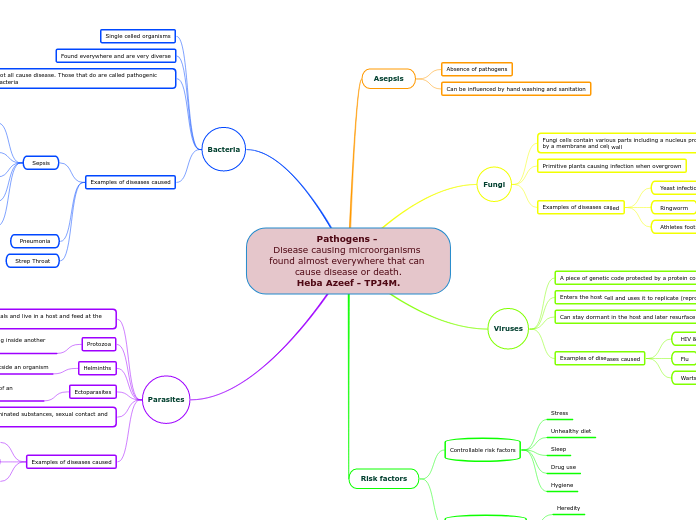
Pathogens -
Disease causing microorganisms found almost everywhere that can cause disease or death.
Heba Azeef - TPJ4M.
Asepsis
Absence of pathogens
Can be influenced by hand washing and sanitation
Fungi
Fungi cells contain various parts including a nucleus protected by a membrane and cell wall
Primitive plants causing infection when overgrown
Examples of diseases called
Yeast infections
Ringworm
Athletes foot
Viruses
A piece of genetic code protected by a protein covering
Enters the host cell and uses it to replicate (reproduce).
Can stay dormant in the host and later resurface
Examples of diseases caused
HIV & AIDS
Flu
Warts
Risk factors
Controllable risk factors
Stress
Unhealthy diet
Sleep
Drug use
Hygiene
uncontrollable risk factors
Heredity
Age
Environmental conditions (ex, pollution)
Bacteria
Single celled organisms
Found everywhere and are very diverse
Not all cause disease. Those that do are called pathogenic bacteria
Examples of diseases caused
Sepsis
Septic shock
Sepsis can turn into septic shock due to drop in blood pressure
High levels of lactic acid left after treatment
Result of blood infection
Occurs due to imbalance in infection fighting chemicals of the body
Can damage organ systems and lead to death, specifically if it becomes septic shock
If caught early, can be treated to improve chances for survival.. Treated with antibiotics and intravenous fluids
Pneumonia
Strep Throat
Parasites
Behave like small animals and live in a host and feed at the expense of the host
Protozoa
Single celled organisms living and multiplying inside another organism
Helminths
Multicellular organisms living inside or outside an organism
Ectoparasites
Multicellular organisms living on and feeding off of an organism
Spread through contaminated substances, sexual contact and insect bites
Examples of diseases caused
Lice
Malaria
Intestinal Worms