How drugs get into, are distributed, and do their job in the body
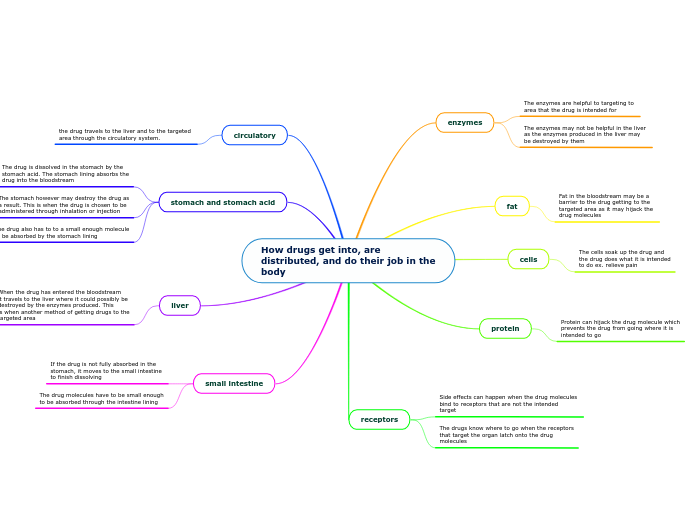
enzymes
The enzymes are helpful to targeting to
area that the drug is intended for
The enzymes may not be helpful in the liver
as the enzymes produced in the liver may
be destroyed by them
fat
Fat in the bloodstream may be a
barrier to the drug getting to the
targeted area as it may hijack the
drug molecules
cells
The cells soak up the drug and
the drug does what it is intended
to do ex. relieve pain
protein
Protein can hijack the drug molecule which
prevents the drug from going where it is
intended to go
receptors
Side effects can happen when the drug molecules
bind to receptors that are not the intended
target
The drugs know where to go when the receptors
that target the organ latch onto the drug
molecules
circulatory
the drug travels to the liver and to the targeted
area through the circulatory system.
stomach and stomach acid
The drug is dissolved in the stomach by the
stomach acid. The stomach lining absorbs the
drug into the bloodstream
The stomach however may destroy the drug as
a result. This is when the drug is chosen to be
administered through inhalation or injection
The drug also has to to a small enough molecule
to be absorbed by the stomach lining
liver
When the drug has entered the bloodstream
it travels to the liver where it could possibly be
destroyed by the enzymes produced. This
is when another method of getting drugs to the
targeted area
small intestine
If the drug is not fully absorbed in the
stomach, it moves to the small intestine
to finish dissolving
The drug molecules have to be small enough
to be absorbed through the intestine lining