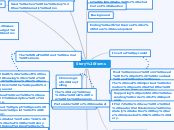
Broadcast story structure
The Wall Street Journal Formula
Chronological storytelling
Most common form used for print, broadcast and online news.
The most important information goes at the top of the story.
Supporting points in descending order of importance.
It's a way to let readers determine inmediately whether they are interested in the story.
Starts with a soft lead, focusing on a person, scene or event.
Goes from the specific to general
The lead can be anecdotal, descriptive or narrative.
The nut graph gives the main point of the story.
"So what"factor: explains what the story is about and why is it important.
The ending usually comes full circle by using a quote or anecdote
Lead-in tells who or what happened.
Ending with current or future development
The story may be told from the beginning to the end
Can start like inverted pyramid
Contains chronological storytelling
Used when the story has dramatic action
Useful when the story has several points of stress
Several key points to list
Starts with a summary lead or a soft lead followed by a nut graph
Helpfull to explain issues such as a budget increase or any controversial proposal
Involves dividing the story into sections by a graphic device
Works best for in-depth stories