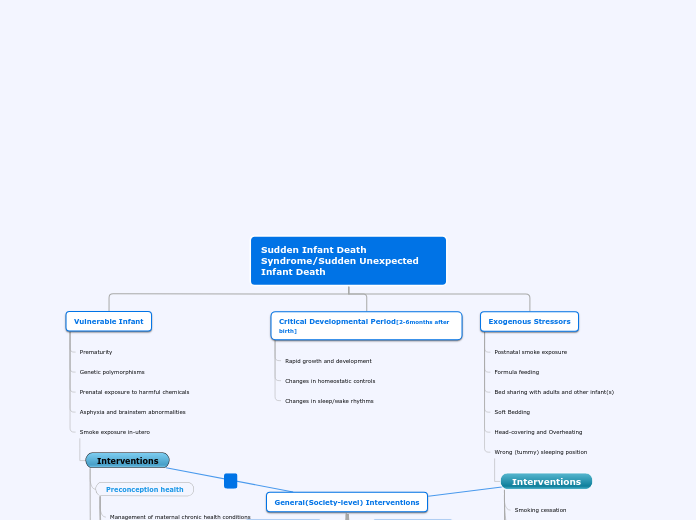
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome/Sudden Unexpected Infant Death
Vulnerable Infant
Prematurity
Genetic polymorphisms
Prenatal exposure to harmful chemicals
Asphyxia and brainstem abnormalities
Smoke exposure in-utero
Interventions
Preconception health
Management of maternal chronic health conditions
Genetic Counselling
Smoking cessation
Mental health support
Support for domestic abuse and partner violence
Adequate nutrition and use of folic acid
Prenatal Care
Birth preparedness and complications readiness
Identification of high-risk pregancies
STI, UTI screening and treatment
Use of doula services if necessary
Regular clinic attendance and fetal growth monitoring
Management of pregnancy-induced hypertension
Perinatal Care
Supervised delivery
Neonatal resuscitation readiness
Undelayed initiation of breastfeeding
Critical Developmental Period[2-6months after birth]
Rapid growth and development
Changes in homeostatic controls
Changes in sleep/wake rhythms
Exogenous Stressors
Postnatal smoke exposure
Formula feeding
Bed sharing with adults and other infant(s)
Soft Bedding
Head-covering and Overheating
Wrong (tummy) sleeping position
Interventions
Smoking cessation
Breastfeeding and breastfeeding support
Infant immunization
Avoid overheating
Back/ supine sleeping
Supervised and awake tummy time
Subtopic