the brain
dopamine is increased in the brain giving a person a rush or high
inhibitory receptors work harder to shut of dopamine making it hard for the body to send dopamine out at the same rate as before
Attaches to pain receptors
signals are not sent to the brain
Enters the blood stream
by some route
Tolerance
leading to dependency
Depression
Lack of motivation
Difficulty concentrating
Loss of consciousness or coma
overdose
Regulation
Schedule II drugs
high potential for abuse
Prescription Drug Monitoring Program
used to combat the opioid crisis by keeping track of prescription to customers state wide
Missouri is the only state that doesn't have one
1915 possession of opioids were illegal if not obtained from a doctor
Synthetics
fentanyl
pentazocine
propoxyphene
dihydrocodeine
hydromorphone
hydrocodone
oxymorphone
oxycodone
meperidine
methadone
Semisynthetics
heroin
Natural products
Codeine
morphine
Recreation and medicinal
works cited
https://www.drugrehab.com/addiction/drugs/inhalants/effects/
https://www.mydr.com.au/addictions/inhalants-tolerance-dependence-and-treatment
https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/methamphetamine
Depressants/Inhalants
depressants & inhalants
GHB
tranquilizers
barbiturates
hypnotics
Benzodiazepines
nitrous oxide
acetone
aerosol
markers
glues
Poppers
Breathed in
All inhalants are used this way even though these chemicals are not intended for that
Nitrites
Nitrous Oxide (inhalant)
laughing gas used for dental work or by pediatrics
Anesthetics
Aerosols, propellants, gases
Volatile Solvents
recreation
medicinal
Come in pill form can be crushed to snort, taken orally, or intravenously
hypnotics (depressants)
used for insomnia
tranquilizers (depressants)
anxiolytics
reduce anxiety
barbiturates & benzodiazepines (depressants)
Narcolepsy
rohypnol
anticonvulsants
used for seizures
Federal & State Law
In 2000 GHB was moved to a shedule I drug
Schedule II drug for high abuse potential
There is no regulation on inhalants because they are regular household items that are being abused to get high
Inhalants
Inhaled
Depressants
Intravenously
Oral Consumption
Insufflation
mood swings
tolerance
seizures
sleep disorder
inhalant
hearing loss
personality changes
memory problems
severe rash
numbness
kidney or liver damage
depressant
high blood pressure
weight gain
sexual issues
depression
inhalants
blurred vision
bloody noses
muscle weakness
trouble breathing
lack of coordination
lightheaded
depressants
fatigue
slow speech
fever
dilated pupils
trouble urinating
sluggishness
3) Distributed throughout the body
effecting the body in various ways
2) Act on the GABA receptors
this slows the brain activity
increases there inhibitory activity
1) Enters the bloodstream
Subtopic
Methamphetamine
stimulant
Intravenous
Oral delivery
hallucinations
severe dental problems
sleep problems
extreme weight loss
decreased appetite
increased heart rate
faster breathing
Increased wakefulness / physical activity
swallowing
In pill form
used for ADHD
snorting
crushed up crystals
smoking
usually in a glass pipe and inhaling the vapors
injecting
diluted in alcohol or water
3) Pumped through out the rest of the body
it stay chemically intake until it reaches the liver where it breaks down into amphetamine
2) Acts on dopamine receptors in the brain
increases levels of dopamine
intense pleasure from the increased levels
1) Distributed through the bloodstream
makes its way to the brain
increased blood pressure and body temperature
violent behavior
change in brain structure and function
effect emotion and memory parts
reduced dopamine levels
memory loss
addiction
intense itching
risky behvavior
increased risk of getting HIV if needles are shared
confusion
Prescribed by a doctor
for a found medical condtion
Federal laws
minimum of 5 years for possesion
Illegal in all states
Felony charge for possession
bitter powder or pill
crystallized rocks
man made in meth labs
Chemically similar to amphetamines
pills
narcolepsy
help treat ADHD
Works CIted
Nicotine: Facts, effects, and addiction. Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/240820#pharmacokinetics_of_nicotineFp-Admin. (2018, October 1).
