Natural Systems
Plate Tectonics
Divergent
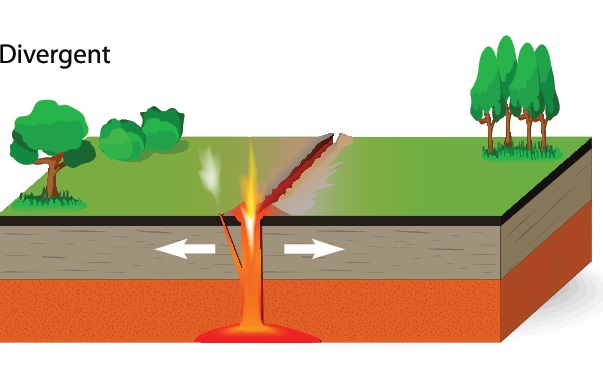
A divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other
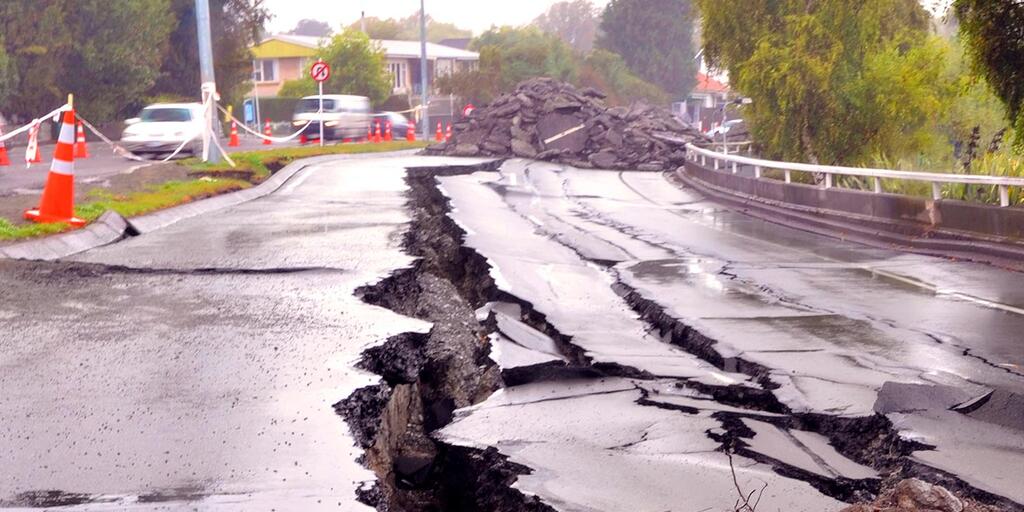

Earthquakes are common along the boundaries

Mid-ocean ridges occur along the boundaries, a new ocean floor is created as the Earth’s tectonic plates spread apart
Transform
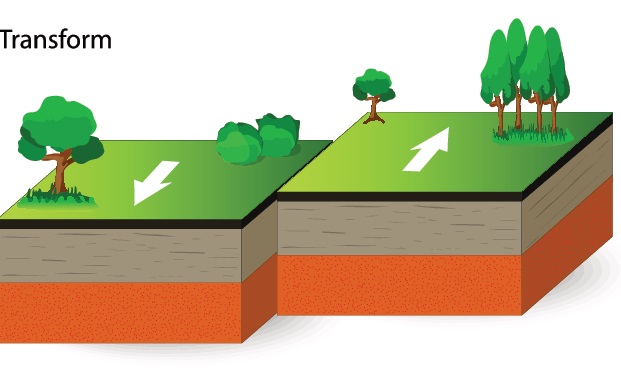
Two plates sliding past each other horizontally creates a transform plate boundary
Crust is cracked and broken at transform boundaries, unlike convergent and divergent boundaries it does not create or destroy the earth's surface

