Gamification Map
Broad Gamification Introduction
Introduction
What makes games popular?
What is this course about?
What is gamification?
How Might Gamification be Valuable?
How to Use it and be Effective?
NOT a Panacea
Must do it WELL
components
pros/cons of different types of gamification
techniques
Specific Applications
for profit vs. nonprofit
specific examples
Why Gamify?
Dedgeball game
checked in to bars, friends checked in too
chicken and egg problem, if no one has app... etc...
founder left company to found FourSquare
problems with dodgeball
dodeball had "engagement gap"
did have much meaninful choices
no progression, no multiple check ins etc.
didn't make checking in a "habit"
solutions
multiple check in's make you "mayor"
badges add progression
automatic checking in
How to Gamify?
thnk like a game designer
think about how to solve your goal as a game
different than "being" a game designer
different than thinking like a gamer
3 elements of a game i like "starcraft"
level playing field competition
variety of choices for strategy
progressive reward system for ladder matches
refer to your customers as "players"
means the player is the center of the game, world revolves around the player
players need a sense of autonomy/control
players PLAY
2 mains goals for a game designer
how to get people to play
how to keep them playing
player journey
should have beginning, middle and end
onboarding - get the user in
scaffolding - how does the game make playing for the user easier
mastery - does the player gain a skill or at least mastery of the game?
how does plants vs zombies give onboarding and scaffolding
explanations of what to do
simplification to start
very easy to start
should have balance
200 to pass go in monopoly is maintaining balance in the game economy
should not favor one group over another
`
create an experience
turntable.fm makes listening to music into a group dj thing
emotional component of games
games are engaging because they are fun.. but what is fun?
what things are fun? (for me)
accomplishing things
organizing things
figuring things out
testing my reflexes
progressing in a system
watching pretty pictures and hearing pretty sounds
winning
Marc Leblanc's 8 Kinds of Fun
Sensation
Subtopic
Fantasy
Narrative
Challenge
Fellowship
Discovery
Expression
Submission
Finalities
fun doesn't just happen, its designed
fun isn't always purely happy and simple
different kinds of fun
finding the fun
thefuntheory.com
videos of how fun concepts are used to make people do things, piano stairs, recycling etc.
just a small progress bar made people put in much more information
feedback is a gamification device
progression - bar fills up
completion - we strive to want to finish
Breaking Games Down
game elements
Tic Tac Toe
board
simplicity
reward lap (drawing the line)
portability
easy to teach and learn
Subtopic
Pyramind - In Order
Dynamics
def. Big Picture, or "Grammar"
Constraints
Emotions
Narrative
tie together
consistent theme or coherence
Progression
start at one place and get to a higher place
gives the player the sense that they will be able to improve
Relationships
people interacting with each other
friends/enemies/partners/etc.
Mechanics
challenges
chance
cooperation
competition
Feedback
Resource Acquisition
Rewards
Transactions
Turns
Win States
Components
Avatars
Badges
Boss Fights
Collections
Combat
Content Unlocking
Gifting
Achievements
Leaderboards
Levels
Points
Quests
Social Graph
Teams
Virtual Goods
PBL - 3 Important Game Elements
Points
Keep Score
Determine Win States
Connect to Rewards
Provide Feedback
Display Progress
Data for Game Designer
Fungible
Badges
Representations of Achievement
Flexibility
Style
Signaling of Performance
Credentials
Collections
Social Display (Status Symbols)
openbadges.org
Leaderboards
Ranking
feedback on competition
can be global or friend/relative player learderboard
Big Problem - actually demotivate
Pitfalls in Focusing on Elements and Rewards
The Elements are not the game
nat all rewards are fun/not all fun is rewarding
cookie cutter is demotivating
Video Games
Reflection Topic:
The things that made me want to play video games include: the ability to discover new worlds, a decent learning curve that was not too hard or too easy, strategy within the context of innovation a la tactics in Starcraft or Halo, the ability to compete with friends or other players online, cool graphics. A total package helped immersion and for me to come back, as opposed to games that seemed a little more thrown together.
Games Are Big!
