Diversity of Living Things
Fungi
Multicellular, heterotrph
Chytridiomycota
Large pores, produce flagellated spores

Algea
Zygomycota
Black spots(sporangia), release spores

Black Bread Mold
Ascomycota
Saclike structures (ascus), prodce two kind of spores(conidia)

Mildews,yeast

Basidiomycota
clublike-mass of hyphae to absorb water,Cap-produce spores
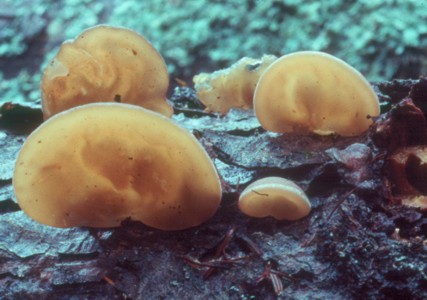
Jelly fungi
Eukaryotes
Multicellular
bigger and more complicated
Plants
multicellular,cell wall, autotroph and sessile
Bryophytes
Tangled, matted growth, no vessels,roots, leaves, stems.

Mosses, Liverworts
Seedless Vascular
Has roots, stems, leaves, produce spores for reproduction

Ferns, Whisktails
Gymnosperms
Reproduce sexually with out water, provides protection, dispersed though various pollination

Pine trees
Angiosperms
Reproduce through flowers and fruit

Tulips, Dandelions, Oaks
Protista
cell wall, uni or multicellular
Feeding strategies
Heterotrophs
Feed on other organisms
Animal like
Sporozoans
no movement
Glardia
Sarcodines
Pseudopods
Amoeba
Flagellates
Flagella-tail like
sperms
Ciliates
Cilia help swim and capture food
Paramecia
Photosynthesis
Sunlight
Plant like
Brown Algae

Kelp
Green Algea

Marino
Diatoms
Pennate
Dinoflagellates
Dinophyceae
Decompose
Decayed matter
Fungus like
Slime moulds
Protostelids
Water moulds
Peronosporales
Animals
Porifera

sea sponge
Cnidaria

jelly fish
developed stinging tentacles
they develop nerves and sting/paralyze prey rather than using
Platyhelminthes

tape worm
simplest organism in which organs occur
-MILESTONE: can also reproduce asexually
Nematoda

pin worms
roundworms and 2 openings in digestive system compared to 1 in Platy.
Chordata
Mammals
placentals
born from mothers uterus attached to placenta
Magnorder Xenarthra

sloths
marsupials
live birth
Diprotodontia

kangaroo
monotremes
lay eggs
monotremata

platypus
Subphyla =
Monkey
Cephalochordata
Urochordata
Vertebrata
Superclass =
Tetrapods
Amphibia

frog
-Gas exchange across moist
skin
-External fertilization in water
-Adults live on land, but require moist environment
Mammilia

lion
Mammary glands – produce milk for young -Body hair ( = insulation, camoflague, waterproofing, defense)
-Endothermic, four-chambered hearts, highly developed brains
-Specialized teeth
Arthopoda

Spider
Chelicerata
Myriapoda
chilopoda

centipede
diplopoda

millipede
pauropoda
symphyla
Crustacea
branchipoda
Hexapoda
insects or incecta
Have joint limbs unlike Echino. and other phylums + internal airways
Echinoderms

star fish
Radial symmetry and nerves extend everywhere (they don't have a real head and body is made up of tightly interweaved muscles)
Mollusca