A well known transform plate boundary is the San Andreas Fault, which is responsible for many of California’s earthquakes
Convergent
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Oceanic-continental_destructive_plate_boundary_LABELED1-56c559c43df78c763fa341bf.png)
When two plates come together, it is known as a convergent boundary
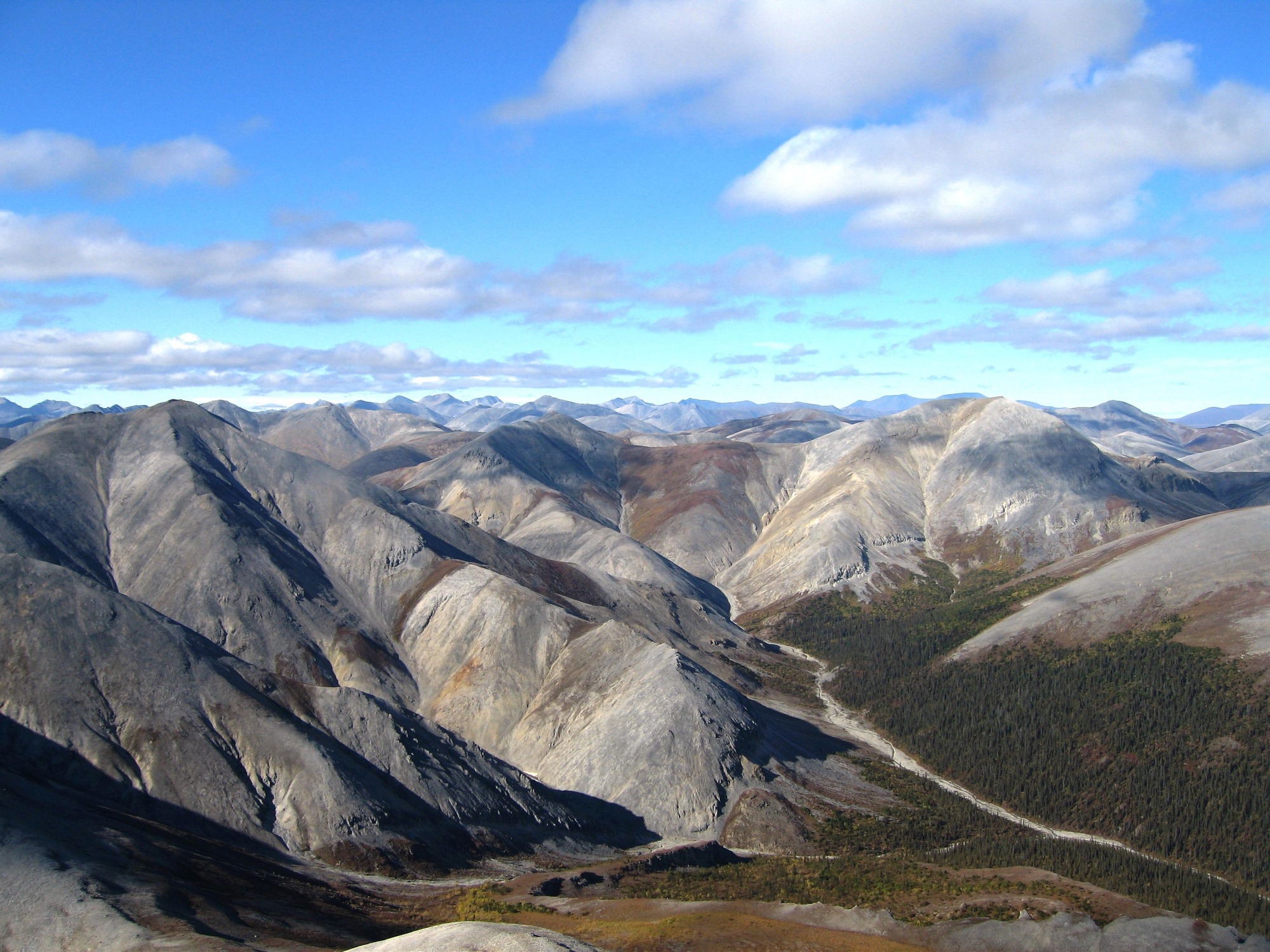