$60 Billion dollars - bigger than hollywood and growing faster
global in-game market:7.3 billion
97% of kids play video games
average gamer is 30 years old
almost half video game players are women
men for shooters
women for social games
New Types of Games
sandbox games
Minecraft
Building
Civilization
SimCity
Social Building
Sims
Farmville
MMOG
WoWarcraft
Puzzle
Portal, Portal 2
Angry Birds
Core Elements of Games that Are Real World Important
Digital Building Blocks
Analytics
Mobility
Social Networks
Cloud Storage and Processing
Non-digital
Rewards Programs
eg. Credit Cards
Management and Marketing Research
Real World Already Resembles Gamification
Frequent Flyer Level-ups
Sales Perks for Being the Best
Weight Watchers - social team gaming
Starbucks Card - Reward
CCards - Badges = Platinum Cards etc.
History
1912 - Toys in Cracker Jack Boxes
1980s
Thomas Malone - MIT - What Makes Things Fun to Learn?
James Paul Gee book
2002 - on
Serious Games Initiative
eg. simulatinig the battlefield for the military
Games for Change
social impact games
teach systemic impact thinking
2003 - Conundra
failed
Subtopic
Subtopic
2005 - Bunchball
2010 - Gamification takes off
TED Talks
Books
Magazine Profiles
What is gamification?
In non-game contexts
game elements
toolbox for designing games
some elements:
points
levels
quests or missions
avatars
social graphs
game design techniques
approaches to game design
how to "think" like a game designer
non-game is anything other than the game for its own sake
eg. playing to encourage an action
eg. playing to get a job
eg. playing to learn something
eg. being healthy
examples
Nike+
establish goals get medals
connect with friends
still going out to run
Zombies Run
run from zombies
can collect power ups
can involve your friends
more immersive experience than nike+
What is a Game?
Wittgenstein:
cannot define a game
cannot define the boundaries
Bernard Suits:
took on Wittgenstein
Elements
Pre-lusory goal
way to win the game
Rules
Lusory Attitude
player voluntarily follows the rules
think the game means something
Voluntarily overcoming arbitrary obstacles
J. Huizinga:
Book: Homo Ludens argues that games and play are essential to what makes us human
incl. religion, government, justice etc.
Concept: The Magic Circle
There is a circle or boundary that defines the game from the real world
where the game matters, the rules matter, and it is another world
try to put the user in the magic circle
Why Study?
significant up and coming business practice
they are powerful tools
link to aspects of how our minds work eg:
psychology
motivation
design
strategy
technology
focus on social networks and current tech
not that easy or obvious
needs to be done well
needs to be done ethically
needs to be done relevantly and in context
Where Can Gamification Be Used?
External
Marketing
Sales
eg. Club Psyche
points and rewards
integrates with the show it promotes
results
visits to site up
mercandise sales up
pagesviews up
sharing up
relatively simple/big impact
Internal
for employess
crowdsourcing
using groups to attack a problem
productivity enhancment
eg. Windows 7
localization problem
used gamification - language qualification game
played for prestige and competition within complany
mind-numbing activity turned fun
found over 7,000 bugs
Behavior Change
Health
Sustainablility
Social Change
Finance
eg. Speeding
police monitors of speed give feedback
causes behavior loop
slows you down
monitor that records liscence plates
fine people who speed
fines go into a pool
people who don't speed are entered into a lottery
used in stockholm
Motivational Design and Psychology
Why?
People do things for stuff other than rewards
5.1 excersize:
task - get people to save their change in one place
1- explain the benefits of saving change and being organized
2- make it easy for them to save change by providing examples, framework and a system
3- tantalize them with a goal that saving change can produce
4- remind them with updates and badges earned for successfully saving change
2 Major Fields of Psychology
Behaviorism
Black Box Approach
we are conscious, don't worry about what goes on inside the head, only the behavior
Conditioning
classical conditioning - stimulus plus response for simple pavlovian conditioning
ring the bell for dinner - start salivating
operant conditioning - feedback loop
stimulus plus response plus stimulus etc. = learning
consequences are important
Behavioral Economics
thinking about what people actually do without the why
people make 'mistakes' consistently
eg. loss aversion
eg. power of default states - ie. opt-out vs opt-in
confirmation bias
Relevant Takeaways for Gamification
Observation:
Look at what people actually do
often different than what you think they will do
Importance of Feedback Loops
can condition through consequences
eg. Farmville - Crops Withering over time creates an appointment mechanci
people had to habitually check in - very behavioral approach
eg. MLB Badges - why were fans so obsessed?
partly a behavioral feedback loop
5.3 Excersize
Game I played: Starcraft 2
One behavioral mechanism was the strategy forums that continually updated the new ways to approach the game, and reinforced the community through the elevation of better players through status and study.
