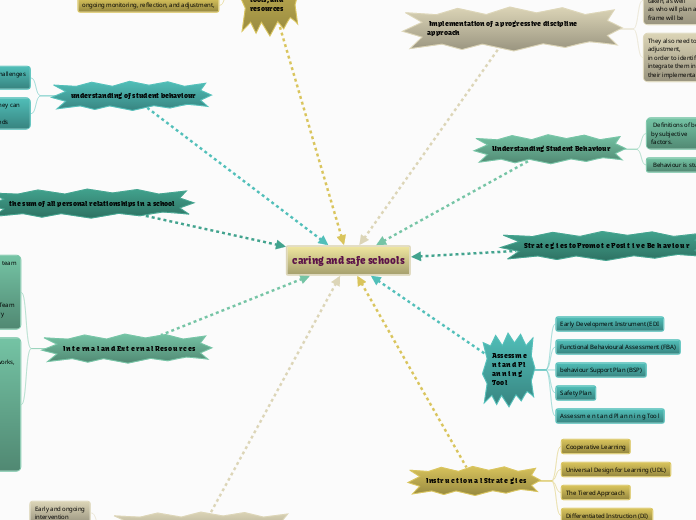
caring and safe schools
Implementation of a progressive discipline approach
System and school
leaders need to identify a range of appropriate actions to be taken, as well
as who will plan and carry out the actions, and what the time frame will be
They also need to plan for ongoing monitoring, reflection, and adjustment,
in order to identify further needed improvements and integrate them into
their implementation processes.
Understanding Student Behaviour
Definitions of behaviour are variable and may be influenced by subjective
factors.
Behaviour is student and situation dependent.
Str at e g i es to Promo t e Posi t i v e Be h av io u r
Direct Teaching of Social Skills
Restorative Practices
A Problem-Solving Approac
Assessm e n t an d Pl an n i n g Too l
Early Development Instrument (EDI
Functional Behavioural Assessment (FBA)
behaviour Support Plan (BSP)
Safety Plan
Assessm e n t an d Pl an n i n g Too l
Instr u c t io n a l Str at e g i es
Cooperative Learning
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
The Tiered Approach
Differentiated Instruction (DI)
nowledge of strategies, tools, and resources
who will plan and carry out the actions, and what the time frame will b
ongoing monitoring, reflection, and adjustment,
understanding of student behaviour
f the types of intellectual and emotional challenges
students may face
identify appropriate strategies, tools, and resources they can use
to address specific challenges and meet identified needs
the sum of all personal relationships in a school
members of the school community demonstrate respect for others
all members feel safe, comfortable, and accepted
In t e rn a l an d Ex t e rn a l Reso u rc es
In-school/multidisciplinary team
• Safe school team
• Student success team
• Special education team
• Support services
• System Multidisciplinary Team
• Special education advisory
committee (SEAC)
• Parents
• Service providers
• Community partners (e.g., school-community networks,
local businesses, police services, hospital services)
• Information from research
• Professional associations
• Provincial government agencies
(e.g., child and youth mental health centres,
children’s aid societies)
• Municipal government services
(e.g., public health units, mental health agencies)
• Experts (e.g., researchers, specialists)
• Postsecondary institutions
• Early childhood facilities
• Parenting centre
Strategies and tools for specific purposes
Early and ongoing
intervention
Prevention