Colliding plates can cause the edges of one or both plates to buckle up into mountain ranges
At convergent plate boundaries, oceanic crust is often forced down into the mantle where it begins to melt
Regions & Resorces
Western Cordillera

Comprised mainly of mountains separated by plateaus and valleys
The area is lightly populated most people live in urban areas as well as farming or mining towns

Popular tourist destinations include Banff and Jasper National Park and Vancouver
Minerals

We use minerals to build skyscrapers, cars, electronic devices and fossil fuels to power our day to day lives
Minerals are non–renewable natural resources and Sustainable mineral development is used to ensure mineral use is kept to a minimum amount without having a negative impact on economic growth
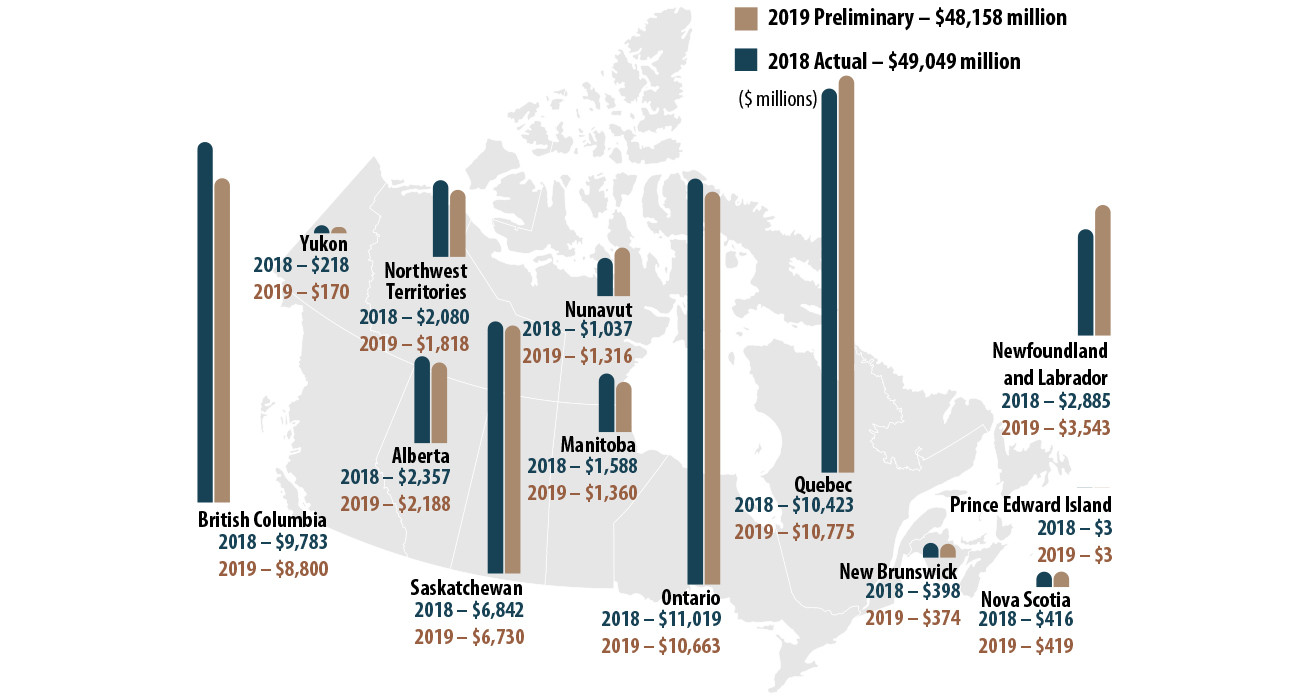
Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan, accounted for over three-quarters of Canada's total value of mineral production in 2019
Trees

Provide wood for construction, furniture, paper and building homes

Forestry is the industry that uses trees- Forestry is the science managing, using, and repairing forests
Trees remove pollution from the atmosphere, So it is very important that we are able to replenish the earth's forests
Forces
Volcanoes