Reinforcement through Rewards
much of PBL Gamification is like this
Reward Structures
Different Types of Rewards - One Typology of Rewards
Cognitive Evaluation Theory
tangible/intangible
expected/unexpected
Contingency
non-contingent - u get the reward no matter what
engagement-contingent - get a reward just for starting
completion-contingent
performance-contingent
5.4 Excersize:
The cruise reward for staying on the site is an intangible, unexpected engagement (arguably completion) contingent reward
Reward Schedules
Continuous - get a reward every time
Fixed Ratio - every N number of times you take an action you get a reward
Fixed Interval
based only on time not amount of action
Variable
most interesting because brain cant recognize patterns
competitive/non-competitive
vs. other people makes reward variable
expected/unexpected
brains love a sense of surprise
help make people addicted so not always a good thing...
Reinforcement
Limits of Behaviorism
Leaves out important things:
people might avoid something not to learn, but just so they don't get caught
why do people like lotteries?
purely behaviorist approach seperates the person from their humanity
can lead to social problems like fascism etc.
Dangers of Behaviorism
manipulation
hedonic treadmill
if people only respond to a reward, they will change back when the reward is not there...
kill the rewards by making them so expected
over-emphasis on status
Subtopic
Cognitivism
Intrinsic Rewards
love something just to be doing it
Extrinsic Rewards
doing an action for something
SAPS framework - its a higherarchy from the standpoint of the company rewarding their employees
Status - will make us cool
Access - will give us access to something more
Power -
Stuff
Rewards can actually demotivate someone that would otherwise enjoy something intrinsically
the reward substitutes
studied examples:
creative things like drawing
day care pickup
blood donating
teacher salaries
usually happen with an activity thats "interesting"
reward types do matter:
tangible rewards substitute highly
surprise rewards do not influence that much
performance contingent
if the reward objectifies your accomplishments, it is demotivational
if it is encouraging and fills you with a sense of accomplishment, its not
self determination theory - motivation spectrum - worst motivators to best
1- amotivation
not motivated
2- extrinsic
1-external regulation
forced to
2 - introjection
take an external motivation and make it our own eg status
3 - identification
user can identify some motivation in doing the thing eg. learn math for business etc.
4 - integration
complete alignment between my goals and the thing i'm doing eg. excersize
3- intrinsic
motivating in and of itself
what leads to intrinsic motivation?
competence
feedback that makes you feel good
autonomy
self reliance
feeling of control
not predetermined
relatedness
connects you to something else
Subtopic
Design
Design Thinking - ideas of how design should go into thinking about creating ANYTHING
purposive - everything should tie into the purpose you are going for
human centered - designed around people, specifically;come up with solutions for PEOPLE, not robots; useful, not just a set of objectives
balance - between analytical and creative thinking; use abductive reasoning sometimes - inference from the best possible explanation
iterative - expect not to get it right the first time; improving with each iteration; prototyping and playtesting
6 Step Gamification Design Process "D6"
1 Define
What are your business objectives?
what are the ultimate goals?
eg. foursquare
social sharing
increases value the more people that use it (concept in decentralization)
influencer marketing
locating people that are influencers an d encouraging them to be an active participant with deals or badges or whatever
List and Rank your possible objectives
Eliminate means to ends - eg badges are not a real objective for the business, just a stepping stone (and objective for the user)
Justify Objectives
2 Delineate
What do you want users to do?
