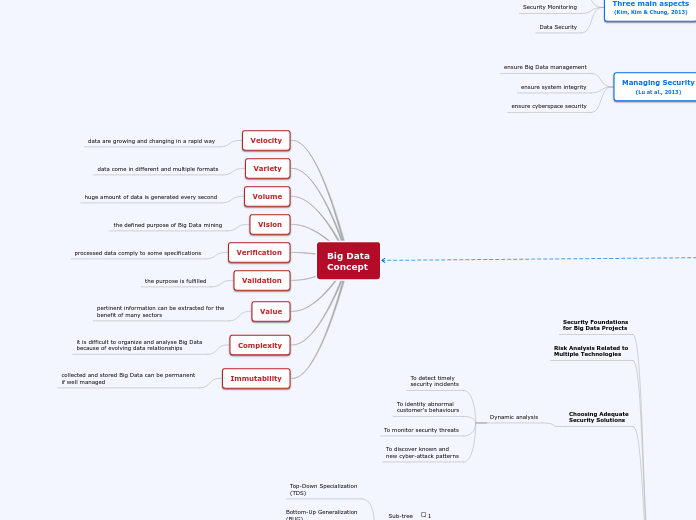
Big Data
Concept
Velocity
data are growing and changing in a rapid way
Variety
data come in different and multiple formats
Volume
huge amount of data is generated every second
Vision
the defined purpose of Big Data mining
Verification
processed data comply to some specifications
Validation
the purpose is fulfilled
Value
pertinent information can be extracted for the
benefit of many sectors
Complexity
it is difficult to organize and analyse Big Data
because of evolving data relationships
Immutability
collected and stored Big Data can be permanent
if well managed
Big Data
Security
Security Challenges
Big Data Nature
Adding security layers may slow system performances
and affect dynamic analysis
It is difficult to handle data classification and management
of large digital disparate sources
Sharing data over many networks increase security risks
The Need to Share
Information
Multiple connections with different levels
of securities
Data sharing associated with advanced
analytics techniques
Discovering confidential information
Illegal access to network's traffics
Correlation attacks, arbitrary identification,
intended identification attacks, etc
Multiple Security
Requirements
To handle information security while managing
massive and rapid data streams
Security tools should be flexible and easily scalable
There is a need to find a balance between multiple
security requirements, privacy obligations, system
performance and rapid dynamic analysis
Inadequate Traditional
Solutions
e.g.: types of data encryption
slow the performance
are time-consuming
are not efficient
New Security Tools
Lack of Maturity
Data Anonymization
Should be achieved without affecting system
performance or data quality
Traditional anonymization techniques are based
on several iterations and time consuming computations
may affect data consistency
may slow down system performance
It is difficult to process and analyse anonymized
Big Data
Compatibility with Big
Data Technologies
some security techniques are incompatible
with commonly used Big Data technologies
(e.g.: MapReduce)
It is mandatory to verify their compatibility
with organization Big Data requirements and
existing infrastructure components.
(Zhao et al., 2014)
Information Reliability
and Quality
It is important to verify Big Data sources
authenticity and integrity before analysing
data
It is difficult to assess the authenticity and
integrity of all various data sources
Data have to be filtered, organized and
contextualized before performing any analysis
Compliance to Security
Laws Regulations and Policies
Deal with multiple laws and regulations
(Tankard, 2012)
Big Data analytics may be in conflict
with some privacy principles.
Need of Big Data Experts
need for advanced security analysis experts
(Constantine, 2014)
Big Data Security on Social Networks
Can prevent terrorist and security
attacks and assess citizens' satisfaction
regarding public services
Detect rapidly abnormal patterns and
ensure a real-time monitoring of
alarming events
aims to ensure
a real-time monitoring to detect vulnerabilities,
security threats and abnormal behaviours
a granular role-based access control
a robust protection of confidential information
a generation of security performance indicators
Three main aspects
(Kim, Kim & Chung, 2013)
Information Security
Security Monitoring
Data Security
Managing Security
(Lu at al., 2013)
ensure Big Data management
ensure system integrity
ensure cyberspace security
Security Solutions
Security Foundations
for Big Data Projects
Risk Analysis Related to
Multiple Technologies
Choosing Adequate
Security Solutions
Dynamic analysis
To detect timely
security incidents
To identity abnormal
customer's behaviours
To monitor security threats
To discover known and
new cyber-attack patterns
Anonymization of Confidential
or Personal Data
Models for data
anonymization
Sub-tree
Top-Down Specialization
(TDS)
Bottom-Up Generalization
(BUG)
Hybrid approach
(TDS + BUG)
t-closeness
m-invariance
k-anonymity
l-diversity
Data Cryptography
Homomorphic Cryptography
Cloud Background Hierarchical
Key Exchange (CBHKE)
Centralized Security
Management
Data Confidentiality and
Data Access Monitoring
Security Surveillance
and Monitoring
Data Loss Prevention
(DLP)
Security Information and Event
Management (SIEM)
dynamic analysis of security
events