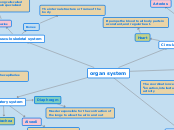
organ system
Musculoskeletal system
Bones
The internal structure or frame of the body
Muscles
Consists of bundles of long cells called muscle fibres that contain specialized proteins
Ligaments
They are tough, elastic connective tissues that holds bones together at the joints
Circulatory system
Blood vessels
Capilleries
Tiny blood vessels with very thin walls that enables the exchange of gasses, and nutrients
Arteries
It carries blood to your heart
Veins
It carries blood towards your heart
It transports blood to all body parts
Blood
Carries oxygen, and nutrients to all boy parts through blood vessels
Heart
It pumps the blood to all body parts in a constant, and regular beat.
Nervous system
Ganglia
A structure containing a number of nerve cell bodies
Nerves
Fibers of sensory and motor neutrons
Spinal cord
A bundle of nerve fibres and associated tissue that is in close in the spine
Brain
The coordination centre of the sensation, intellectual and nervous activity
Digestive system
Stomach
Its main function is to hold food and the process of digestion, nerves in the stomach signal when we have had enough food
Intestine
It has cells that produces mucus, it contains smooth muscle that contracts and relaxes
Esophagus
It is a muscular tube that contracts and relaxes to allow the food to slide onto the stomach
Mouth
Processes food and breaks it down in two ways chemically: by secreting enzymes ( saliva), and mechanically: using teeth and tongue.
Respiratory system
Diaphragm
Muscle responsible for the contraction of the lungs to allow the air in and out
Alveoli
Allows exchanging of gaseous
Nose/Mouth
Air is inhaled through it
Trachea
Air passes through the two parts of the lungs
Bronchi
The trachea branches off into the bronchi, which delivers the air to the lungs
Lungs
Provides oxygen for the capillaries and exhales CO2