MPM2D0 Final Exam
Trigonometry
Trigonometry deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. The basic trigonometric functions—sine, cosine, and tangent—are used extensively in geometry, physics, and engineering.

Soh Cah Toa
Basic Trigonometric Ratios:
Sine: sin 𝜃
Opposite
--------------
Hypotenuse
Cosine: cos 𝜃
Adjacent
---------------
Hypotenuse
Tangent:
tan 𝜃
Opposite
------------
Adjacent
Pythagorean Theorem
Formula
Relates the sides of a right-angled triangle.
Sine law
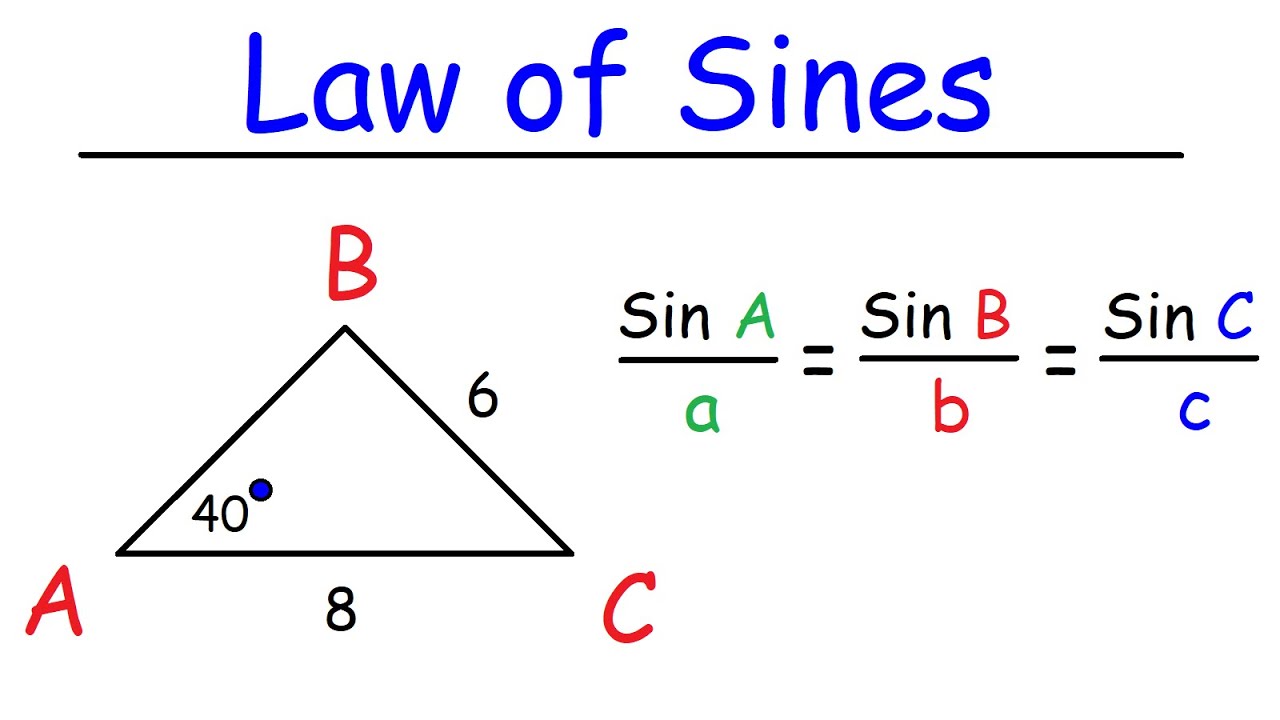
Formula
In any plane triangle, the ratio of the sides is equal to the ratio of the sines of the angles opposite to those sides.
Cosine Law
Formula
In trigonometry, the Cosine Rule says that the square of the length of any side of a given triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the length of the other sides minus twice the product of the other two sides multiplied by the cosine of angle included between them.
Polynomials
Polynomials are algebraic expressions involving a sum of powers of a variable with constant coefficients. Understanding polynomials is crucial for solving equations, graphing, and simplifying algebraic expressions. Key concepts include factoring, graphing, and operations on polynomials.