A volcanic eruption is one of the most powerful forces on Earth

Earth’s mountains are entirely or almost entirely the result of volcanic activity. These include volcanic islands like the Hawai’ian hotspot volcanoes

Some diffrent kinds of volcanoes are composite, shield, cinder cones and lava domes
Wind
Wind erosion is referred to as eolian erosion
Erosion is defined as the set of natural processes that loosen and transport weathered or unweathered solid material

An example is when Wind carries small pieces of rock away from the side of a mountain
Ice

Frozen water (ice) expands and breaks rocks apart

A glacier's weight, combined with its gradual movement, can drastically reshape the landscape over hundreds or even thousands of years

Glacier National Park is an example of this, it has mountains that began forming from ice erosion over 130 million years ago
Rock Cycle
Sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks form near the earth's surface at relatively low temperatures and with pressure from things like erosion by water, ice or wind

Examples of the rock are sandstone, limestone, and shale

Sedimentary rock often contains fossils of plants and animals millions of years old
Igneous

Igneous rock is formed when magma cools and makes crystals
About 95% part of earth’s crust is made up of igneous rock

Examples of the rock are granite, basalt,and obsidian
Metamorphic
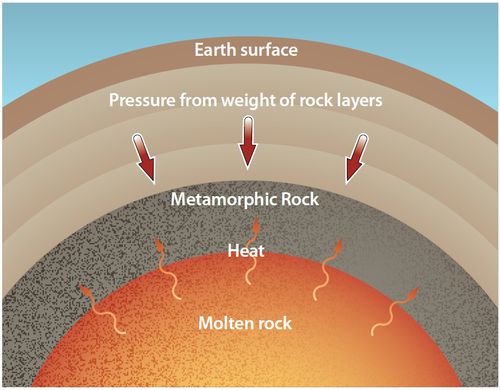
Metamorphic Rock is formed when rocky material experiences intense heat and pressure in the crust of the earth
Through the metamorphic process, both igneous rocks and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks

Examples of the rock are gneiss, marble, and schist
Eras
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era began 248 million years ago and ended 65 million years ago
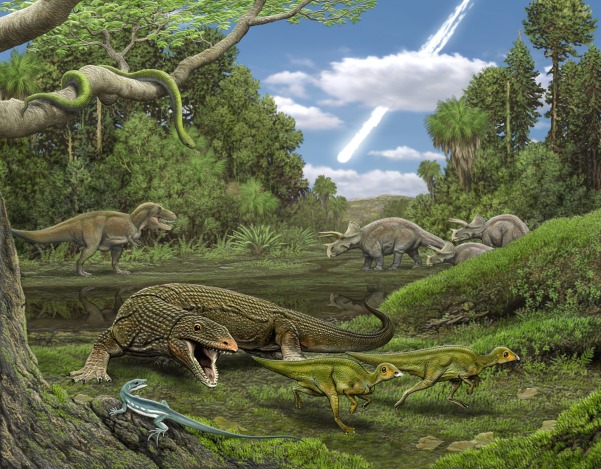

