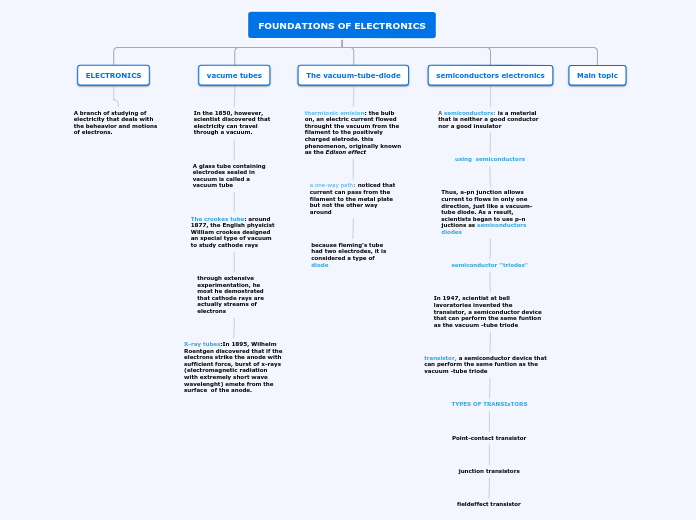
FOUNDATIONS OF ELECTRONICS
Main topic
semiconductors electronics
A semiconductors: is a meterial that is neither a good conductor nor a good insulator
using semiconductors
Thus, a-pn junction allows current to flows in only one direction, just like a vacuum-tube diode. As a result, scientists began to use p-n juctions as semiconductors diodes
semiconductor ''triodes''
In 1947, scientist at bell lavoratories invented the transistor, a semiconductor device that can perform the same funtion as the vacuum -tube triode
transistor, a semiconductor device that can perform the same funtion as the vacuum -tube triode
TYPES OF TRANSIsTORS
Point-contact transistor
junction transistors
fieldeffect transistor
The vacuum-tube-diode
thermionic emision: the bulb on, an electric current flowed throught the vacuum from the filament to the positively charged eletrode. this phenomenon, originally known as the Edison effect
a one-way path: noticed that current can pass from the filament to the metal plate but not the other way around
because fleming's tube had two electrodes, it is considered a type of diode
vacume tubes
In the 1850, however, scientist discovered that electricity can travel through a vacuum.
A glass tube containing electrodes sealed in vacuum is called a vacuum tube
The crookes tube: around 1877, the English physicist William crookes designed an special type of vacuum to study cathode rays
through extensive experimentation, he most he demostrated that cathode rays are actually streams of electrons
X-ray tubes:In 1895, Wilhelm Roentgen discovered that if the electrons strike the anode with sufficient force, burst of x-rays (electromagnetic radiation with extremely short wave wavelenght) emete from the surface of the anode.
ELECTRONICS
A branch of studying of electricity that deals with the beheavior and motions of electrons.