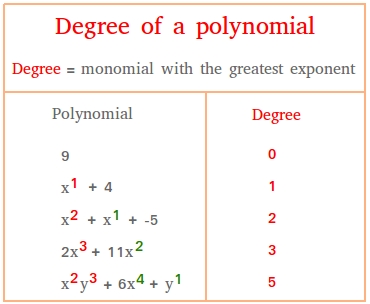
Degree of Polynomial
The degree is the highest exponent of the variable in the polynomial.
A polynomial with degree 1 is called a linear polynomial, degree 2 is quadratic, degree 3 is cubic, and so on.
Linear Systems
Slope-intercept form
Point–slope form
General Form
Analytic Gemotry
Analytic Geometry connects algebra and geometry using coordinate systems. This involves studying lines, circles, and other geometric figures through algebraic equations.
Equation of a Line
Slope-Intercept Form
m = Slope
b = y-intercept
Slope-Point Form
Use this form when you know a point and the slope
Distance Formula
Used to find the distance between two points in the coordinate plane
Important in geometric problems, finding the length of a line segment
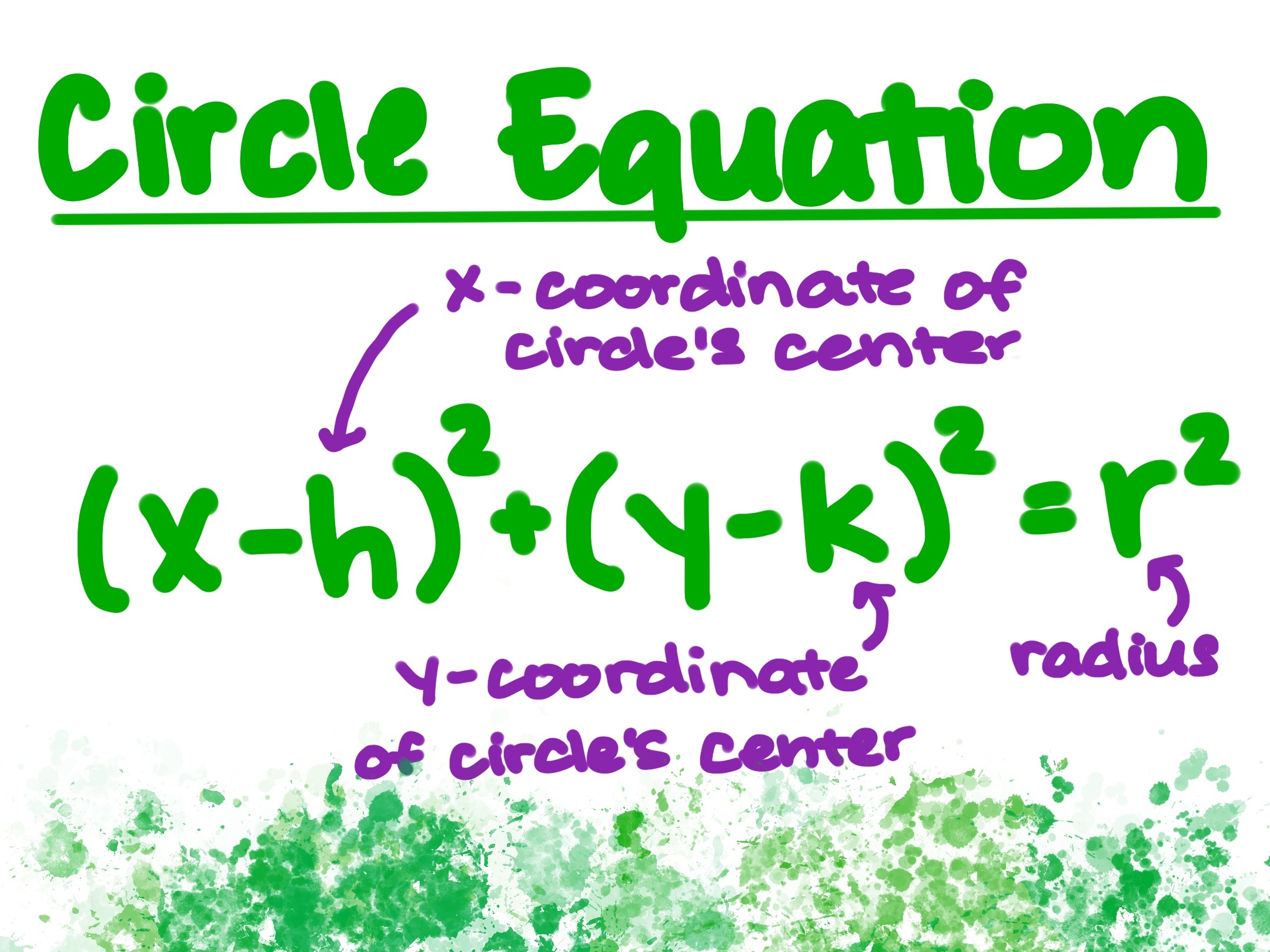
Equation of a Circle
Center: (h,k)
Radius: r

Special case: If h = 0, k = 0, this is the equation
Midpoint Formula
Gives the coordinates of the midpoint between two points
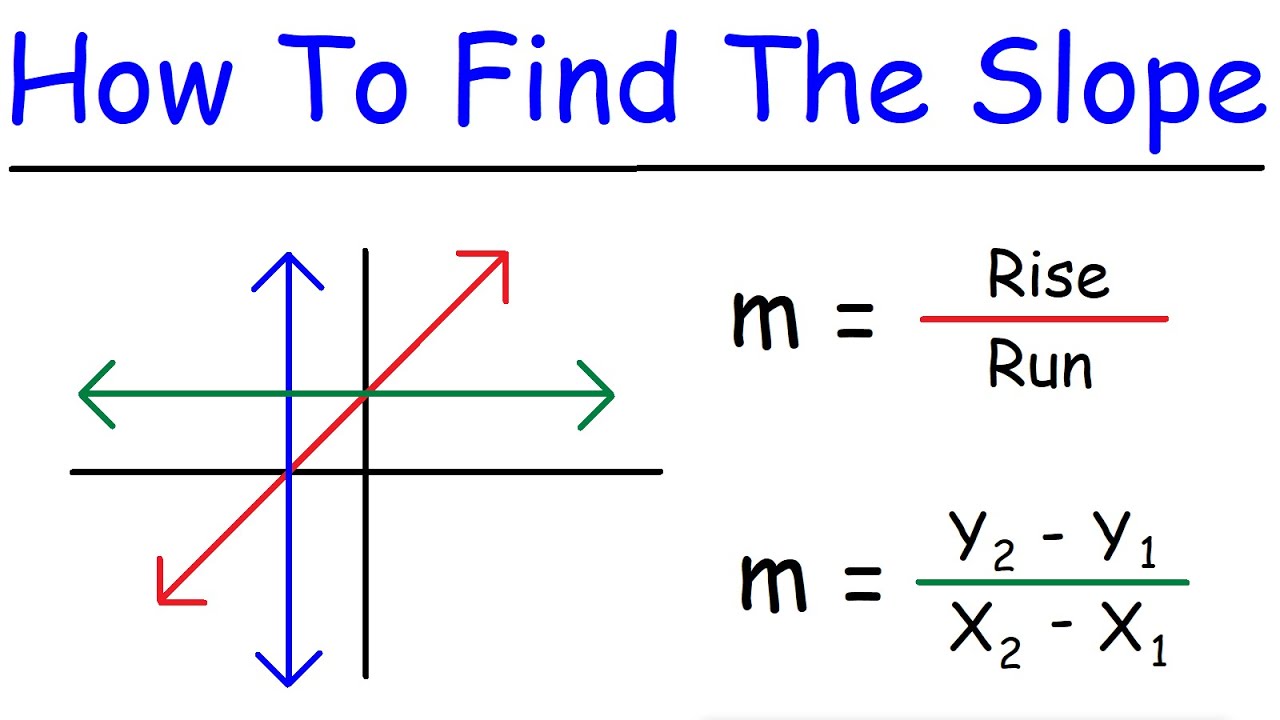
Slope of a Line
The slope describes the steepness and direction of a line
Positive slope: Line rises from left to right
Negative slope: Line falls from left to right
Zero slope: Horizontal line
Undefined slope: Vertical line
Quadratics
Quadratic Formula
the quadratic formula is a closed-form expression describing the solutions of a quadratic equation. Other ways of solving quadratic equations, such as completing the square, yield the same solutions.
Standard form
Factored Form
Vertex Form
Methods of solving: factoring, completing the square, quadratic formula