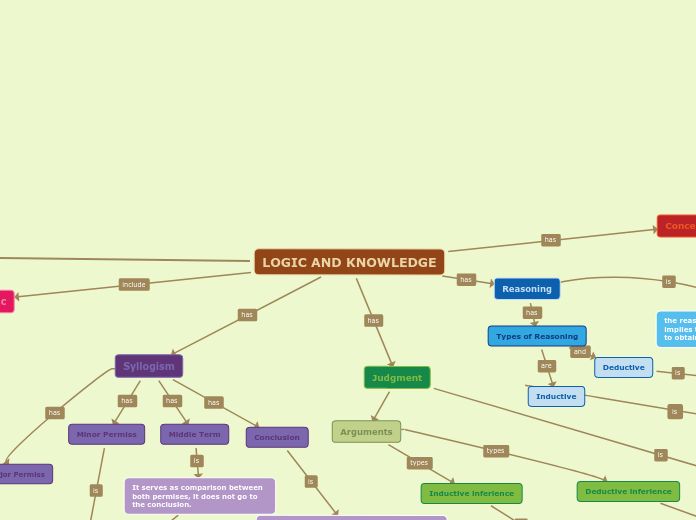
LOGIC AND KNOWLEDGE
Modern Logic
Propositional Logic
Deals with analyzing formally valid reasoning based on their prepositions.
Quantificational Logic
Is focused on the relation between a quantity and the prepositions.
Class Logic
It focuses on indicating the beloning or non-beloning of an element within a set, according to the properties it shares with it.
Syllogism
Major Permiss
Minor Permiss
Where is the subject of the conclusion or Minor Term (S).
Fallacies
Attack to the person
Any condition of the person who issues an opinion.
Appeal to popularity
When we support our arguments in poplular opinions.
False generalization
Consists in generalizing from very few observed cases.
Petition of principle
In making an argument, one of the permises is again and again established a conclusion.
Appeal to authority
When an idea or argument is not analyzed but is taken for garanted as correct or valid.
Appeal to ignorance
When it is intended to offer the ignorance of something as an explanition to evade responsability.
Appeal to emotions
Seeks to expose an idea that moves the feeling.
Appeal to force
Use of force -physical or verbal- to impose a vision or opinion.
Where is the predicate of the conclusion or Major Term (P).
Middle Term
It serves as comparison between both permises, it does not go to the conclusion.
Conclusion
Where the relation between S and P is established, considering that M does not appear in this proposition.
Judgment
the judgment is a complex mental operation that anunciates the relation between two or more conepts
Arguments
Deductive inferience
Leads to unecessary conclusions; part of the facts and absolute security.
Inductive inferience
We start from various observations made about the same fact or object, so that the conclusion is a statement that can be generalized to all cases that share the properties observed so far.
Logic principles
Principle of identity
The word and statement of our inferiences must have the same unique meaning.
Principle of non-contradiction
It is impossible to affirm that a proposition is true and false as the same time and uder the same time circumstances.
Principle of excluded middle
To decide that a permiss is tru or false.
Principle of sufficent reason
Principle of excluded middle
It tell us that by having two statements that contradict each other.
Reasoning
the reasoning is mental operation since it implies the relation between two judgments to obtain a new one as conclusion.
It starts from an idea, a concept, it is verified in experience, it is reasoned, thought and related to other facts and from there some result is inferred or extracted. The process by which the subject relates two judgments, to infer a third, is called reasoning.
Types of Reasoning
Deductive
Consists of formulation of the law of general conclusion based on the observation
Inductive
Concept
Concept is a mental representation of an object
Ancient Logic
focuses on indicating the belonging or non-belonging of an element within a set, according to the properties it shares with it
Tought and Reasoning
Thought can be defined as all that mental process that occurs due to intellect and rationality.
Lenguage and Comunication
It is the complexity of its structure, since it is directly related to our intellectual capacity and the complexity of our thinking.