作者:ortega carolina 5 年以前
573
NAP SERES VIVOS
作者:ortega carolina 5 年以前
573

更多类似内容
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
Nuclear energy originates from the splitting of uranium atoms – a process called fission.
This generates heat to produce steam, which is used by a turbine generator to generate electricity. Because nuclear power plants do not burn fuel, they do not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of Nuclear Energy.
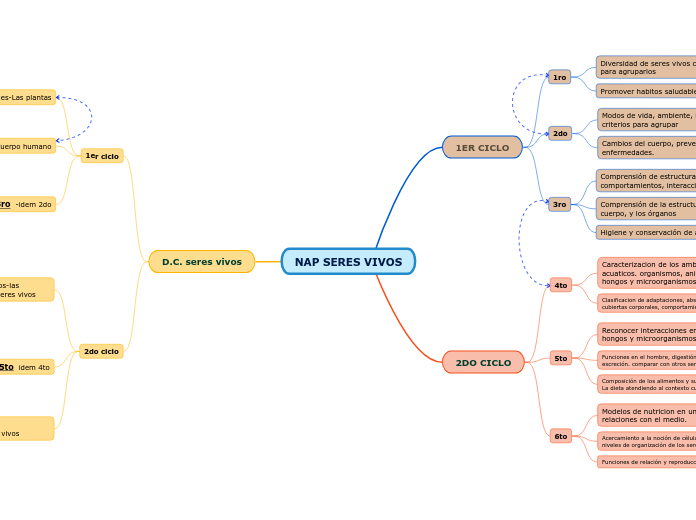
Adaptaciones morfofisiologicas al vuelo.
Sistemas de organos, sitema reproductor femenino y masculino. el ciclo menstrual. prevención de ITS. Hormonas en el desarrollo.
Los medios acuáticos y humedales del territorio provincial y nacional, adaptaciones de los seres vivos.
La transformacion de los alimentos, alimentación humana y diversidad de dietas segun el contextos sociocultural
Microorganismos beneficiosos y perjudiciales para la sociedad.
Medios aeroterrestres del territorio provincial y nacional. adaptaciones morfofisiológicas de los seres vivos a medios fríos y al desierto, y sus impacto.
Reproducción sexual y asexual, estructuras de sosten en plantasy animales.
Caracteristicas y clasificacion de los seres vivos (animales, plantas, hongos pluricelulares y microorganismos.
Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen.
It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
Name the advantages and disadvantages of Hydrogen fuel.
cuidado de la salud, enfermedades contagiosas. prevención de enfermedades contagiosas. el sitema osteoartromuscular,(órganos)
Respuestas a cambios ambientales, en las plantas a lo largo del año
Relaciones entre las dietas y las estructuras.
Cambios en las personas
Relaciones entre estructuras y el ambiente
Partes y tipos de plantas.
Partes del cuerpo humano
Diversidad en los animales vertebrados e invertebrados.
There are many different types of energy, which all fall into two primary forms – kinetic and potential.
Energy can transform from one type to another, but it can never be destroyed or created.
Nuclear energy is stored in the nucleus of atoms.
This energy is released when the nuclei are combined (fusion) or split apart (fission).
Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms to produce electricity.
What element do they use to fuel nuclear power plants?
Thermal energy is created from the vibration of atoms and molecules within substances. The faster they move, the more energy they possess and the hotter they become. Thermal energy is also called heat energy.
Give examples of heat energy.
Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects; as objects move faster, more energy is stored.
Examples of motion energy include wind, a flowing river, etc.
Give more examples.
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Thermal energy storage is achieved with widely differing technologies.
Depending on the specific technology, it allows excess thermal energy to be stored and used hours, days, months later, at scales ranging from the individual process, to building or town.
What are 3 types of thermal energy?
The battery acquires its charged condition either by recharging or in the manufacturing of the unit.
During discharge, the chemical on the anode releases electrons, and ions in the electrolyte undergo an oxidation reaction.
Name the particular compounds in which energy is stored:
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy.
Write down the main components of a typical flywheel.