organization assignment
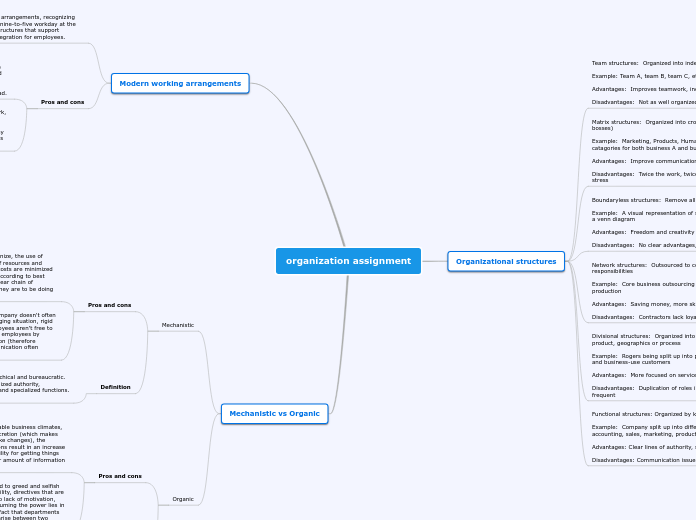
Organizational structures
Team structures: Organized into independant teams
Example: Team A, team B, team C, etc
Advantages: Improves teamwork, increases ideas/creativity
Disadvantages: Not as well organized, inefficiencies
Matrix structures: Organized into cross functional teams (2 bosses)
Example: Marketing, Products, Human ressources, etc catagories for both business A and business B forming a grid
Advantages: Improve communication through the company
Disadvantages: Twice the work, twice the deadlines and more stress
Boundaryless structures: Remove all tradional barriers
Example: A visual representation of said structure resembles a venn diagram
Advantages: Freedom and creativity
Disadvantages: No clear advantages, difficult to manage
Network structures: Outsourced to contractors, key responsibilities
Example: Core business outsourcing inventory and/or production
Advantages: Saving money, more skilled at a given job
Disadvantages: Contractors lack loyalty to your business
Divisional structures: Organized into department by customer, product, geographics or process
Example: Rogers being split up into personal-use customers and business-use customers
Advantages: More focused on service or efficient production
Disadvantages: Duplication of roles in departments is quite frequent
Functional structures: Organized by key business skills
Example: Company split up into different departments (ie. accounting, sales, marketing, production)
Advantages: Clear lines of authority, specialized
Disadvantages: Communication issues
Modern working arrangements
Definition: defining flexible work arrangements, recognizing the constraints of the traditional nine-to-five workday at the office and exploring workplace structures that support flexibility and better work-life integration for employees.
Pros and cons
Pros: improves productivity and efficiency, can improve employee retention, can help decrease costs, improving the balance of a work-life and a home-life, minimizes traffic and the stresses of commuting during rush hours, increased feeling of personal control over schedule and work environment, and reduces employee burnout due to overload.
Cons: there is no clear dividing line between home and work, may not work efficiently without supervision, some employees/employers may be distrusting with their peers because they can't physically see their productivity, and may slow down the pace of work team production because of this restricted collaboration.
Mechanistic vs Organic
Mechanistic
Pros and cons
Pros: relatively easier and simpler to organize, the use of specialization helps for proper utilization of resources and maximization of productivity, supervision costs are minimized as all the subordinates perform activities according to best their capabilities, and because there is a clear chain of command, employees always know what they are to be doing at any given time.
Cons: works most effectively when the company doesn't often need to adapt effectively to a rapidly changing situation, rigid control and job specialization means employees aren’t free to be creative problem-solvers, and grouping employees by function contribute to departmental isolation (therefore interdepartmental cooperation and communication often suffer).
Definition
Definition: The organization is hierarchical and bureaucratic. It is characterized by its highly centralized authority, formalized procedures and practices, and specialized functions. Rapid change isn't a challenge.
Organic
Pros and cons
Pros: work best in fluid and unpredictable business climates, employees exercise a great deal of discretion (which makes them very responsive and quick to make changes), the employee's wide-ranging job descriptions result in an increase in the general acceptance of responsibility for getting things done, and there is a significantly larger amount of information sharing among employees.
Cons: the lack of boundaries could lead to greed and selfish motives instead of corporate responsibility, directives that are given may become unproductive due to lack of motivation, leadership may become ineffective assuming the power lies in the employee’s hands, and due to the fact that departments are self-governing, conflict can easily arise between two departments that don’t see things the same way.
Definition
Definition: An organization that is characterized by its flatness (communications and interactions are horizontal), its low specialization (knowledge resides wherever it is most useful), and its decentralization (a great deal of formal and informal participation in decision making).