Chapter 1 Introduction to Business
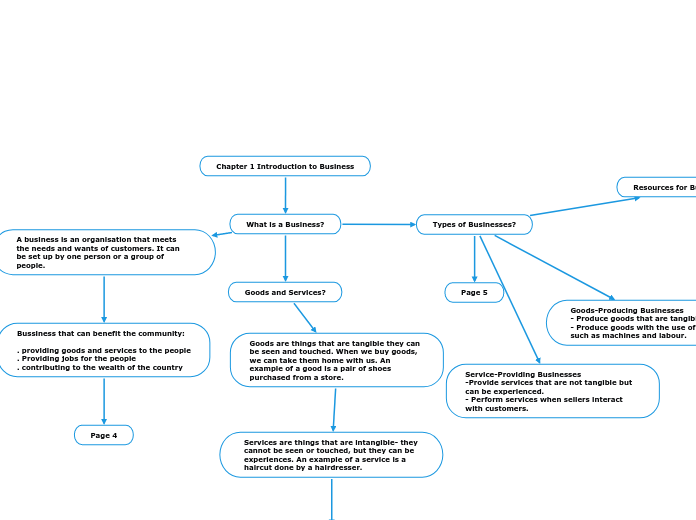
What is a Business?
A business is an organisation that meets the needs and wants of customers. It can be set up by one person or a group of people.
Bussiness that can benefit the community:
. providing goods and services to the people
. Providing jobs for the people
. contributing to the wealth of the country
Page 4
Goods and Services?
Goods are things that are tangible they can be seen and touched. When we buy goods, we can take them home with us. An example of a good is a pair of shoes purchased from a store.
Services are things that are intangible- they cannot be seen or touched, but they can be experiences. An example of a service is a haircut done by a hairdresser.
Page 4
Types of Businesses?
Goods-Producing Businesses
- Produce goods that are tangible
- Produce goods with the use of resources such as machines and labour.
Service-Providing Businesses
-Provide services that are not tangible but can be experienced.
- Perform services when sellers interact with customers.
Page 5
Resources for Businesses Activities
Page 6
ENTERPRISE : THE ABILITY TO TAKE RISKS IN PRODUCING GOODS AND SERVICES. ENTREPRENEURS ARE THE PEOPLE WHO STARTED THE BUSINESS..
CAPITAL : THE BUILDINGS, EQUIPMENT, MACHINERY AND MONEY WHICH ARE USED TO PRODUCE GOODS AND SERVICES. It also includes the money needed to start the business.
LANDS : THE NATURAL RESOURCES SUCH AS SEA, FORESTS, MINERALS AND LAND. Land is needed to grow crops and build factories and facilities to produce goods and services for customers.
LABOUR : THE EFFORTS OF THE WORKERS INVOLVED IN THE PRODUCTION OF GOODS AND SERVICES. For examples, waiters, chef and restaurant managers from the labour force of a restaurant. Office staff, engineers and construction workers form the labour force of a construction business.
Changing Business Environment
DIRECT COMPETITION: COMPETITORS SELLING SAME OR SIMILAR GOODS AND SERVICES. For example, taxi companies and private hire car companies are direct competitors as both provide private transportation on demand.
INDIRECT COMPETITION: COMPETITORS SELLING GOODS AND SERVICES THAT SATISFY THE SAME NEEDS AND WANTS OF CUSTOMERS. These goods and services may fall under different categories. For example, cinemas face indirect competition from providers of escape room games as both satisfy customers wants for entertainment.
Page 8
BUSINESSES ARE CHALLENGED BY TRENDS
EXAMPLE: GRAB CAR
CHANGING CUSTOMER EXPECTATIONS
TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT
BUSINESSES SHOULD BE AWARE OF TRENDS THAT MAY AFFECT THEIR BUSINESSES.
THEY SHOULD CONTINUALLY IMPORVE WAYS BUSINESS ACTIVITIES ARE CARRIED OUT TO CREATE NEW CUSTOMER EXPERIENCES TO ATTRACT CUSTOMERS.
Changing Customer Expectations
Customer expectations refer to what customers want from the businesses they are buying from. This includes quality goods and services and the overall experience they have with the business.
Technological development refers to advancements or innovations in technology that help to improve our quality of life and environment. It includes the use of digital technology on the Internet and any improvements to business activities, such as the use of automation to serve customer faster.
Page 10 to 11