Elements and Principles
Music (Familiar)
Elements
Melody – The main tune of a song. Example: The opening theme of Harry Potter.
Rhythm – The pattern of beats and timing. Example: A steady drumbeat in pop music.
Harmony – Multiple notes played together. Example: Chords in a choir or band.
Dynamics – Volume changes in music. Example: A soft intro building into a loud chorus.
Tempo – The speed of a piece. Example: A fast tempo in electronic dance music.
Timbre – The unique sound of an instrument/voice. Example: A violin sounds different from a piano, even on the same note.
Principles
Balance – How different instruments work together. Example: Orchestra sections blending their sounds. Smells Like Teen Spirit by Nirvana does this by balancing between heavy guitar, bass, and drums while keeping the vocals clear
Contrast – Using soft vs. loud, fast vs. slow. Example: A quiet verse leading to a powerful chorus. A song that does this is Bohemian Rhapsody, by Queen
Repetition – Patterns and repeated themes. Example: The chorus repeating in pop songs. A song that does this is Rolling in the Deep, by Adele, or We Will Rock You, by Queen.
Unity & Variety – Keeping a song cohesive while adding new elements. Example: A jazz piece maintaining a theme but improvising sections. A song that does this is Hotel California, by the Eagles.
Architecture (New)
Elements
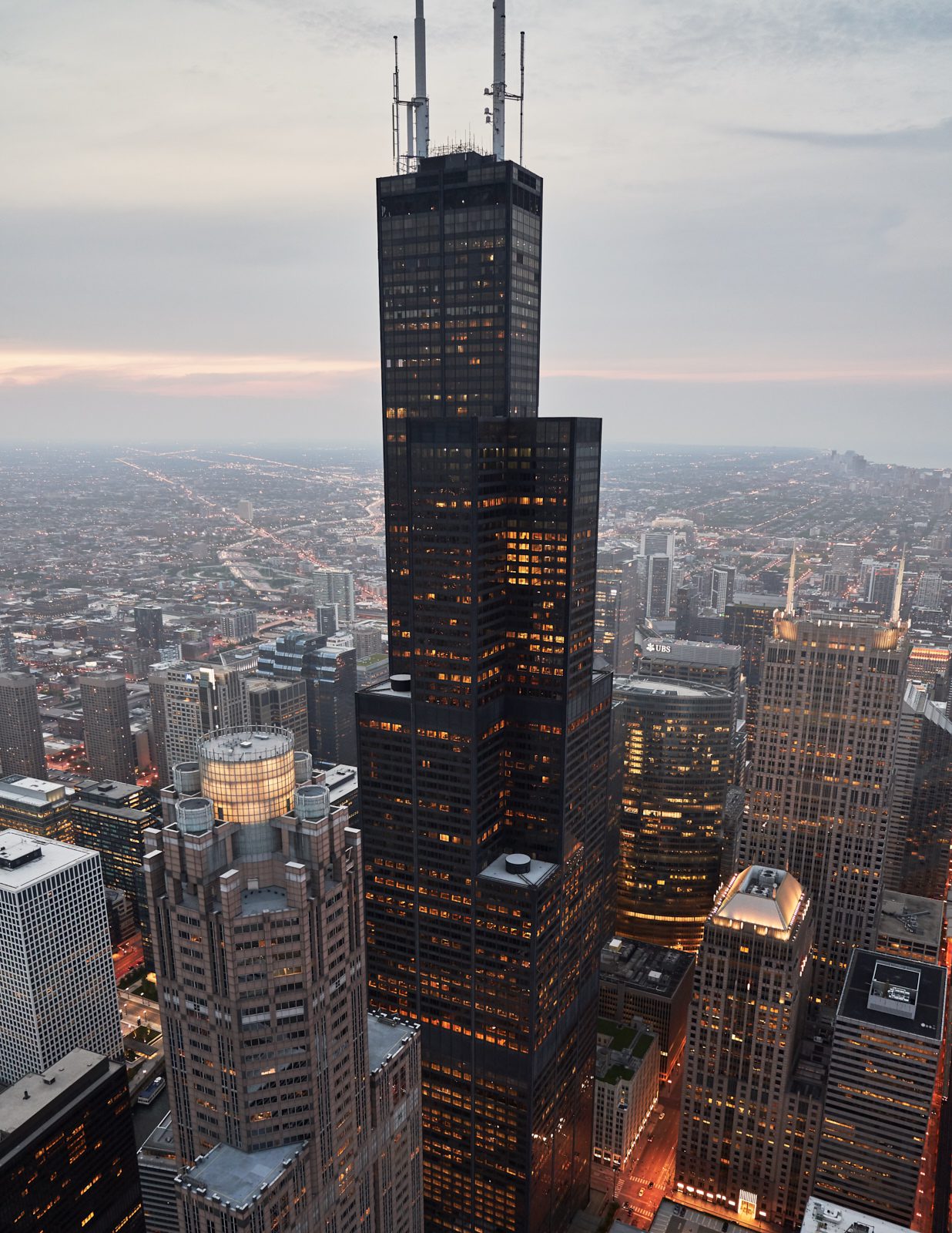
Line – The shape of a building’s edges. Example: Vertical lines in skyscrapers. building that shows this is Willis tower in Chicago
Form – The 3D shape of a structure. Example: A dome on a cathedral. A building that shows this is the Pantheon in Rome

Space – How open or enclosed a building feels. Example: High ceilings in a church create openness. building that shows this is the Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris

Texture – The feel/look of materials. Example: Smooth glass vs. rough brick. An example of this is the Guggenheim Museum in New York, the museum’s exterior is made of smooth concrete which contrasts with the texture of the rough brick buildings in its surroundings.

Color – The emotional impact of colors. Example: White buildings feel modern; red brick feels traditional. A building that shows this is the Sydney Opera House

Light & Shadow – How natural/artificial light interacts with a space. Example: Stained glass windows casting colored light. A building that shows this is the Sagrada Família in Barcelona

Principles
Balance – Symmetry or asymmetry in a building’s design. Example: A perfectly symmetrical palace such as the Palace of Versailles in France

Proportion & Scale – How parts relate in size. Example: Huge columns on ancient Greek temples like the Parthenon in Athens, Greece.

Rhythm – Repeating elements like windows or columns. Example: A row of evenly spaced arches such as the Great Mosque of Córdoba

Unity & Variety – Keeping a consistent style while adding uniqueness. Example: A modern glass tower in a historic city such as the Louvre Pyramid