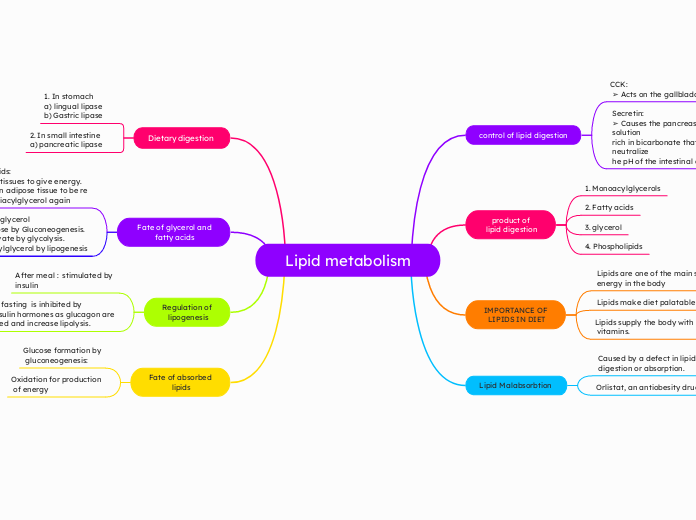
Lipid metabolism
control of lipid digestion
CCK:
➢ Acts on the gallbladder and pancreas
Secretin:
➢ Causes the pancreas to release a
solution
rich in bicarbonate that helps
neutralize
he pH of the intestinal contents
product of
lipid digestion
1. Monoacylglycerols
2. Fatty acids
3. glycerol
4. Phospholipids
IMPORTANCE OF
LIPIDS IN DIET
Lipids are one of the main sources of
energy in the body
Lipids make diet palatable
Lipids supply the body with fat soluble
vitamins.
Lipid Malabsorbtion
Caused by a defect in lipid
digestion or absorption.
Orlistat, an antiobesity drug
Dietary digestion
1. In stomach
a) lingual lipase
b) Gastric lipase
2. In small intestine
a) pancreatic lipase
Fate of glycerol and
fatty acids
Fate of fatty acids:
1) Oxidation by tissues to give energy.
2) May remain in adipose tissue to be re
esterified into triacylglycerol again
Fate of glycerol
1) Glucose by Gluconeogenesis.
2) Pyruvate by glycolysis.
3) Triacylglycerol by lipogenesis
Regulation of
lipogenesis
After meal : stimulated by
insulin
During fasting is inhibited by
anti-insulin hormones as glucagon are
secreted and increase lipolysis.
Fate of absorbed
lipids
Glucose formation by
gluconeogenesis:
Oxidation for production
of energy