It is known as the age of the dinosaurs because dinosaurs were so widespread and dominant, nothing was overtaking them
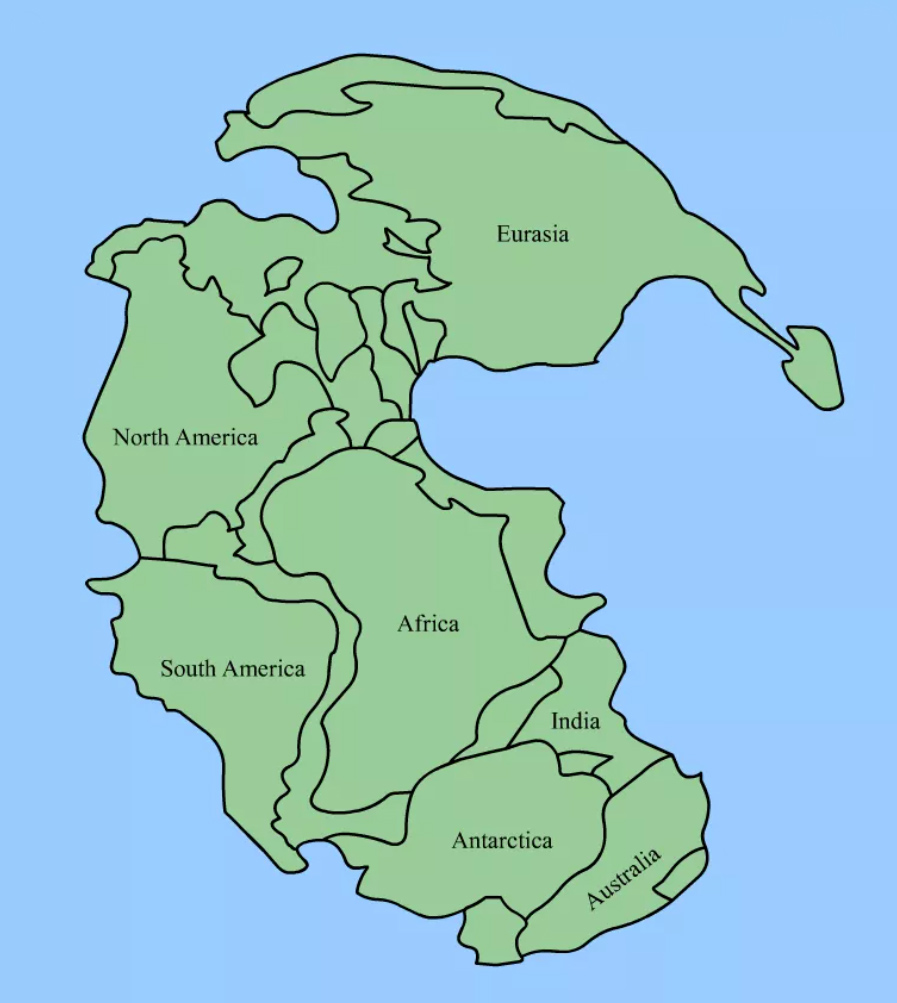
In the Mesozoic era, all of the world’s continents were joined together, known as the supercontinent Pangaea. It completely broke apart at the end of the Mesozoic era
Paleozoic
Spanned from about 544 million years ago to 245 million years ago

