DIFFERENT MODELS AND MATERIAL
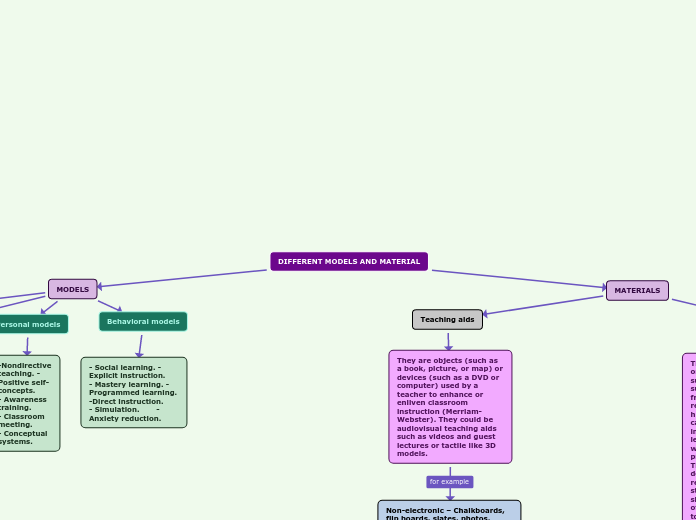
MODELS
Information- Processing models
-Inductive thinking. -Scientific inquiry. -Picture word inductive. - Concept attainment. - Synectics. - Mnemonics. - Advanced organizers. - Inquiry training. -Cognitive growth.
Social models
-Partners in learning. -Structured social inquiry. -Group investigation -Social inquiry. -Laboratory method. -Role playing. -Jurisprudential inquiry.
Personal models
-Nondirective teaching. -Positive self-concepts. - Awareness training. - Classroom meeting. - Conceptual systems.
Behavioral models
- Social learning. -Explicit instruction. - Mastery learning. -Programmed learning. -Direct instruction. - Simulation. -Anxiety reduction.
MATERIALS
Teaching aids
They are objects (such as a book, picture, or map) or devices (such as a DVD or computer) used by a teacher to enhance or enliven classroom instruction (Merriam-Webster). They could be audiovisual teaching aids such as videos and guest lectures or tactile like 3D models.
Non-electronic – Chalkboards, flip boards, slates, photos, telescopes,
Electronic – Powerpoint slideshows, videos, Augmented reality/Virtual reality goggles, AV-room equipment
Classification 2:
Auditory: radios, tape recorders, CD players
Visual: Slides, projectors, digital screens
Audiovisual– Youtube content, Vines (yes, they are helpful), Ted Talks, Live streams, documentaries
Audiovisual and tactile – 3D models, plants, rocks, field visits...
Instructional materials
They are defined as resources that organize and support instruction, such as textbooks, tasks, and supplementary resources (adapted from Remillard & Heck, 2014). It refers to the human and non-human materials and facilities that can be used to ease, encourage, improve and promote teaching and learning activities. They are whatever materials used in the process of instruction (IGI global). The great Soviet encyclopedia defines IMs as educational resources used to improve students’ knowledge, abilities, and skills, to monitor their assimilation of information, and to contribute to their overall development and upbringing.
Traditional resources: lectures, talks, writings, project rubrics, guidelines, textbook primers, reference books, extra-readings, teacher and student-created summaries, workbooks, supplementary material such as flashcards and charts
Digital media: Videos, photos, presentations
Open resources: Expert blogs, open-source journals, public databases, open courseware, forums
Testing resources: Standardized tests, classroom assignments, online submissions, quizzes, essays, collaborative projects.