What is Vaping? Retrieved from https://www.centeronaddiction.org/e-cigarettes/recreational-vaping/what-vaping
Raising the Tobacco Age to 21. (2020, January 9). Retrieved from https://www.tobaccofreekids.org/what-we-do/us/sale-age-21
The Facts about Caffeine in Dietary Supplements. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.crnusa.org/resources/facts-about-caffeine-dietary-supplements-0
Caffeine
3) Causes vascular dilation but in the brain the blood vessels are restricted
quickens the heart rate and oxygen consumption
2) Caffeine binds to the adenosine receptors
Prevents dopamine from being reabsorbed and hang out in the blood stream longer
Allowing your brain to not feel tired
1) Enters Blood Stream
Absorption is rapid after ingestion. Peak blood levels are reached after 30 minutes
Used daily by some for alertness or focus qualities Most common form is in drinks
Coffee, Tea, Soft drinks, Energy drinks
Medicinal
Weight loss Supplements
Zantrex-3
Excedrin
NoDoz
Pills
Weight loss supplements
Migraine medicine
Alertness tablets
Energy Drinks
Soft Drinks
Coffee
Tea
Dietary Supplements
Energy drinks can have higher amounts of caffeine because they are classified as supplements
Naturally Occurring Caffeine
No limits on how much caffeine can be in coffee
As a Food Addictive
The Code of Federal Regulations provides that caffeine in cola-type beverages may be added at levels not to exceed .02% by volume (about 70 mg caffeine per 12 oz. can) (crnusa.org)
Oral Ingestion
Sleep disturbances
Anxiety
Increase the risks of heath attacks
Can reduce the change of pregnancy in women in high amounts
Anxiousness
Dehydration
jittery feeling
Caffeinism
palpitations
gastrointestinal disturbances
twitching
insomnia
nervousness
irritability
Basal metabolic rate might be increased slightly
Irregular heartbeat in large amounts of caffeine consumption
Blood vessels in the brain are constricted
Blood vessel dilation
Cardiovascular system
Reverses the feelings of fatigue
Pleasant feeling
Tobacco
propylene glycol or vegetable glycerin-based liquid with nicotine, flavoring and other chemicals and metals (Centeronaddiction.org)
E Cigarette
Vaping
Tobacco Leaves
Dry
Wet
Cognitive Impairment
Overworking the heart
changing the heart rhythm
change in blood circulation
Chemical Dependency
Want to stop smoking but cant
Heartburn
diarrhea
Peptic ulcers
Dry mouth
Decreased hunger after smoking
Nausea or vomiting
Long Term
Blood clotting tendency
Possible blood restriction
Arteriosclerosis
Lung Disease or Cancer
COPD
Emphysema
Aorta Enlargment
Dependency
Addiction
Short Term
dizziness
disrupted sleep
Increased Oxygen consumption
Increased heart rate
Increased blood pressure
Oral
Recreation Use
Smokeless
Snuff
Chew
Smokeable
Hookah
E-Cigarettes
Cigarettes
Medical Use
Tobacco Replacement Therapy to help quiting
Gum
Classification
Alertness
State Level
19 States passed a Tobacco 21 law
Arkansas, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia and Washington (Tobaccofreekids.org)
Oregon State Law January 1, 2018
Changed the legal age of purchase and consumption from 18 to 21
Federal Level
December 2019
Congress passed a federal law to raise the national age of purchase and consumption to 21
2009 Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act
Authorizing the FDA to regulate tobacco products and implemented rules
1964 First Surgeon General Report
detailed that smoking tobacco increased the risks of lung disease
Before 1890's physicians believed it had medical benefits curing headaches but this was debunked
3) Redistributes to the rest of the body
primarily deactived by the liver
2) It mimics acetylcholine by acting at several cholinergic receptors
First stimulates and then blocks the receptor
1) Enters the Blood Stream
Nicotine the main active chemical in tobacco products Makes its way into the central nervous system.
Works Cited
Alcohol use and safe drinking: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency /article/001944.htm
Gerbis, N. (2020, January 27). How Marijuana Works. Retrieved from https://science.howstuffworks.com/marijuana3.htm
Hanson, K., & Garcia, A. (n.d.). state medical marijuana laws. Retrieved from https://www.ncsl.org/research/health/state-medical-marijuana-laws.aspx
Hinchey-Rohrabacher amendment Archives. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://thecannabisindustry.org/tag/hinchey-rohrabacher-amendment/
Murray, J. B. (1986, January). Marijuana's effects on human cognitive functions, psychomotor functions, and personality. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3009708
Neuroscience. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://faculty.edu/ chudler/alco.html