The 45 million year Ordovician Period is marked in the fossil record for having massive amounts of marine invertebrates. One of the most well known was the trilobite
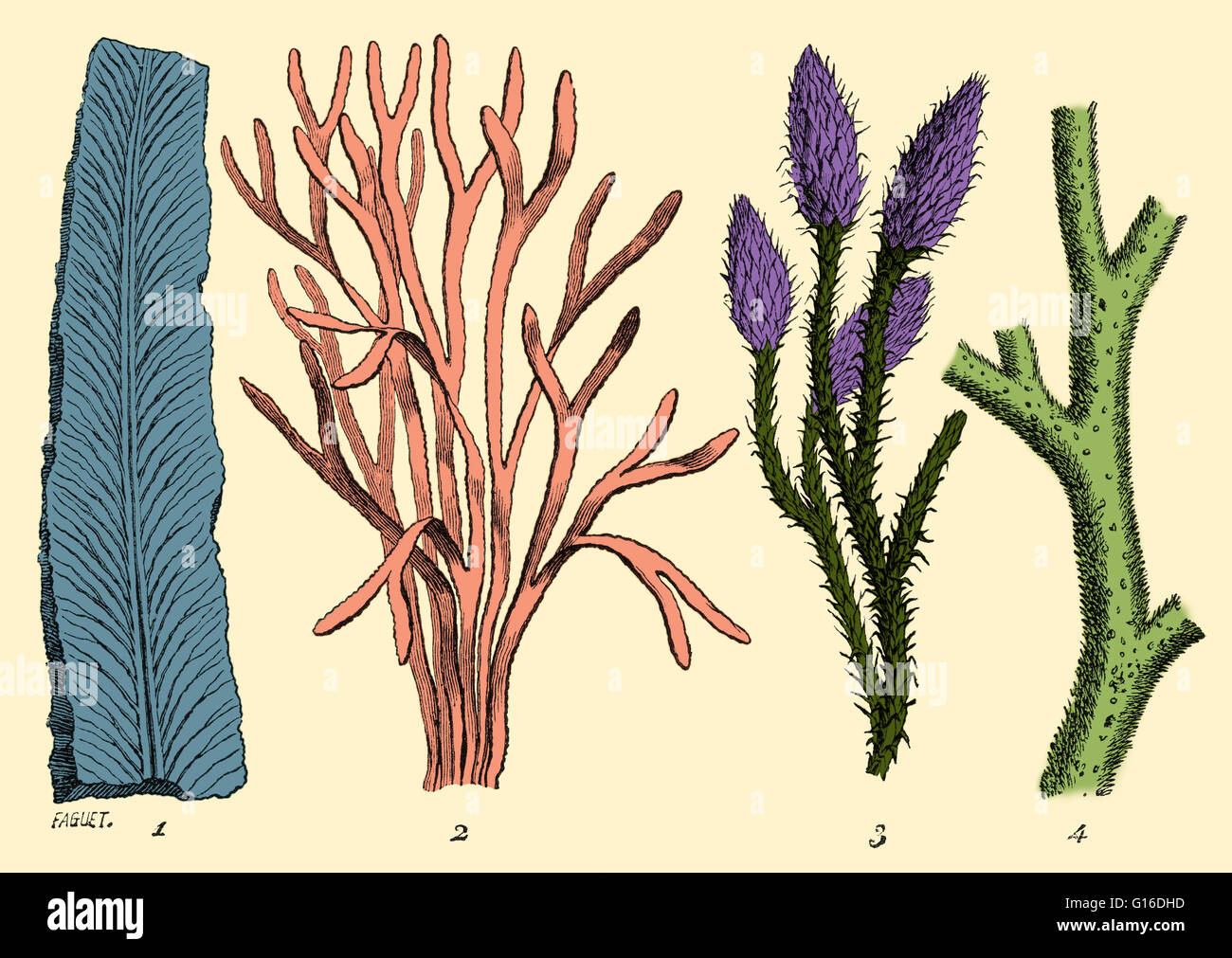

In the Silurian Period plants started evolving, but they most likely did not have leaves or vascular tissue that allows them to absorb water and nutrients
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era is the last major division in time, beginning 65.5 million years ago and continuing until today
It is referred to as the Age of Mammals because many mammals began to rule the earth following the extinction of dinosaurs

Early mammals in the Cenozoic Era were quite large, beavers were as long as 7 feet
Natural Disasters
Tornados

Tornadoes are spinning columns of high winds spiralling around a centre of low atmospheric pressure

The deadliest tornado ever recorded was in Bangladesh in 1989, more than 20 villages were destroyed and around 1,300 people were killed
Tornadoes form when warm, humid air collides with cold, dry air. The warm air rises through the colder air, causing an updraft and When it touches the ground, it becomes a tornado
Forest Fires

Are large uncontrolled infernos that are not limited to a particular continent or environment
Help keep ecosystems healthy and can kill insects and diseases that harm trees

Wildfires that burn near communities can become dangerous and even deadly if they grow out of control. For example, in 2018 when a Camp Fire in Butte County, California almost destroyed the entire town, 86 people died
Earthquakes
The clash of 2 tectonic plates can cause violent earthquakes, they are more common in some parts of the world like California, because the state sits on top of the meeting point or fault of two plates

Other natural disasters can be caused by earthquakes and these can be equally, and sometimes more, destructive like landslides and avalanches
Generally before and after a large earthquake there will be smaller earthquakes