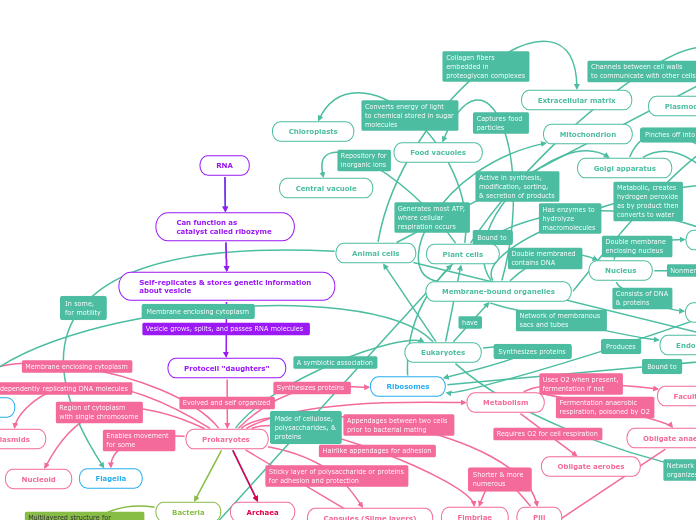
RNA
Can function as
catalyst called ribozyme
Self-replicates & stores genetic information about vesicle
Protocell "daughters"
Prokaryotes
Flagella
Plasma membrane
Plasmids
Nucleoid
Bacteria
Cell wall
Peptidoglycan
Polysaccharides & proteins
Endospores
Archaea
Extremophiles
Extreme thermophiles
Extreme halophiles
Methanogens
Eukaryotes
Animal cells
Extracellular matrix
Cell junctions
Gap junctions
Desmosomes
Tight junctions
Centrosomes
Plant cells
Chloroplasts
Plasmodesmata
Central vacuole
Membrane-bound organelles
Mitochondrion
Food vacuoles
Peroxisome
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Phagocytosis
Autophagy
Nucleus
Nuclear envelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Endoplasmic reticulum
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Cytoskeleton
Intermediate filaments
Maintains cell shape
Formation of nuclear lamina
Anchorage of nucleus
& certain other organelles
Microtubules
Maintains cell shape
Cell motility
Cilia & flagella
Proteins between microtubules
Organelle movement
Kinesin
Vesicle
Motor protein
Vesicle
Chromosome movements
in cell division
Microfilaments
Maintains cell shape
Muscle contraction
Cytoplasmic streaming
Parallel actin filaments
Myosin motor protein
Changes in cell shape
Cell division
Cell motility
Cortex
Inner cytoplasm
Extending pseudopodium
Ribosomes
Metabolism
Facultative anaerobes
Obligate anaerobes
Obligate aerobes
Capsules (Slime layers)
Nutritional Modes
Inorganic chemicals
Chemoautotrophs
Organic compounds
CO2, HCO3-, or
related compound
Light
Photoheterotroph
Photoautotroph
Fimbriae
Pili