What U.S. states have legalized medical marijuana? (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/qa/what-us-states-have-legalized-medical-marijuana
Alcohol
long term
Sleep interruption
Body doesn't enter rem sleep
Organ disease or damage
Brain damage
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
reduction of brain tissue
Liver damage
Cirrhosis
short term
slurred speech
impaired judgement
Impaired coordination
slows heart rate
used to enhance mood or relax
slows down brain and neural functioning
Oral ingestion
absorption through the small intestine after drinking
Effects on cognitive growth
brain damage
Increase risky behavior
driving under the influence
sex without protection
trying drugs
Potential abuse / addiction
Binge drinking
alcohol poisoning
Blacking out
Absorption- mostly in the small intestine to go directly to blood stream
Heart pumps it throughout body
The Liver is the primary organ that breaks down alcohol in the body
Enters the central nervous system
Cerebral Cortex
blurred vision, slurred speech, lower inhibition
Cerebellum
loss of fine motor cordination
Reticular formation
relaxation
Vary individually
Weight
Metabolism
Culture
Gender
Carbonated liquids
Speeds up absorption rate
Food or water
Slows down absorption rate
Must be 21 years old to consume and purchase
In all states
National Minimum Drinking Age Act of 1984
How it’s used (recreation, medicinal)
USES
Libation
spirits, beer, wine
Sterilization
isopropyl
Fuel
ethanol
Solvents- perfumes,toiletries, etc
Common forms
Liqueurs
20-25% Schnapps, Bailey's Irish cream
DIstilled Spirits 40-50%
tequila
whiskey, bourbon
Rum, brandy
Vodka, gin
Wine
20% - port, Madeira, muscatel
12% - red, white, sherry
Beer 2-9%
malt
lagers
stouts
ales
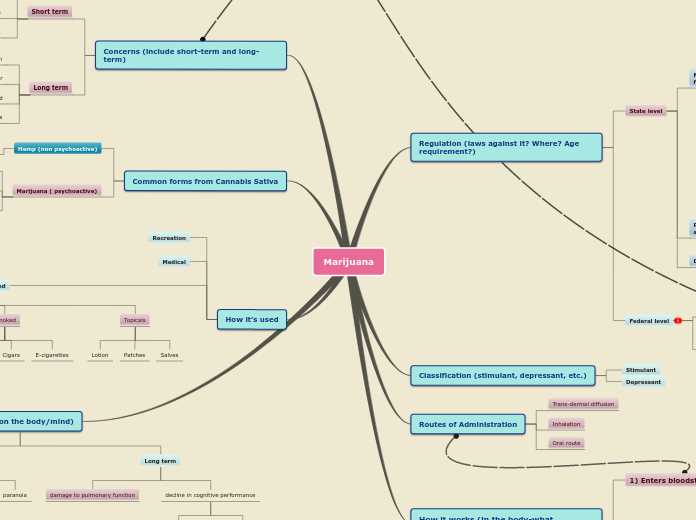
Marijuana
Effects (on the body/mind)
decline in cognitive performance
impaired learning
impaired thinking
damage to pulmonary function
paranoia
anxiety
redden eyes
dry mouth
appetite
increase heart rate
How it’s used
Ways it is used
Topicals
Salves
Patches
Lotion
Smoked
E-cigarettes
Cigars
Joints
Pipes
Eaten
Drinks
Teas
Sodas
Food
Desserts
Candy
Medical
Recreation
Common forms from Cannabis Sativa
Marijuana ( psychoactive)
Hash oil
Resin extracted from the flower
Hashish
Powdery resin on flower
high in THC concentration and potency
Sinsemilla
Mature flower of a female plant
high in THC concentration and 15-20% potency
Hemp (non psychoactive)
CBD
Concerns (include short-term and long-term)
Long term
immune system effects
chronic lung exposure if smoked
Increase in risky behavior
Abuse/ Addiction
Short term
Learning and cognitive impairment
coordination
short term memory
How it works (in the body-what organs/systems effected)
3) Redistrubution to the rest of the body
2) Cannabinoid receptors in the Brain
THC acts on the parts of the brain that have high concentration of cannabinoid receptors that activate neurons
cerebellum
can effect coordination
Hippocampus
short-term memory or recent events
Basal ganglia
unconscious muscle movements
1) Enters bloodstream
THC the main ingredient that produces the high-- enters the bloodstream with in seconds of being inhaled ( the most common form of use) and makes its way to the brain
Routes of Administration
Oral route
Inhalation
Trans-dermal diffusion
Classification (stimulant, depressant, etc.)
Depressant
Stimulant
Regulation (laws against it? Where? Age requirement?)
Federal level
the Rohrabacher–Farr amendment prohibits federal prosecution of individuals complying with state medical cannabis laws
Schedule 1 drug illegal for any use ---it is seen as highly addictive and there are no approved medical or recreational uses on the federal level
State level
Decriminalized in 15 states
Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Maryland, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Rhode Island, U.S. Virgin Islands
Recreational legal for adults 21 years and older in 11 states
Alaska, California, Colorado, Illinois, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Nevada, Oregon, Vermont, and Washington
Medically legal by doctor's recommendation in 33 states for adults 18 and some 21 years old
High CBD and low THC
Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, Wisconsin and Wyoming (WebMD)
All the plant
Alaska
Arizona
Arkansas
California
Colorado
Connecticut
Delaware
District of Columbia
Florida
Hawaii
Illinois
Louisiana
Maine
Maryland
Massachusetts
Michigan
Minnesota
Missouri
Montana
Nevada
New Hampshire
New Jersey
New Mexico
New York
North Dakota
Ohio
Oklahoma
Oregon
Pennsylvania
Rhode Island
Utah
Vermont
Washington
West Virginia (WebMD)