作者:Ashton Lassiter 3 年以前
104
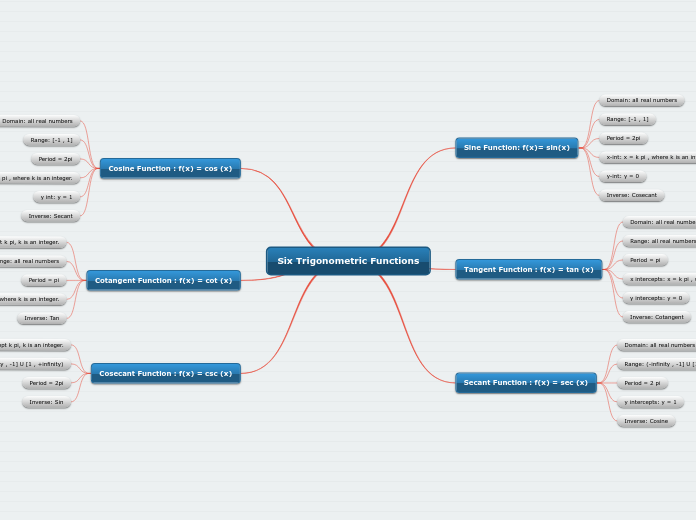
Six Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, including sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant, each have unique characteristics that define their behavior. The sine and cosine functions have a domain of all real numbers and a range between -1 and 1.