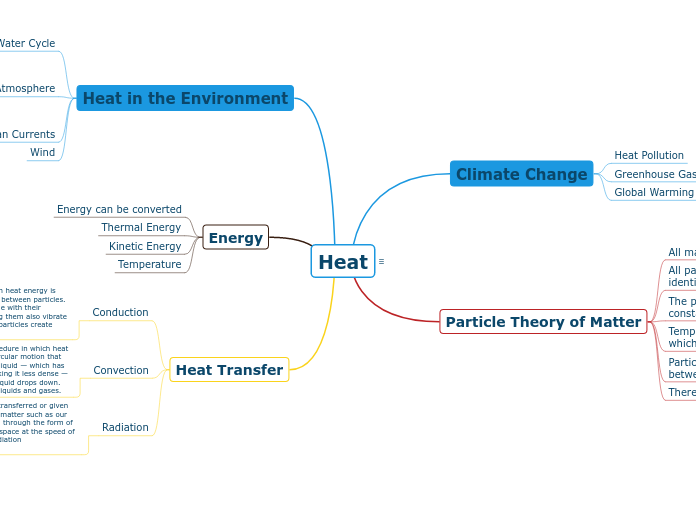
Heat
Climate Change
Heat Pollution
Greenhouse Gases
Global Warming
Particle Theory of Matter
All matter is made up of particles.
All particles of one substance are identical.
The particles of matter are in constant motion.
Temperature affects the speed at which particles move.
Particles have forces of attraction between them.
There are spaces between particles.
Heat in the Environment
Water Cycle
Layers of Atmosphere
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere
Ocean Currents
Wind
Energy
Energy can be converted
Thermal Energy
Kinetic Energy
Temperature
Heat Transfer
Conduction
Conduction simply works when heat energy is transmitted through collisions between particles. These vibrating particles collide with their neighbouring particles, making them also vibrate faster and as we know faster particles create heat.
Convection
Convection is a common procedure in which heat is transferred that includes circular motion that happens when warmer air or liquid — which has faster-moving molecules, making it less dense — rises, while the cooler air or liquid drops down. Convection can only occur in liquids and gases.
Radiation
Radiation is energy that is transferred or given off from various sources of matter such as our Sun. Radiation is translated through the form of waves and travels through space at the speed of light. You could also call radiation “electromagnetic waves”.