Where to next?
Where to next?
Now that you have completed your SWOT analysis and strategy, where to next?
- You can return to this map to change SWOT elements or change their priorities
- You can review the strategies to gain agreement and turn them into plans & actions
- Do you have enough strengths? What is missing? Ensure that these gaps are listed as weaknesses
- You can examine the most important weaknesses and threats in detail, and use the map to further break them down into root causes
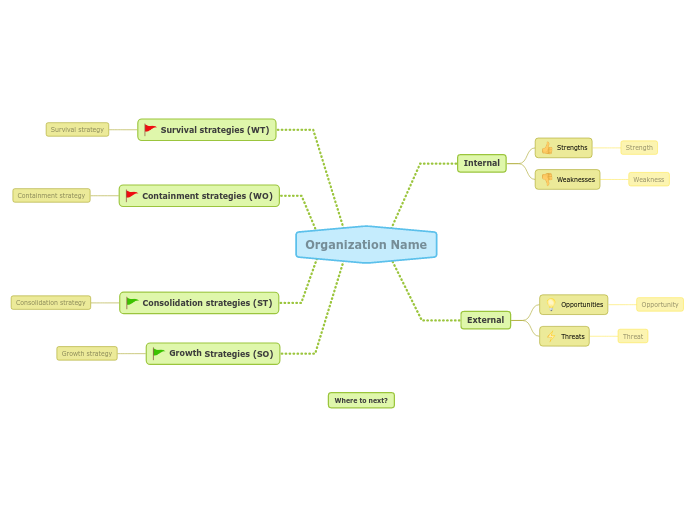
Organization Name
Enter your organization name
Type in the organization or area that is the subject of this analysis. You might find it helpful to add the date for reference so that you can review changes at a later date.
Growth Strategies (SO)
Growth strategy
Add a growth strategy
Review each of the highest-ranked strengths facing your organization'''.
- Are they connected in some way?
- Is the strength helping to take advantage of an opportunity?
- If the strength is not maintained, does this reduce the chances of success with an opportunity?
For example, if your product performs well, and new legislation is going to raise questions about your competitor's products, then you could maximize this situation by prioritizing your own product performance.
Consolidation strategies (ST)
Consolidation strategy
Add a consolidation strategy
Review each of the highest-ranked strengths facing your organization, and compare them with each of the highest-ranked threats.
- Are they connected in some way?
- Is a strength helping to protect you from a threat?
- Could the impact of a threat increase if you do not maintain this strength?
For example, if you have recognized specialist knowledge that gives you an advantage, but there is a threat that new technology could decrease your market, then it would make sense to develop the same level of specialist knowledge in new technologies.
Containment strategies (WO)
Containment strategy
Add a containment strategy
Review each of the highest-ranked weaknesses facing your organization, and compare them with each of the highest-ranked opportunities.
- Are they connected in some way?
- Is the weakness preventing you from taking advantage of an opportunity?
- If the weakness gets worse, does this push the opportunity further away?
For example, if there is unmet demand in the market, but you have old and slow production equipment, then you cannot take advantage of this opportunity. A containment strategy would be to improve capacity with newer equipment.
Survival strategies (WT)
Survival strategy
Add a survival strategy
Review each of the highest-ranked weaknesses facing your organization, and compare them with each of the highest-ranked threats.
- Are they connected in some way?
- Is this weakness a threat?
- Could the impact of a threat get worse if the weakness gets worse?
For example, if a strong competitor is a threat, and unhappy customers are a weakness, then your customers might simply move to your competitor. A survival strategy would be to work on improving customer satisfaction.
External
Threats
Threat
Add an external threat that might negatively impact your organization.
Examples include strong competitors, negative market trends, technologies becoming obsolete, new disruptive technologies.
Rate the importance of this threat:
- Critical - could affect the survival of the organization
- Major - would disrupt operations and require recovery
- Minor - would cause a few problems that we can handle or adapt to
Opportunities
Opportunity
Add an external opportunity that you could take advantage of.
Examples include social or business trends, fashions, changes in legislation, new technologies, innovations, weak competitors.
Rate the importance of this opportunity by clicking one of the icons below:
- Strategic- success here would take the organization nearer to its goals
- Possible - we could do this, but it would be a different direction
- Maybe - we might do this if we cannot find anything else
Internal
Weaknesses
Weakness
Add an internal weakness that is negatively affecting success.
Examples: under-staffing, lack of skills, unreliable or inefficient equipment, unhappy customers, unhappy staff, missed deadlines.
Rate the importance of this weakness by clicking one of the icons below:
- Critical it regularly causes real problems
- Survivable we find ways to work around it
- Minor it would be nice if we fixed it
Strengths
Strength
Add an internal strength
Examples: good people, skills, location, technology, equipment, specialized knowledge, brand reputation, proven abilities, financial resources, partnerships.
Rate the importance of this strength by clicking one of the icons below:
- Critical could not operate without it
- Helpful it makes things go better
- Bonus nice to have, but could continue without it