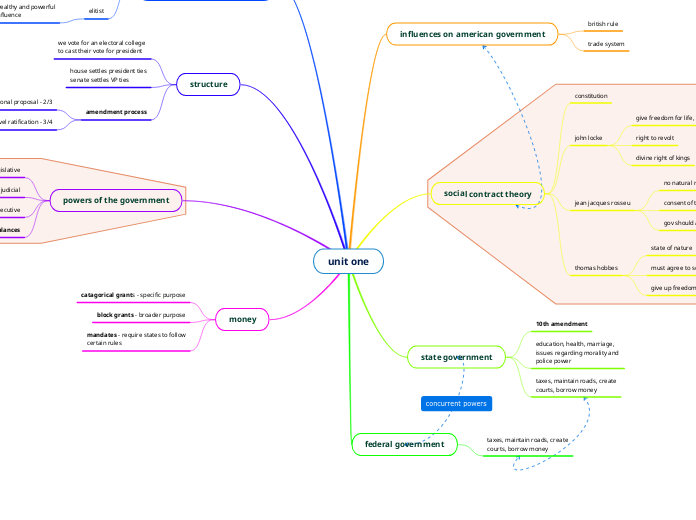
unit one
influences on american government
british rule
trade system
social contract theory
constitution
john locke
give freedom for life, liberty, property
right to revolt
divine right of kings
jean jacques rosseu
no natural right to govern others
consent of the people
gov should aim to restore freedoms given up
thomas hobbes
state of nature
must agree to social contract
give up freedom, gain structure
state government
10th amendment
education, health, marriage,
issues regarding morality and
police power
taxes, maintain roads, create
courts, borrow money
federal government
taxes, maintain roads, create
courts, borrow money
representative democratic
theories
participatory
direct citizen
influence
pluralist
non-governmental
group influence
elitist
wealthy and powerful
influence
structure
we vote for an electoral college
to cast their vote for president
house settles president ties
senate settles VP ties
amendment process
national proposal - 2/3
state level ratification - 3/4
powers of the government
legislative
article 1, section 8
judicial
article 2, section 1
executive
article 3, section 1 and 2
checks and balances
money
catagorical grants - specific purpose
block grants - broader purpose
mandates - require states to follow
certain rules