snail
Foot for movement, bigger organs and mantle for protection (Shell)
pollinators help spread seeds
Prokaryotes
Unicellular
small, simple, commonly know as bacteria
Eubacteria
rigid cell walls wot peptidyglocan and flagella for movement
Rod shaped
E. Coli
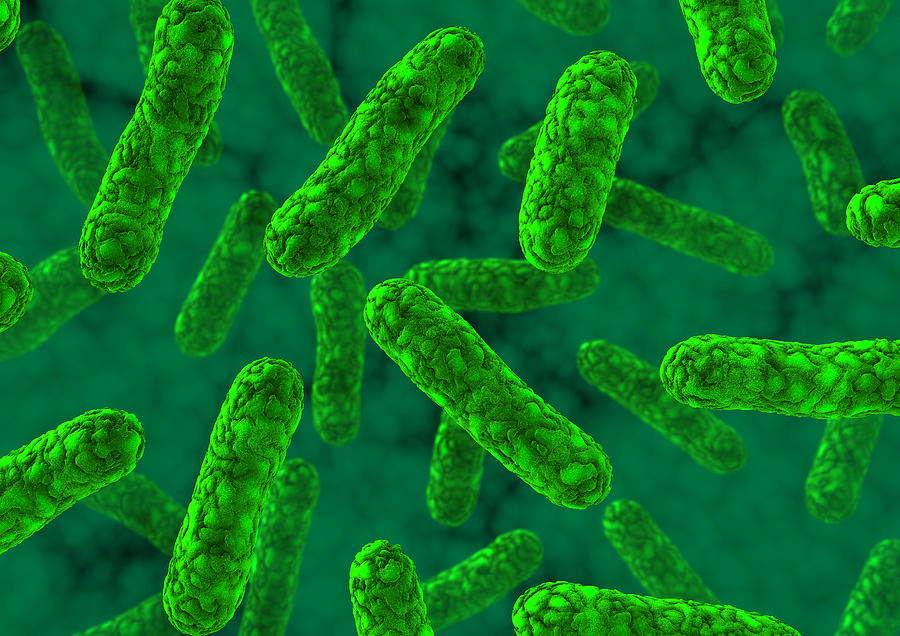
found in lower intestine of warm blooded
organisms
Spherical
Streptococcus
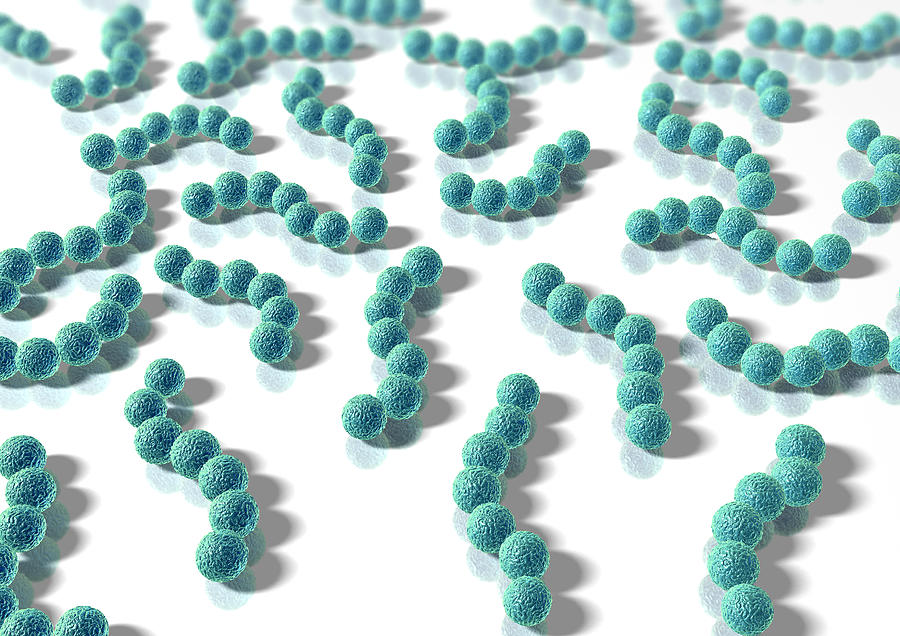
remains in chains after dividing
Spiral
Spirillum

has a twisted shape
Archaebacteria
similar to bacteria, cell wall without peptodyglocan
Methanogens
no oxygen environments
Halophiles
thrive in high salt concentrations
Thermoacidophiles
extreme salt environments
Psychrophiles
cold environments