Should be as specific as possible
eg. I want to find the best people to hire at this job
eg. I want people to buy paper towels
what are the success metrics? in gamification terms "win states"
what are the analytics? how do you measure these win states?
eg. DAU/MAU
daily average users/monthly average users
how often do people come back?
higher is closer to 1, people who visit the site are coming back more frequently
eg. virality
rate at which people refer their friends
eg. volume
level of usage and engagement and what people are doing
3 Describe
What Motivates your Players?
eg. world of warcraft
players need to find other players with specific skills
players may need items
Barle Model of Player Types

4 Devise Activity Loops
Engagement Loops
Motivation
Feedback
Action
a game Ive used an engagement loop in is Starcraft/ the ladder system makes you want to win, the action is playing the game to win, and the feedback is winning and seeing your rank improve
Progression Loops
specific steps to achieve your objective, start to finish
one example
starts with onboarding, getting the player into the game
then climbing and resting alternately
maybe boss fights periodically
finally reach the end and you can look back and see your mastery
Good games should have both types of loops
5 Don't forget the Fun
Why would someone want to do this? Is it REALLY fun?
fitocracy seems dedicated to making fun
linked in progress bar - even this has a small amount of fun
protein folding - game site that actually allows players to help figure out new protein types
6 Deploy
PBL
Gamification Pyramid
Subtopic
Design Choices
Taking Stock: Two Approaches
Doing
Feeling
Should We Gamify?
Motivation
emotional connections
or, make boring tasks interesting
Meaningful Choices
Structure
Potential conflicts
Case Study: Stack Overflow
website where you ask coding questions and answer them
how did they motivate people to do this?
First they asked "What Is Programming?"
incentivized working together, uses points and badges
Enterprise Gamification
What Motivates People in the Workplace?
Rewards
Extrinsic
Compensation - ie give you something for something you don't really want to do
Skill Development
Information
leaderboards and info about how to do better can motivate
Corporate (or other) Citizenship
Fun (in the workplace)
eg. the face game, at zappos
Game vs Job
sometimes the game can take people away from their job
types of job game motivation
in role
gamification works well here with future skills
citizenship
gamification works well here with core skills
type of skill: core skills, unique to a person skill, future skill
Playbor - combination of play and labor
have to be careful not to encourage cutthroat competition or "cracking the whip"
can use games to replace messed up motivation systems with ones that are more accurate, and more effective
Gamification for Good
Whats different about gamification for social good?
inherent relatedness
should you get rewards for doing good?
behavior change
Examples: 4 Categories
Health and Wellness
Zamzee - device that keeps track of how active you are; targeted toward low income teenagers; PBLs, rewards, etc.
Superbetter - set up your own gamified system of self improvement
Energy and Evironment
OPOWER - uses peer pressure and neighbor experiments to encourage people to save energy
Recyclebank - earn points by recycling to redeem for rewards
Education
challenge is to make sure it is benefitting education
openbadges.org - virtual diplomas
Government
Motivational - lots of workers
customer service - interacts with voters, etc.
promotion of its policies and programs
Social Good Techniques
ex. CAPRI - parking relief sites
feedback and rewards
monitoring
communal pressure - activates social norms as opposed to competition
Kukui Cup (Univ. of Hawaii)
uses competition to make students use less power
competition works for social good because the pride in winning is wrapped up with the pride in doing good
impact - shows just what good the game playing or site is doing for the world
ex practically green
chance - creates interest in the same gamified system so can just be used to enhance to fun of the game
Behavior Change - Habit Formation
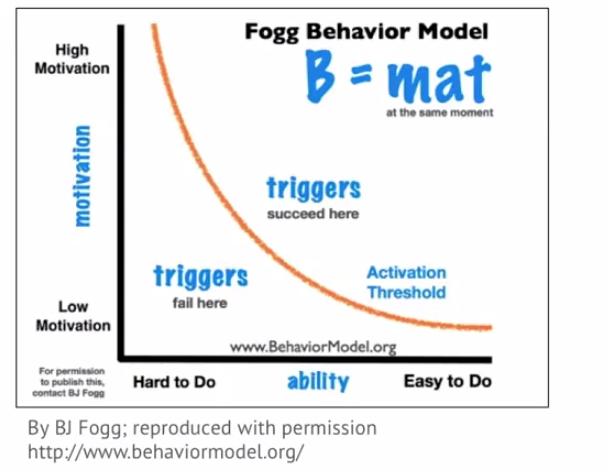
Fogg Behavior Model
motivation and ability tradeoffs
trigger timing
trigger types
sparks
facilitators
signal
triggers loops
engagement loop -> motivation
progression loops -> percieved ability
good games trigger effectively