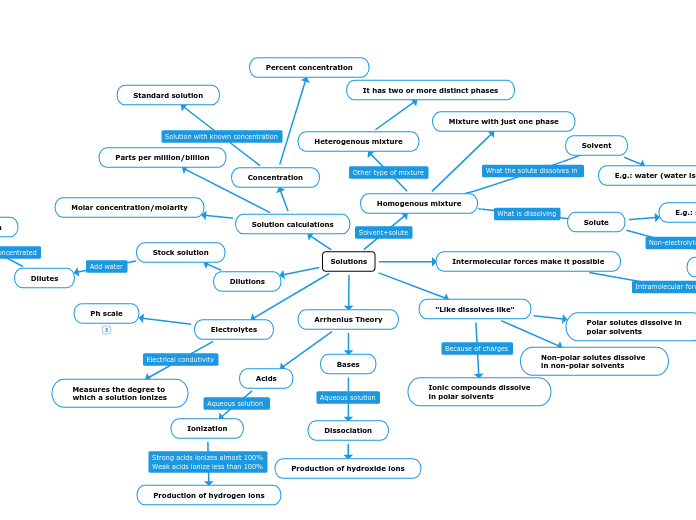
Solutions
Homogenous mixture
Solvent
E.g.: water (water is polar)
Solute
E.g.: salt and sugar
Solute that does not dissociate
Heterogenous mixture
It has two or more distinct phases
Mixture with just one phase
Intermolecular forces make it possible
It can interfere depending on the polarity
"Like dissolves like"
Polar solutes dissolve in
polar solvents
Non-polar solutes dissolve
in non-polar solvents
Ionic compounds dissolve
in polar solvents
Arrhenius Theory
Acids
Ionization
Production of hydrogen ions
Bases
Dissociation
Production of hydroxide ions
Electrolytes
Measures the degree to
which a solution ionizes
Ph scale
Dilutions
Stock solution
Dilutes
Changes the concentration
Solution calculations
Concentration
Percent concentration
Standard solution
Parts per million/billion
Molar concentration/molarity